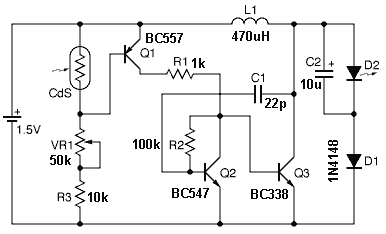
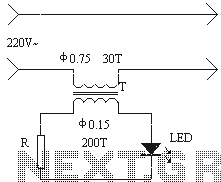
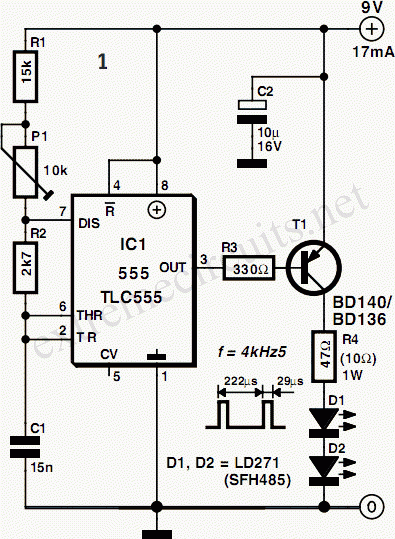
A control circuit diagram 555 pairs steady mode
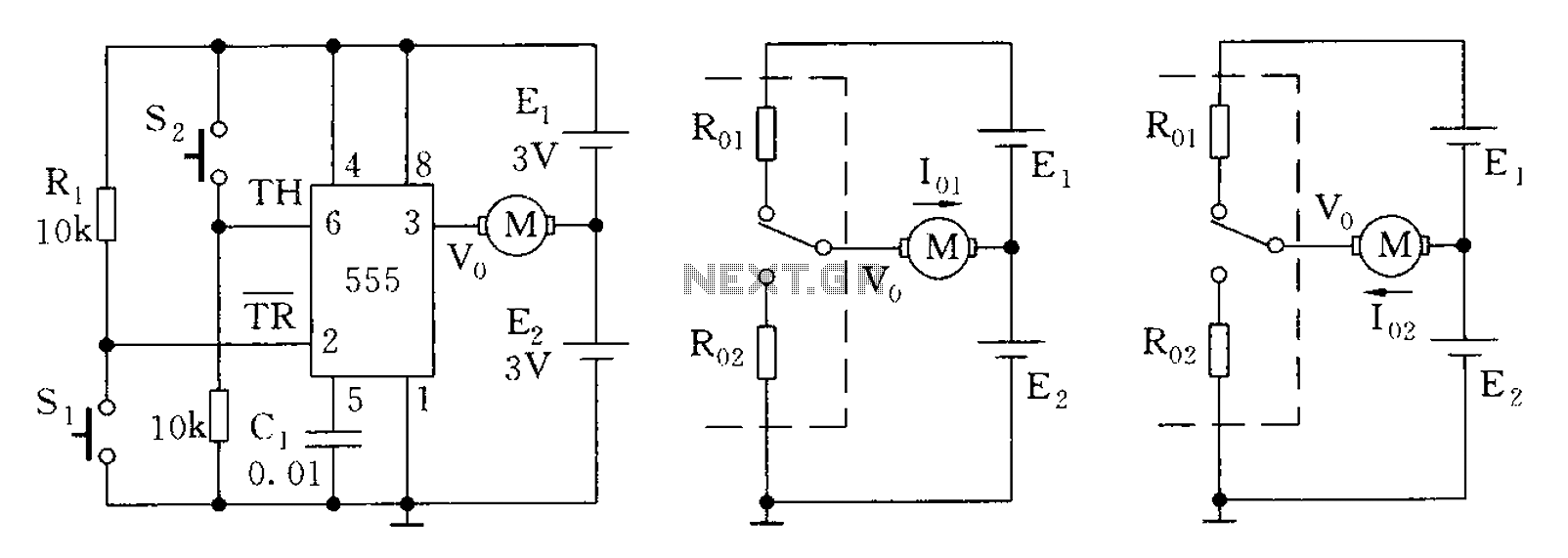
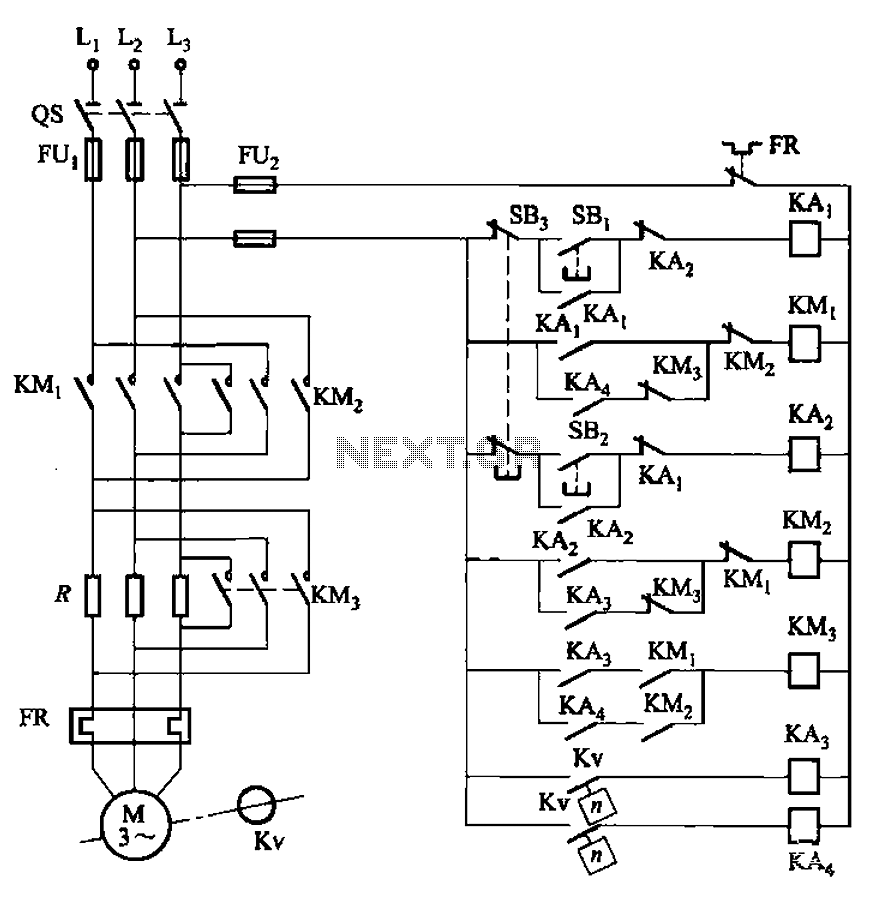
The 555 timer in bistable mode has fewer applications compared to its stable and monostable modes. Bistable mode refers to the circuit configuration based on the R-S (Reset-Set) trigger mode. An example of this is a micro-motor reversing control circuit diagram.
The 555 timer IC is a versatile component commonly used in various electronic circuits. In bistable mode, the 555 timer operates as a flip-flop, allowing it to maintain its output state until it receives a triggering pulse. This mode is particularly useful in applications where two stable states are required, such as in memory storage, toggle switches, or motor control circuits.
In the context of a micro-motor reversing control circuit, the bistable configuration allows for the control of the motor's direction. The circuit typically consists of a 555 timer, resistors, capacitors, and the micro-motor itself. When a trigger pulse is applied to the reset or set pin of the 555 timer, it changes the output state, thus reversing the direction of the motor.
The circuit diagram for this application would illustrate the connections between the 555 timer and the motor, as well as the necessary components to ensure proper operation. Resistors are used to set the timing characteristics, while capacitors may be included to filter noise or stabilize the power supply. The output of the timer directly controls the motor driver circuit, which may include transistors or relays to handle the motor's power requirements.
Overall, the bistable mode of the 555 timer offers a reliable solution for controlling devices such as micro-motors, providing a simple yet effective means of toggling between two states based on external inputs.555 bistable mode, stable and non-stable than single modes of application is relatively less. Bistable mode means that the circuit composed by R-S trigger mode. As shown by a m icro-motor reversing bistable mode control circuit diagram. 7b9bd92f536999.jpg onload if (this.width 620) this.wih 620; onclick window.open (this.src) style cursor: pointer alt Click to enlarge /
