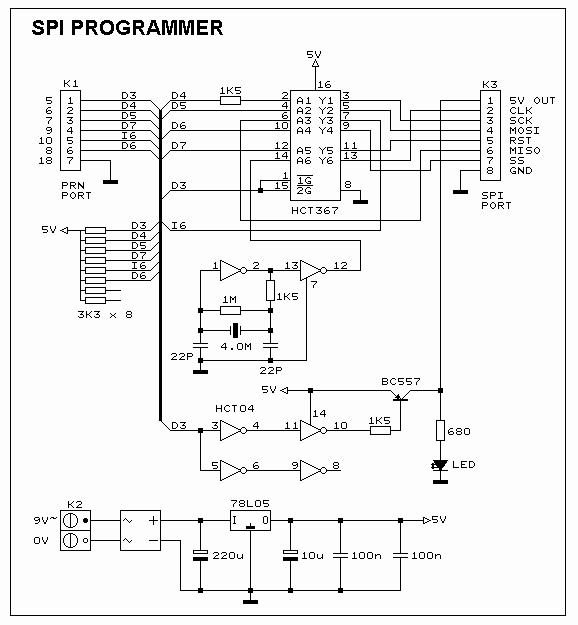
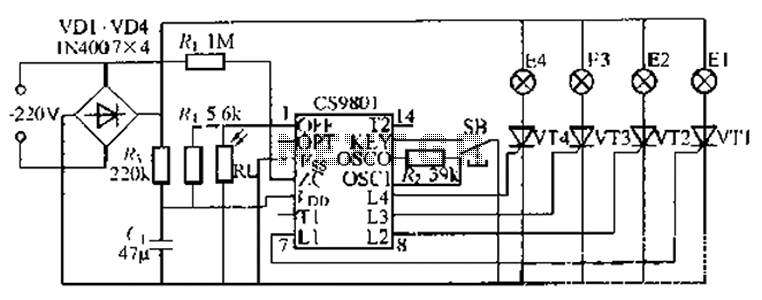
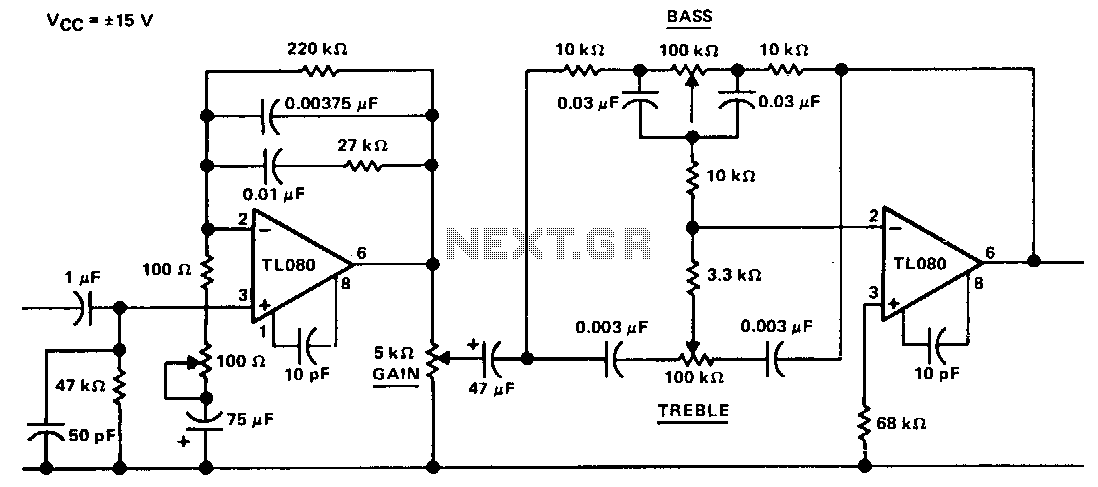
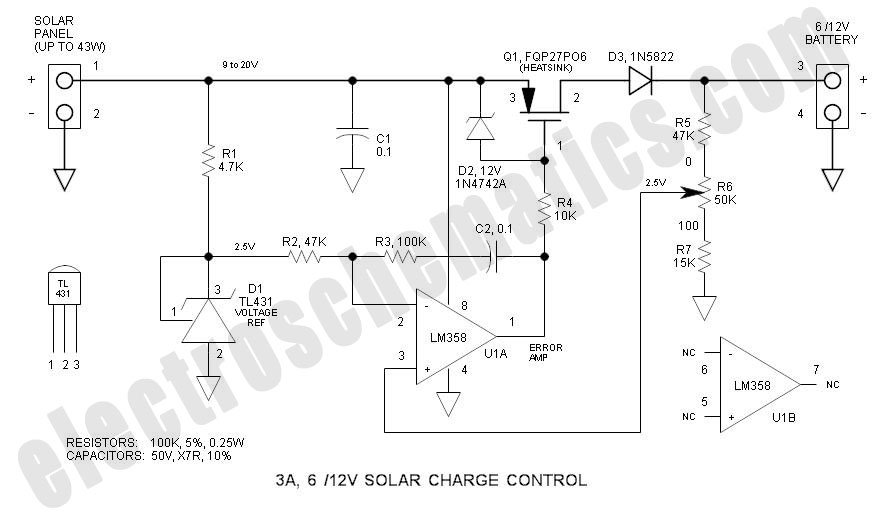
Amplifier Cool-Down Circuit Circuit

This cool-down relay circuit utilizes an integrated circuit (IC) timer to control a relay, which maintains the operation of the blower for a specified time delay determined by timer U3. The capacitance value of C2 can be adjusted to either extend or reduce the duration of the delay, depending on requirements.
The cool-down relay circuit is designed to enhance the operational efficiency of systems requiring a cooling period after shutdown, such as HVAC systems or industrial equipment. The core component, timer U3, typically configured as a monostable multivibrator, generates a pulse that activates the relay upon receiving a trigger signal.
The relay acts as a switch that keeps the blower motor operational for a predetermined time, ensuring that residual heat is effectively dissipated from the system. The time delay is primarily influenced by the values of the timing capacitor (C2) and the timing resistor (R1), which work in conjunction with the timer's internal circuitry. By altering the capacitance of C2, one can fine-tune the delay period to meet specific cooling requirements.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, ensuring that the relay coil does not generate voltage spikes that could damage the timer or other sensitive components. A power supply circuit is necessary to provide the appropriate voltage levels for the timer and relay operation.
