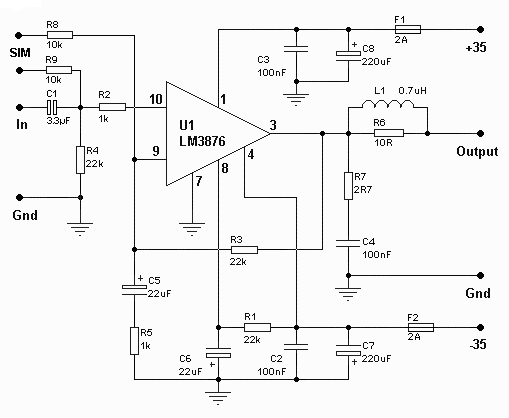
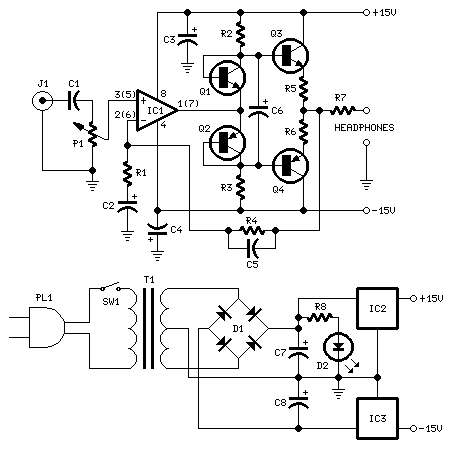
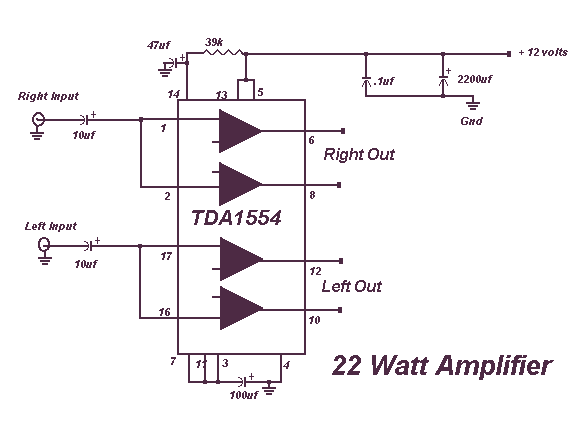
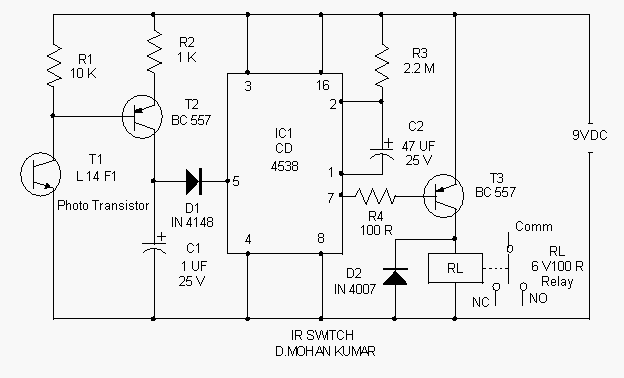
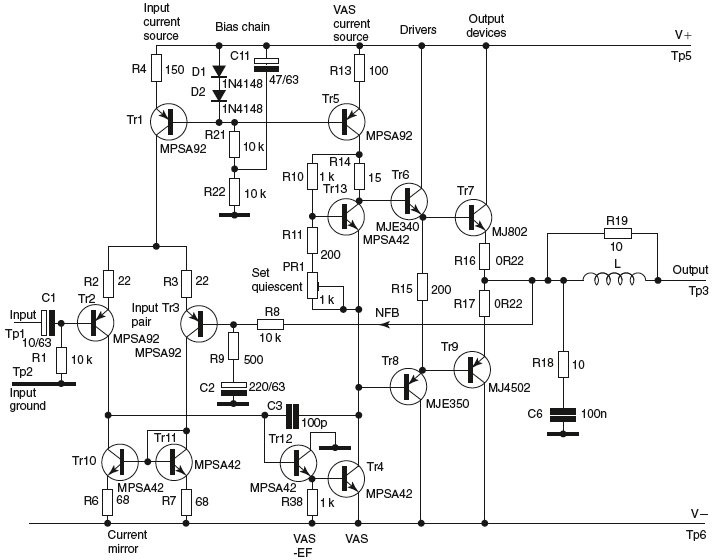
1500 Watt RF Amplifier Circuit
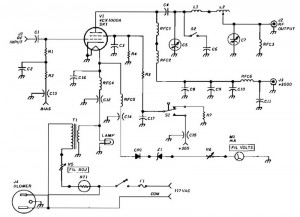
1500 Watt RF Amplifier circuit can be utilized to drive a transmitter antenna. It is also applicable for powering RF high power sources, microwave heating, and other uses.
The 1500 Watt RF Amplifier circuit is designed to amplify radio frequency signals, making it suitable for various applications in the field of telecommunications and microwave technology. This amplifier is capable of driving a transmitter antenna, ensuring that the RF signal is transmitted with sufficient power to reach the desired range.
The circuit typically consists of high-power transistors or RF power MOSFETs that are configured in a push-pull arrangement to enhance efficiency and linearity. The input stage of the amplifier may include impedance matching networks to optimize the power transfer from the source to the amplifier. This is crucial for minimizing signal reflections and maximizing output power.
The design may also incorporate a heat sink or cooling system, as high power levels can generate significant heat that must be dissipated to prevent damage to the components. Additionally, the amplifier circuit may include protection features such as over-temperature shutdown, over-current protection, and RF output monitoring to ensure reliable operation.
For microwave heating applications, the amplifier can be configured to operate at specific frequencies, allowing it to efficiently deliver energy to materials for heating purposes. This versatility makes the 1500 Watt RF Amplifier a valuable component in various industrial, scientific, and telecommunications applications.
Overall, the 1500 Watt RF Amplifier circuit represents a robust solution for high-power RF amplification, offering flexibility for a range of uses from driving antennas to facilitating microwave heating processes.1500 Watt RF Amplifier circuit can be used to drive your transmitter antenna, it can also include driving to the source of the RF high power, microwave heating, and more. 🔗 External reference
The 1500 Watt RF Amplifier circuit is designed to amplify radio frequency signals, making it suitable for various applications in the field of telecommunications and microwave technology. This amplifier is capable of driving a transmitter antenna, ensuring that the RF signal is transmitted with sufficient power to reach the desired range.
The circuit typically consists of high-power transistors or RF power MOSFETs that are configured in a push-pull arrangement to enhance efficiency and linearity. The input stage of the amplifier may include impedance matching networks to optimize the power transfer from the source to the amplifier. This is crucial for minimizing signal reflections and maximizing output power.
The design may also incorporate a heat sink or cooling system, as high power levels can generate significant heat that must be dissipated to prevent damage to the components. Additionally, the amplifier circuit may include protection features such as over-temperature shutdown, over-current protection, and RF output monitoring to ensure reliable operation.
For microwave heating applications, the amplifier can be configured to operate at specific frequencies, allowing it to efficiently deliver energy to materials for heating purposes. This versatility makes the 1500 Watt RF Amplifier a valuable component in various industrial, scientific, and telecommunications applications.
Overall, the 1500 Watt RF Amplifier circuit represents a robust solution for high-power RF amplification, offering flexibility for a range of uses from driving antennas to facilitating microwave heating processes.1500 Watt RF Amplifier circuit can be used to drive your transmitter antenna, it can also include driving to the source of the RF high power, microwave heating, and more. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713