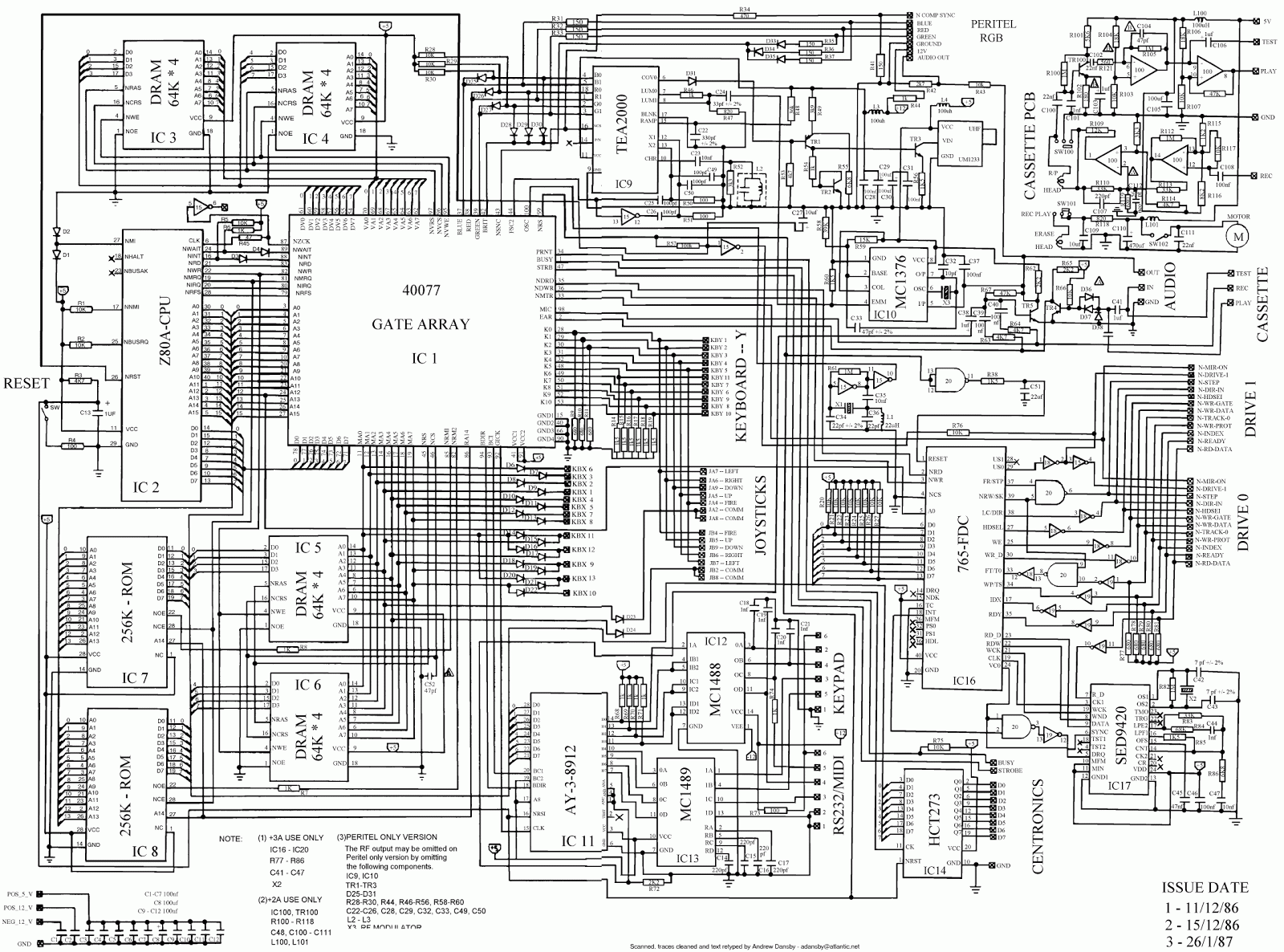
Amplifier Circuit using MOSFET Output Stage
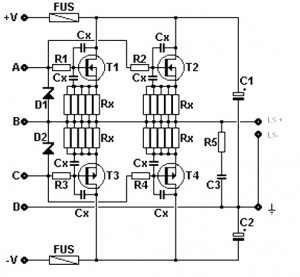
Amplifier circuit featuring a MOSFET output stage, serving as an alternative to the output stage that utilizes bipolar transistors. Advantages of the MOSFET amplifier include ease of operation, the ability to handle hundreds of watts with straightforward parallel configurations, a negative temperature coefficient, and rapid switching times.
