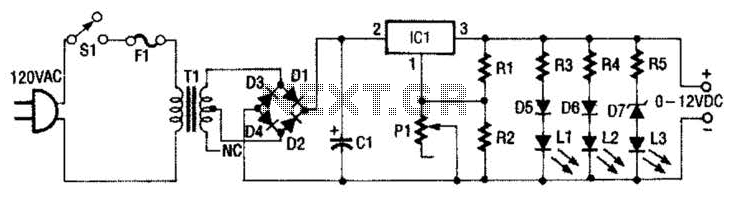
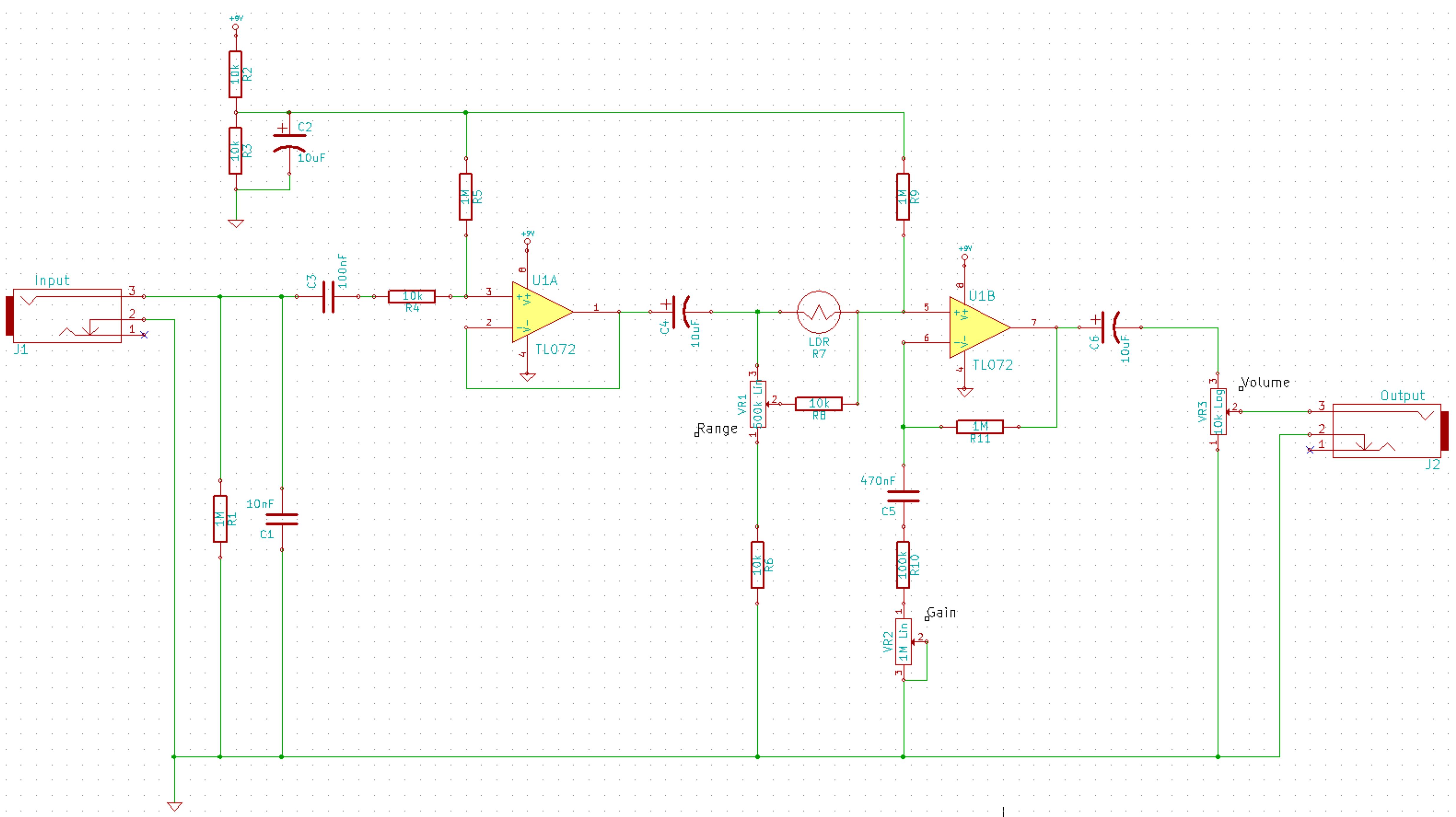
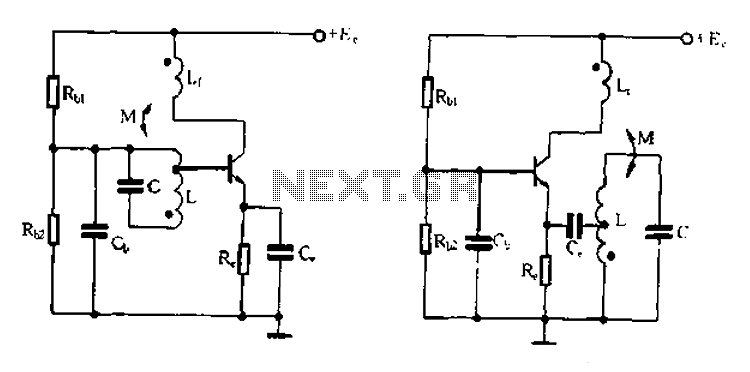
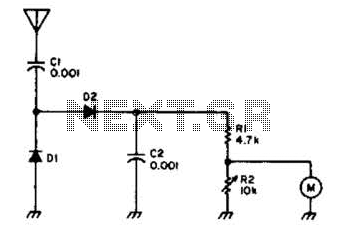
50 impedance RF2320 linear amplification circuit diagram
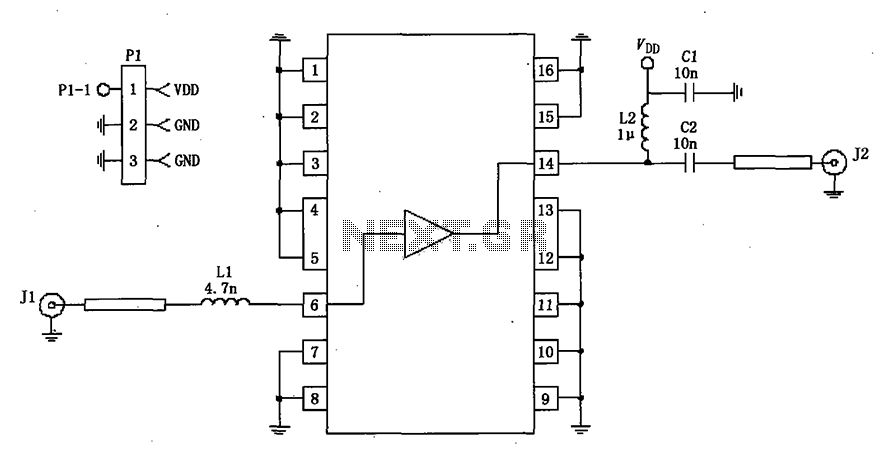
A 50-ohm impedance is illustrated in the RF2320 linear amplifier circuit, which is configured for input and output using transmission lines and inductive or capacitive components to create a matching network.
The RF2320 linear amplifier circuit is designed to operate with a 50-ohm impedance, which is a standard value in RF applications, ensuring optimal power transfer and minimal signal reflection. The input and output stages of the amplifier utilize transmission lines, which are critical for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing losses. These transmission lines can be implemented using microstrip or stripline technologies, depending on the PCB design and the desired frequency characteristics.
The matching network is an essential component in this circuit, as it ensures that the amplifier is properly matched to the source and load impedances. This matching can be achieved through the use of inductive or capacitive components, which can be configured in various ways, such as L-networks, T-networks, or π-networks, depending on the specific requirements of the application. The choice of components and their values will depend on the frequency of operation and the specific characteristics of the RF2320 amplifier.
Properly designing the matching network involves calculating the necessary component values to achieve the desired impedance transformation. This can be accomplished using techniques such as Smith chart analysis or computer-aided design (CAD) tools to simulate the circuit performance. The goal is to achieve a flat frequency response over the desired bandwidth while maintaining low insertion loss and high return loss.
In summary, the RF2320 linear amplifier circuit, with its 50-ohm impedance configuration, effectively utilizes transmission lines and matching networks to optimize performance for RF applications. The careful selection and arrangement of inductive and capacitive components are crucial for achieving the desired operational characteristics.50 impedance as shown in Figure grounds RF2320 linear amplifier circuit configured, input, output, using the transmission line and inductive or capacitive constitute matching n etwork.
