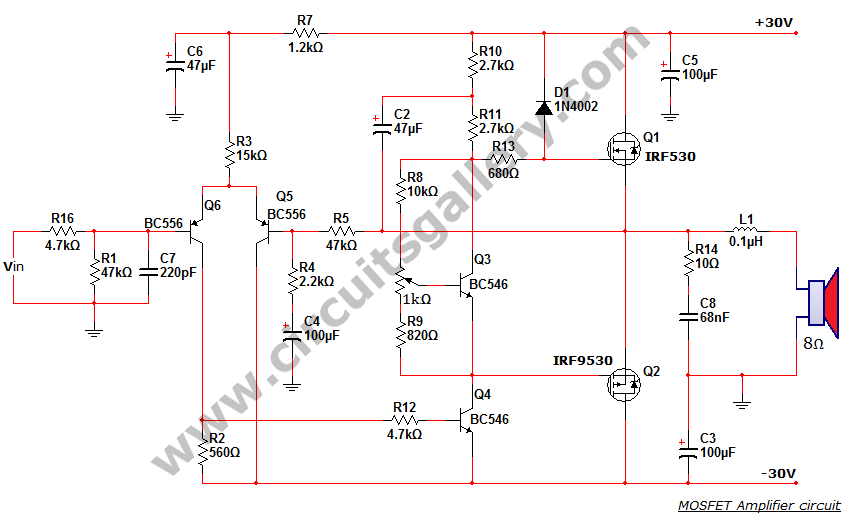
1KHZ Sine Wave Generator Circuit
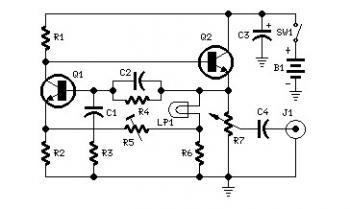
Set R5 to read 1V RMS on an audio millivoltmeter connected to the output with R7 rotated fully clockwise, or to view a sine wave of 2.828V peak-to-peak amplitude on the oscilloscope. An audio amplifier is an electronic device that amplifies low-power audio signals, which are primarily composed of frequencies between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz—the human hearing range—to a level suitable for driving loudspeakers. It serves as the final stage in a typical audio playback chain. The preceding stages in this chain include low-power audio amplifiers that perform functions such as pre-amplification, equalization, tone control, mixing/effects, and sources of audio like record players, CD players, and cassette players. Most audio amplifiers require these low-level inputs to conform to line levels. While the input signal to an audio amplifier may measure only a few hundred microwatts, its output can reach tens, hundreds, or thousands of watts. More information about power audio amplifiers can be found on Wikipedia. A video tutorial is available that demonstrates how to build a simple audio amplifier based on the LM386 amplifier chip, which can be constructed for less than $20 (or possibly under $8 in some countries) and can be used to amplify any low-level audio signal, including those from a guitar, bass, or MP3 player.
An audio amplifier circuit typically consists of several key components, including resistors, capacitors, and the main amplification device, which in this case is the LM386 chip. The LM386 is a low-voltage audio power amplifier that is designed for battery-operated devices. It operates with a supply voltage ranging from 4V to 12V and can deliver up to 1 watt of output power into an 8-ohm load, making it suitable for small audio applications.
The circuit configuration often includes a gain-setting resistor connected between pins 1 and 8 of the LM386, allowing for adjustable amplification. For a standard gain of 20, no external components are needed; however, if higher gain is required, a resistor can be added. Bypass capacitors are also placed across the power supply pins to filter out noise and stabilize the voltage supply, improving the amplifier's performance.
Input signals are typically coupled to the amplifier through capacitors to block any DC offset, ensuring that only the AC audio signal is amplified. The output is connected to a speaker through an output capacitor, which blocks DC while allowing the amplified audio signal to pass through to the speaker.
In practical applications, this audio amplifier circuit can be used in a variety of settings, from personal audio systems to DIY projects. By following the schematic provided in the video tutorial, users can assemble the circuit on a breadboard or a PCB, making it an accessible project for those looking to enhance their audio capabilities without significant investment.Set R5 to read 1V RMS on an Audio Millivoltmeter connected to the output with R7 rotated fully clockwise, or to view a sinewave of 2. 828V Peak-to-Peak amplitude on the oscilloscope. An audio amplifier is an electronic amplifier that amplifies low-power audio signals (signals composed primarily of frequencies between 20 - 20 000 Hz, the human range
of hearing) to a level suitable for driving loudspeakers and is the final stage in a typical audio playback chain. The preceding stages in such a chain are low power audio amplifiers which perform tasks like pre-amplification, equalization, tone control, mixing/effects, or audio sources like record players, CD players, and cassette players.
Most audio amplifiers require these low-level inputs to adhere to line levels. While the input signal to an audio amplifier may measure only a few hundred microwatts, its output may be tens, hundreds, or thousands of watts. More explanation about power audio amplifier can be found at wikipedia. org This is a video tutorial about how to a very simple audio amplifier based on the LM386 amplifier chip.
It can be built for less than $20 (or might be less than $8 in some countries) and used to amplify any low level audio signal including a guitar, bass or mp3 player. 🔗 External reference
An audio amplifier circuit typically consists of several key components, including resistors, capacitors, and the main amplification device, which in this case is the LM386 chip. The LM386 is a low-voltage audio power amplifier that is designed for battery-operated devices. It operates with a supply voltage ranging from 4V to 12V and can deliver up to 1 watt of output power into an 8-ohm load, making it suitable for small audio applications.
The circuit configuration often includes a gain-setting resistor connected between pins 1 and 8 of the LM386, allowing for adjustable amplification. For a standard gain of 20, no external components are needed; however, if higher gain is required, a resistor can be added. Bypass capacitors are also placed across the power supply pins to filter out noise and stabilize the voltage supply, improving the amplifier's performance.
Input signals are typically coupled to the amplifier through capacitors to block any DC offset, ensuring that only the AC audio signal is amplified. The output is connected to a speaker through an output capacitor, which blocks DC while allowing the amplified audio signal to pass through to the speaker.
In practical applications, this audio amplifier circuit can be used in a variety of settings, from personal audio systems to DIY projects. By following the schematic provided in the video tutorial, users can assemble the circuit on a breadboard or a PCB, making it an accessible project for those looking to enhance their audio capabilities without significant investment.Set R5 to read 1V RMS on an Audio Millivoltmeter connected to the output with R7 rotated fully clockwise, or to view a sinewave of 2. 828V Peak-to-Peak amplitude on the oscilloscope. An audio amplifier is an electronic amplifier that amplifies low-power audio signals (signals composed primarily of frequencies between 20 - 20 000 Hz, the human range
of hearing) to a level suitable for driving loudspeakers and is the final stage in a typical audio playback chain. The preceding stages in such a chain are low power audio amplifiers which perform tasks like pre-amplification, equalization, tone control, mixing/effects, or audio sources like record players, CD players, and cassette players.
Most audio amplifiers require these low-level inputs to adhere to line levels. While the input signal to an audio amplifier may measure only a few hundred microwatts, its output may be tens, hundreds, or thousands of watts. More explanation about power audio amplifier can be found at wikipedia. org This is a video tutorial about how to a very simple audio amplifier based on the LM386 amplifier chip.
It can be built for less than $20 (or might be less than $8 in some countries) and used to amplify any low level audio signal including a guitar, bass or mp3 player. 🔗 External reference