The described amplifier circuit employs MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) in its output stage, which offers several benefits over traditional bipolar transistor amplifiers. The simplicity of operation is a key feature, as MOSFETs can be driven directly by low-voltage control signals, reducing the complexity of the driving circuitry. This characteristic allows for straightforward integration into various applications, including audio amplifiers and power amplifiers for RF signals.
The design can easily accommodate high power levels, with the capability of handling hundreds of watts through parallel configurations of multiple MOSFETs. This parallel arrangement not only enhances the overall power output but also distributes thermal load, allowing for more efficient heat dissipation. The negative temperature coefficient of MOSFETs is advantageous in preventing thermal runaway, as an increase in temperature leads to a decrease in current, providing a natural form of thermal regulation.
Rapid switching times are another significant advantage of MOSFETs, making them suitable for high-frequency applications. This feature is particularly beneficial in pulse-width modulation (PWM) applications and Class D amplifiers, where efficiency and performance are critical.
In terms of circuit design, the MOSFET output stage typically includes a driver circuit that can provide the necessary gate voltage to switch the MOSFETs on and off efficiently. Additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and sometimes inductors may be included to shape the frequency response and stability of the amplifier. Feedback mechanisms can also be integrated to enhance linearity and reduce distortion, ensuring high-fidelity audio reproduction or signal amplification.
Overall, the use of MOSFETs in amplifier circuits presents a modern approach that combines efficiency, simplicity, and high performance, making it a preferred choice in contemporary electronic design.Amplifier circuit with MOSFET output stage, as a substitute for the output stage based on bipolar transistors. Advantages MOSFET Amplifier : simplicity of operation, hundreds of watts with a simple parallel, negative temperature coefficient and fast switching times
🔗 External reference
The described amplifier circuit employs MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) in its output stage, which offers several benefits over traditional bipolar transistor amplifiers. The simplicity of operation is a key feature, as MOSFETs can be driven directly by low-voltage control signals, reducing the complexity of the driving circuitry. This characteristic allows for straightforward integration into various applications, including audio amplifiers and power amplifiers for RF signals.
The design can easily accommodate high power levels, with the capability of handling hundreds of watts through parallel configurations of multiple MOSFETs. This parallel arrangement not only enhances the overall power output but also distributes thermal load, allowing for more efficient heat dissipation. The negative temperature coefficient of MOSFETs is advantageous in preventing thermal runaway, as an increase in temperature leads to a decrease in current, providing a natural form of thermal regulation.
Rapid switching times are another significant advantage of MOSFETs, making them suitable for high-frequency applications. This feature is particularly beneficial in pulse-width modulation (PWM) applications and Class D amplifiers, where efficiency and performance are critical.
In terms of circuit design, the MOSFET output stage typically includes a driver circuit that can provide the necessary gate voltage to switch the MOSFETs on and off efficiently. Additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and sometimes inductors may be included to shape the frequency response and stability of the amplifier. Feedback mechanisms can also be integrated to enhance linearity and reduce distortion, ensuring high-fidelity audio reproduction or signal amplification.
Overall, the use of MOSFETs in amplifier circuits presents a modern approach that combines efficiency, simplicity, and high performance, making it a preferred choice in contemporary electronic design.Amplifier circuit with MOSFET output stage, as a substitute for the output stage based on bipolar transistors. Advantages MOSFET Amplifier : simplicity of operation, hundreds of watts with a simple parallel, negative temperature coefficient and fast switching times
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713