The RF2320 linear amplifier circuit is designed to operate with a 50-ohm impedance, which is a standard value in RF applications, ensuring optimal power transfer and minimal signal reflection. The input and output stages of the amplifier utilize transmission lines, which are critical for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing losses. These transmission lines can be implemented using microstrip or stripline technologies, depending on the PCB design and the desired frequency characteristics.
The matching network is an essential component in this circuit, as it ensures that the amplifier is properly matched to the source and load impedances. This matching can be achieved through the use of inductive or capacitive components, which can be configured in various ways, such as L-networks, T-networks, or π-networks, depending on the specific requirements of the application. The choice of components and their values will depend on the frequency of operation and the specific characteristics of the RF2320 amplifier.
Properly designing the matching network involves calculating the necessary component values to achieve the desired impedance transformation. This can be accomplished using techniques such as Smith chart analysis or computer-aided design (CAD) tools to simulate the circuit performance. The goal is to achieve a flat frequency response over the desired bandwidth while maintaining low insertion loss and high return loss.
In summary, the RF2320 linear amplifier circuit, with its 50-ohm impedance configuration, effectively utilizes transmission lines and matching networks to optimize performance for RF applications. The careful selection and arrangement of inductive and capacitive components are crucial for achieving the desired operational characteristics.50 impedance as shown in Figure grounds RF2320 linear amplifier circuit configured, input, output, using the transmission line and inductive or capacitive constitute matching n etwork.