In summary, this cool-down relay circuit effectively manages the cooling process by utilizing a timer to control the relay, with adjustable components allowing for customization of the delay period based on the application's thermal management needs. This cool-down relay circuit uses an IC timer to drive a relay, which keeps the blower on for a time delay from timer U3. The value of C2 can be changed to lengthen or shorten the time, as needed.
The cool-down relay circuit is designed to enhance the operational efficiency of systems requiring a cooling period after shutdown, such as HVAC systems or industrial equipment. The core component, timer U3, typically configured as a monostable multivibrator, generates a pulse that activates the relay upon receiving a trigger signal.
The relay acts as a switch that keeps the blower motor operational for a predetermined time, ensuring that residual heat is effectively dissipated from the system. The time delay is primarily influenced by the values of the timing capacitor (C2) and the timing resistor (R1), which work in conjunction with the timer's internal circuitry. By altering the capacitance of C2, one can fine-tune the delay period to meet specific cooling requirements.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, ensuring that the relay coil does not generate voltage spikes that could damage the timer or other sensitive components. A power supply circuit is necessary to provide the appropriate voltage levels for the timer and relay operation.
In summary, this cool-down relay circuit effectively manages the cooling process by utilizing a timer to control the relay, with adjustable components allowing for customization of the delay period based on the application's thermal management needs. This cool-down relay circuit uses an IC timer to drive a relay, which keeps the blower on for a time delay from timer U3. The value of C2 can be changed to lengthen or shorten the time, as needed.