The 555 timer IC is a versatile component commonly used in various electronic circuits. In bistable mode, the 555 timer operates as a flip-flop, allowing it to maintain its output state until it receives a triggering pulse. This mode is particularly useful in applications where two stable states are required, such as in memory storage, toggle switches, or motor control circuits.
In the context of a micro-motor reversing control circuit, the bistable configuration allows for the control of the motor's direction. The circuit typically consists of a 555 timer, resistors, capacitors, and the micro-motor itself. When a trigger pulse is applied to the reset or set pin of the 555 timer, it changes the output state, thus reversing the direction of the motor.
The circuit diagram for this application would illustrate the connections between the 555 timer and the motor, as well as the necessary components to ensure proper operation. Resistors are used to set the timing characteristics, while capacitors may be included to filter noise or stabilize the power supply. The output of the timer directly controls the motor driver circuit, which may include transistors or relays to handle the motor's power requirements.
Overall, the bistable mode of the 555 timer offers a reliable solution for controlling devices such as micro-motors, providing a simple yet effective means of toggling between two states based on external inputs.555 bistable mode, stable and non-stable than single modes of application is relatively less. Bistable mode means that the circuit composed by R-S trigger mode. As shown by a m icro-motor reversing bistable mode control circuit diagram. 7b9bd92f536999.jpg onload if (this.width 620) this.wih 620; onclick window.open (this.src) style cursor: pointer alt Click to enlarge /