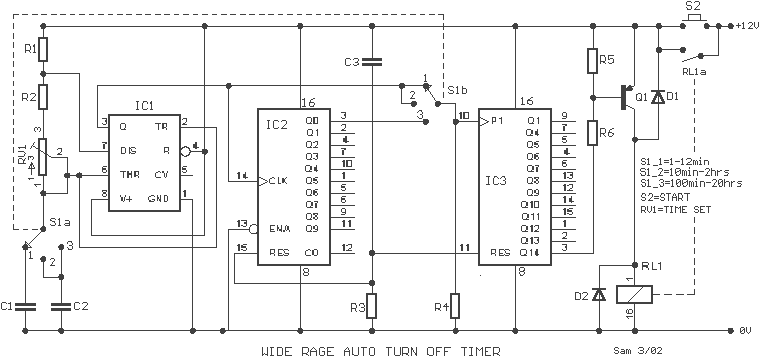
asymmetric timer
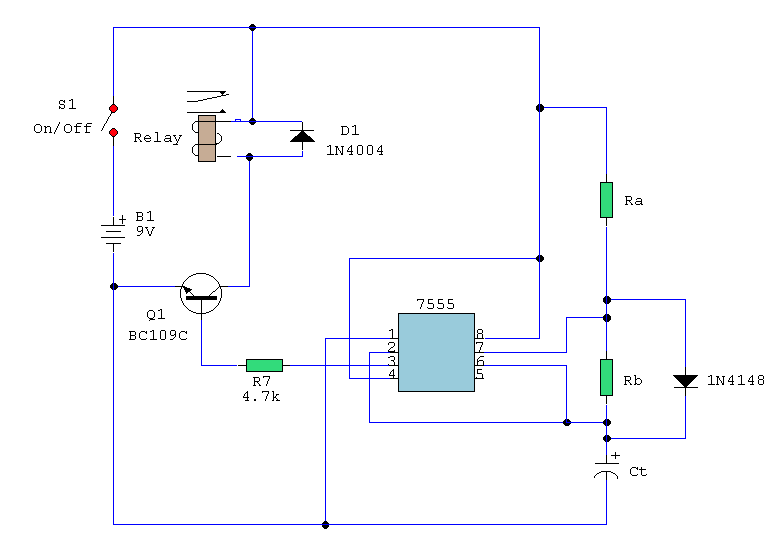
A simple astable timer is constructed using a 555 timer IC. The mark (on) and space (off) durations can be set independently. The timing circuit comprises resistors Ra, Rb, and capacitor Ct. The capacitor Ct charges through resistor Ra, which is in series with a 1N4148 diode. The discharge path for the capacitor is through resistor Rb into pin 7 of the IC. This configuration allows both halves of the timing period to be adjusted independently. It is important to note that the formula for T(on) does not consider the series resistance and forward voltage drop of the 1N4148 diode, making it an approximation. Conversely, T(off) is unaffected by diode D1, resulting in a precise timing calculation.
The astable multivibrator configuration using the 555 timer operates continuously, switching between its high and low states to create a square wave output. The timing cycle consists of two intervals: the high state duration (T(on)) and the low state duration (T(off)). The output frequency (f) of the oscillator can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(Ra + 2Rb) \cdot Ct} \]
where Ra and Rb are the resistances in ohms, and Ct is the capacitance in farads. The high state duration (T(on)) can be determined by:
\[ T(on) = (Ra + Rb) \cdot Ct \]
and the low state duration (T(off)) is given by:
\[ T(off) = Rb \cdot Ct \]
In this configuration, when the output is high, capacitor Ct charges through resistor Ra and the diode, allowing for a faster charge time due to the diode's forward conduction. Once the voltage across Ct reaches approximately two-thirds of the supply voltage (Vcc), the 555 timer switches states, and the capacitor begins to discharge through resistor Rb into pin 7. The discharge continues until the voltage drops below one-third of Vcc, at which point the cycle repeats.
To ensure accurate timing, it is crucial to select appropriate values for resistors Ra and Rb, as well as the capacitor Ct. The choice of components will influence the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform. Additionally, external factors such as temperature and component tolerances can affect the timing accuracy, particularly for T(on), which is approximated due to the diode's characteristics. In practical applications, this astable timer circuit can be utilized in various timing, pulse generation, and oscillation applications, making it a versatile component in electronic design.A simple astable timer made with the 555, the mark (on) and space (off) values may be setindependently. The timing chain consists of resistors Ra, Rb and capacitor Ct. The capacitor, Ct charges via Ra which is in series with the 1N4148 diode. The discharge path is via Rb intointo pin 7 of the IC. Both halves of the timing period can now be set inde pendently. Please note that the formula for T(on) ignores the series resistance and forward voltageof the 1N4148 and is therefore approximate, but T(off) is not affected by D1 and is thereforeprecise. 🔗 External reference
The astable multivibrator configuration using the 555 timer operates continuously, switching between its high and low states to create a square wave output. The timing cycle consists of two intervals: the high state duration (T(on)) and the low state duration (T(off)). The output frequency (f) of the oscillator can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(Ra + 2Rb) \cdot Ct} \]
where Ra and Rb are the resistances in ohms, and Ct is the capacitance in farads. The high state duration (T(on)) can be determined by:
\[ T(on) = (Ra + Rb) \cdot Ct \]
and the low state duration (T(off)) is given by:
\[ T(off) = Rb \cdot Ct \]
In this configuration, when the output is high, capacitor Ct charges through resistor Ra and the diode, allowing for a faster charge time due to the diode's forward conduction. Once the voltage across Ct reaches approximately two-thirds of the supply voltage (Vcc), the 555 timer switches states, and the capacitor begins to discharge through resistor Rb into pin 7. The discharge continues until the voltage drops below one-third of Vcc, at which point the cycle repeats.
To ensure accurate timing, it is crucial to select appropriate values for resistors Ra and Rb, as well as the capacitor Ct. The choice of components will influence the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform. Additionally, external factors such as temperature and component tolerances can affect the timing accuracy, particularly for T(on), which is approximated due to the diode's characteristics. In practical applications, this astable timer circuit can be utilized in various timing, pulse generation, and oscillation applications, making it a versatile component in electronic design.A simple astable timer made with the 555, the mark (on) and space (off) values may be setindependently. The timing chain consists of resistors Ra, Rb and capacitor Ct. The capacitor, Ct charges via Ra which is in series with the 1N4148 diode. The discharge path is via Rb intointo pin 7 of the IC. Both halves of the timing period can now be set inde pendently. Please note that the formula for T(on) ignores the series resistance and forward voltageof the 1N4148 and is therefore approximate, but T(off) is not affected by D1 and is thereforeprecise. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713