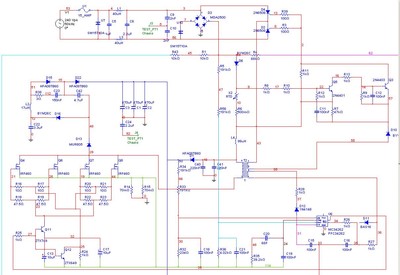
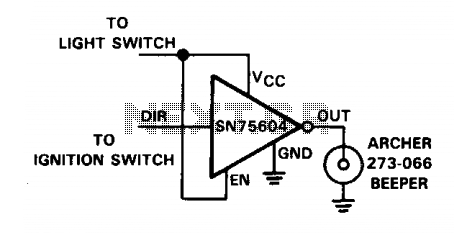
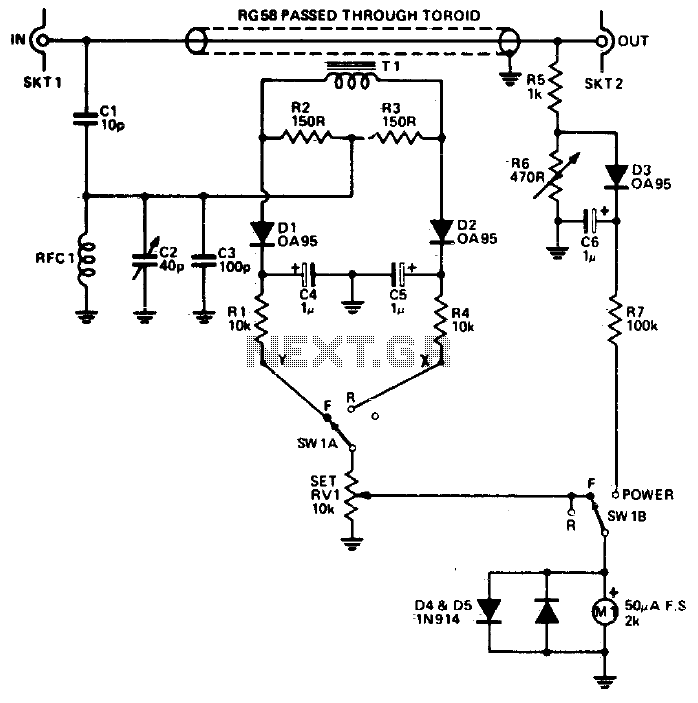
Inductive switching power supply circuit diagram
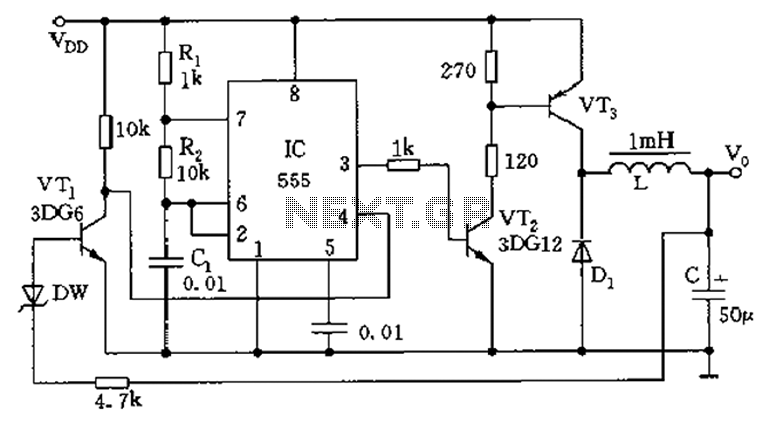
The circuit consists of a 555 timer configured as an astable multivibrator along with resistors R1 and R2 and capacitor C1. It generates an oscillation frequency of approximately 10 kHz with a duty cycle close to 50%. Transistors VT2 and VT3 function as switches to enhance current usage. When the square wave output from the oscillator is high, VT2 and VT3 conduct, allowing the inductor (L) to discharge. When the output is low, the energy stored in the inductor is supplied to the load through a freewheeling diode. In the event of overvoltage, diode DW breaks down, causing transistor VT1 to saturate and conduct, resulting in a very low voltage (approximately 0.7V) at point C. This action resets the 555 timer, effectively stopping the oscillation and serving as a regulator to maintain dynamic balance.
The described circuit utilizes a 555 timer in an astable configuration, which continuously switches between high and low states, thus generating a square wave output. The timing components, R1, R2, and C1, dictate the frequency and duty cycle of the oscillation. The output frequency of around 10 kHz is suitable for various applications, including pulse width modulation (PWM) and signal generation.
Transistors VT2 and VT3 are employed to manage the current flow effectively. When the output from the 555 timer is high, these transistors are turned on, allowing current to flow through the inductor (L). This action causes the inductor to store energy in its magnetic field. As the output transitions to low, the inductor releases its stored energy, which is directed to the load via a freewheeling diode. This diode prevents back EMF generated by the inductor from damaging the circuit components, ensuring safe operation.
The circuit also incorporates protective measures against overvoltage conditions. When the voltage exceeds a predetermined threshold, the breakdown of diode DW triggers the saturation of transistor VT1. This causes a significant drop in voltage at point C, effectively resetting the 555 timer and halting the oscillation. This feature is crucial for maintaining the stability of the circuit and preventing damage due to excessive voltage levels.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a robust method for generating oscillations while incorporating current management and protective features, making it suitable for various electronic applications requiring precise timing and regulation.As illustrated, 555 and R1, R2, C1 composition astable multivibrator, the oscillation frequency is about 10kHz, duty cycle close to 50%. VT2, VT3 switch as expanding the use of current use. When the square wave oscillator is high, VT2, VT3 conduction, the LC discharge; is low, L energy storage through freewheeling diode circuit power supply to the load. When overvoltage, DW breakdown, VT1 saturated conduction, c was very low ( 0.7V), 555 reset to stop, play the role of regulator and dynamic balance.
The described circuit utilizes a 555 timer in an astable configuration, which continuously switches between high and low states, thus generating a square wave output. The timing components, R1, R2, and C1, dictate the frequency and duty cycle of the oscillation. The output frequency of around 10 kHz is suitable for various applications, including pulse width modulation (PWM) and signal generation.
Transistors VT2 and VT3 are employed to manage the current flow effectively. When the output from the 555 timer is high, these transistors are turned on, allowing current to flow through the inductor (L). This action causes the inductor to store energy in its magnetic field. As the output transitions to low, the inductor releases its stored energy, which is directed to the load via a freewheeling diode. This diode prevents back EMF generated by the inductor from damaging the circuit components, ensuring safe operation.
The circuit also incorporates protective measures against overvoltage conditions. When the voltage exceeds a predetermined threshold, the breakdown of diode DW triggers the saturation of transistor VT1. This causes a significant drop in voltage at point C, effectively resetting the 555 timer and halting the oscillation. This feature is crucial for maintaining the stability of the circuit and preventing damage due to excessive voltage levels.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a robust method for generating oscillations while incorporating current management and protective features, making it suitable for various electronic applications requiring precise timing and regulation.As illustrated, 555 and R1, R2, C1 composition astable multivibrator, the oscillation frequency is about 10kHz, duty cycle close to 50%. VT2, VT3 switch as expanding the use of current use. When the square wave oscillator is high, VT2, VT3 conduction, the LC discharge; is low, L energy storage through freewheeling diode circuit power supply to the load. When overvoltage, DW breakdown, VT1 saturated conduction, c was very low ( 0.7V), 555 reset to stop, play the role of regulator and dynamic balance.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713