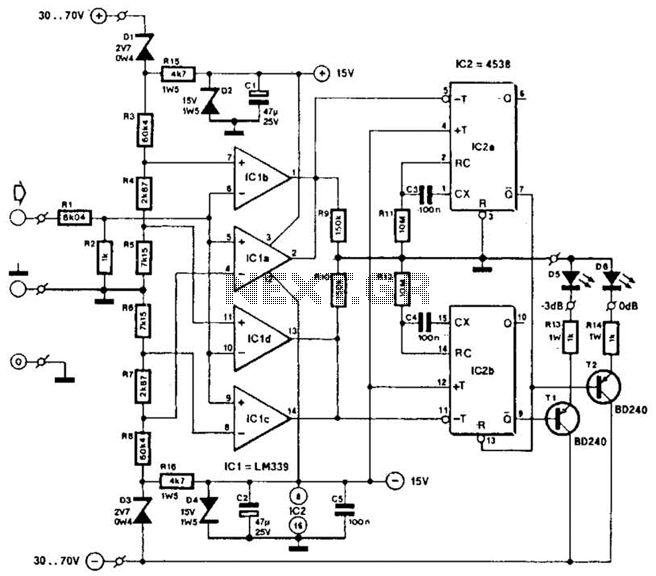
Ac/Dc Indicator
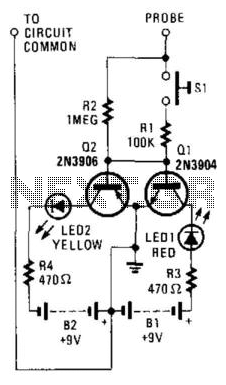
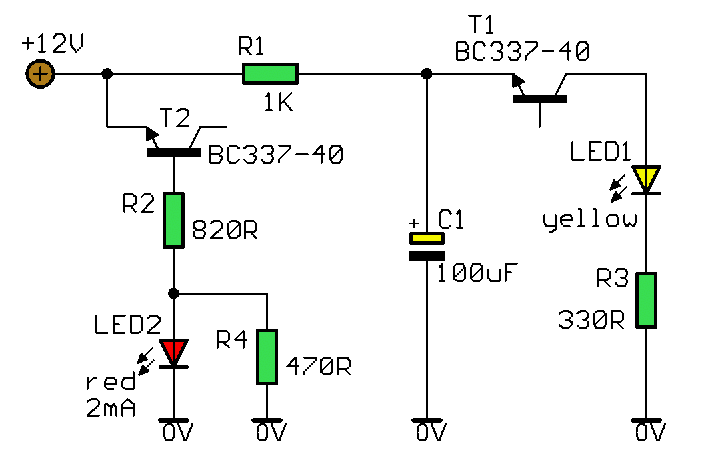
This circuit utilizes two switching transistors and two LEDs to differentiate between low-level AC and DC signals. A lit red LED indicates a positive DC signal, while a lit yellow LED signifies a negative DC signal. If the input signal is AC, both LEDs will illuminate.
The described circuit employs two transistors configured as switches to control the illumination of two LEDs based on the nature of the input signal. The transistors are arranged to respond to voltage levels indicative of positive and negative DC signals, as well as alternating current (AC) signals.
In this setup, the positive DC signal activates the first transistor, which in turn powers the red LED. Conversely, the second transistor is triggered by a negative DC signal, lighting the yellow LED. When an AC signal is present, the rapid alternation of voltage levels causes both transistors to switch on and off in a manner that results in both LEDs lighting up simultaneously.
The circuit can be designed using NPN or PNP transistors depending on the desired response characteristics. Resistors can be added in series with the LEDs to limit current and protect them from excessive voltage. Additionally, a diode may be placed in parallel with each LED to prevent reverse voltage from damaging the components when the signal polarity changes.
This circuit is particularly useful in applications where signal type identification is crucial, such as in audio signal processing, sensor outputs, or communication systems. The simplicity and effectiveness of this design make it an excellent choice for low-level signal detection and analysis. By using two switching transistors and two LEDs, this circuit can distinguish low-level ac and dc signals. If the red LED i lluminates, the signal is positive dc. If the yellow LED lights, the signal is negative dc. If the signal is ac, both LEDs will light. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs two transistors configured as switches to control the illumination of two LEDs based on the nature of the input signal. The transistors are arranged to respond to voltage levels indicative of positive and negative DC signals, as well as alternating current (AC) signals.
In this setup, the positive DC signal activates the first transistor, which in turn powers the red LED. Conversely, the second transistor is triggered by a negative DC signal, lighting the yellow LED. When an AC signal is present, the rapid alternation of voltage levels causes both transistors to switch on and off in a manner that results in both LEDs lighting up simultaneously.
The circuit can be designed using NPN or PNP transistors depending on the desired response characteristics. Resistors can be added in series with the LEDs to limit current and protect them from excessive voltage. Additionally, a diode may be placed in parallel with each LED to prevent reverse voltage from damaging the components when the signal polarity changes.
This circuit is particularly useful in applications where signal type identification is crucial, such as in audio signal processing, sensor outputs, or communication systems. The simplicity and effectiveness of this design make it an excellent choice for low-level signal detection and analysis. By using two switching transistors and two LEDs, this circuit can distinguish low-level ac and dc signals. If the red LED i lluminates, the signal is positive dc. If the yellow LED lights, the signal is negative dc. If the signal is ac, both LEDs will light. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713