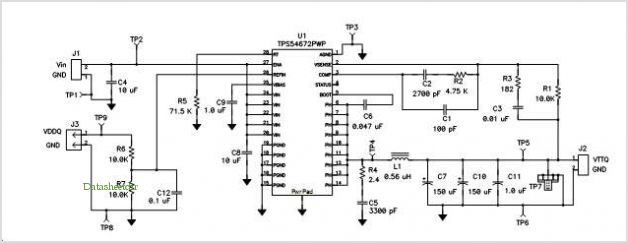
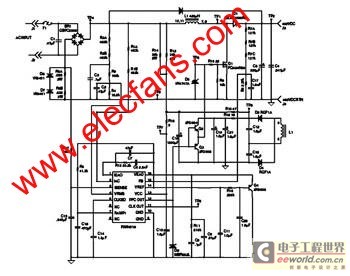
Active inductor
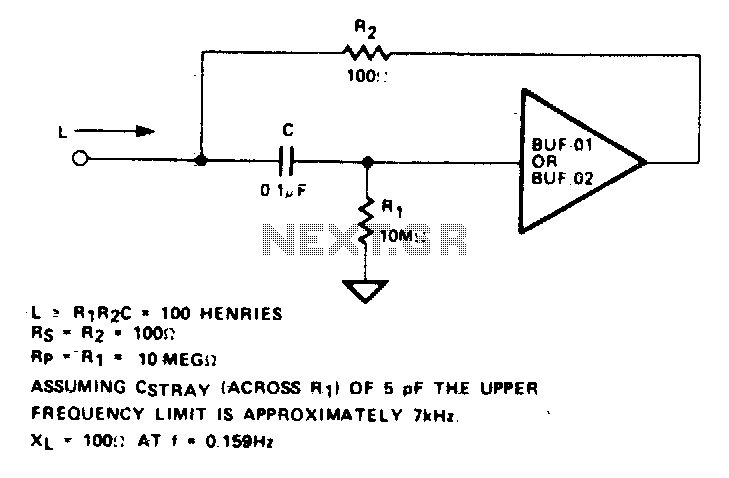
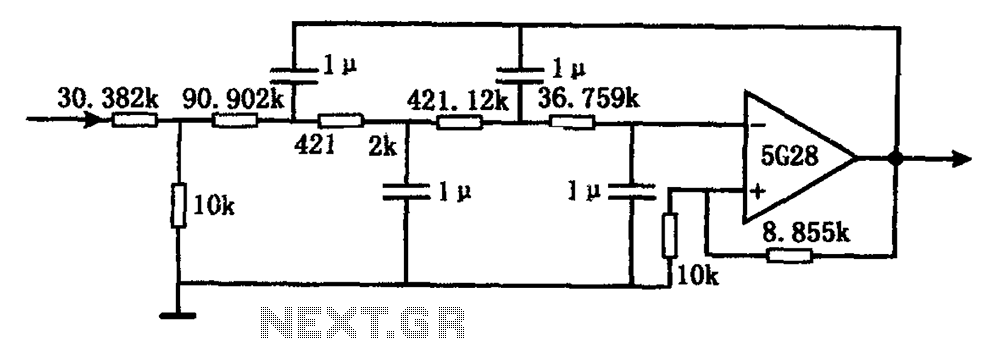
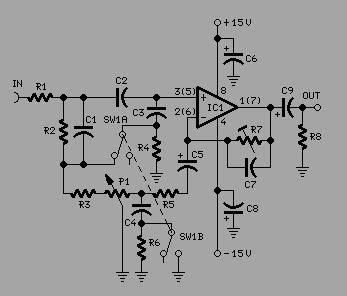
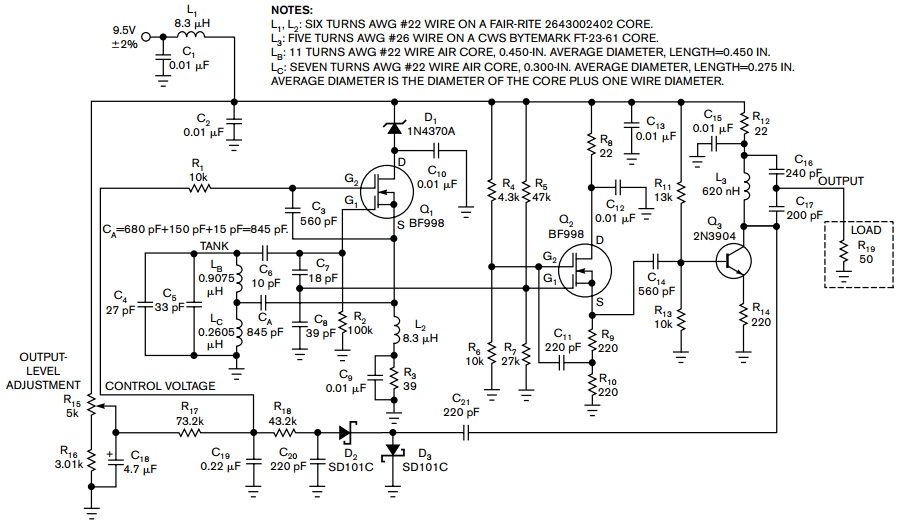
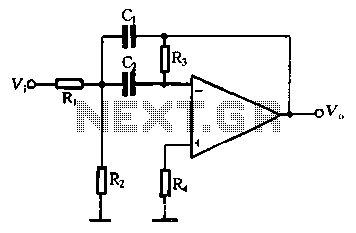
An active inductor is implemented using an eight-lead integrated circuit (IC), two carbon resistors, and a small capacitor. A typical commercial inductor with a value of 50 henries may occupy up to five cubic inches.
An active inductor circuit provides a compact and efficient alternative to traditional passive inductors. The design utilizes an eight-lead IC, which integrates multiple functions necessary for the operation of the active inductor. The two carbon resistors are employed to set the gain and stability of the circuit, while the small capacitor is used for frequency compensation and filtering purposes.
In this configuration, the active inductor operates by utilizing feedback mechanisms within the IC to emulate the inductive behavior. This allows for a significant reduction in physical size compared to conventional inductors, which can be bulky and occupy considerable space. The use of an active inductor can be particularly advantageous in applications requiring high inductance values, such as RF circuits, where traditional inductors would be impractical due to their size and weight.
The integration of the components within an IC also enhances performance characteristics, such as bandwidth and response time, making active inductors suitable for modern electronic applications. Overall, the active inductor represents a significant advancement in circuit design, providing a space-efficient and high-performance solution for inductive components in electronic systems.An active inductor is realized with an eight-lead IC, two carbon resistors, and a small capacitor A commercial inductor of 50 henries may occupy up to five cubic inches. 🔗 External reference
An active inductor circuit provides a compact and efficient alternative to traditional passive inductors. The design utilizes an eight-lead IC, which integrates multiple functions necessary for the operation of the active inductor. The two carbon resistors are employed to set the gain and stability of the circuit, while the small capacitor is used for frequency compensation and filtering purposes.
In this configuration, the active inductor operates by utilizing feedback mechanisms within the IC to emulate the inductive behavior. This allows for a significant reduction in physical size compared to conventional inductors, which can be bulky and occupy considerable space. The use of an active inductor can be particularly advantageous in applications requiring high inductance values, such as RF circuits, where traditional inductors would be impractical due to their size and weight.
The integration of the components within an IC also enhances performance characteristics, such as bandwidth and response time, making active inductors suitable for modern electronic applications. Overall, the active inductor represents a significant advancement in circuit design, providing a space-efficient and high-performance solution for inductive components in electronic systems.An active inductor is realized with an eight-lead IC, two carbon resistors, and a small capacitor A commercial inductor of 50 henries may occupy up to five cubic inches. 🔗 External reference