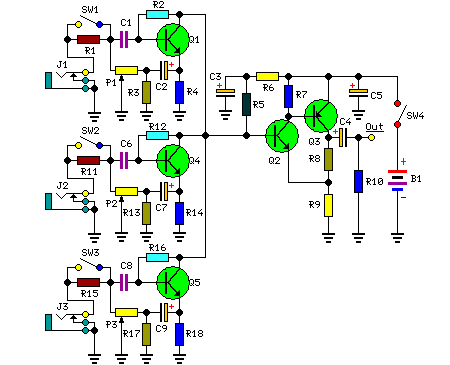
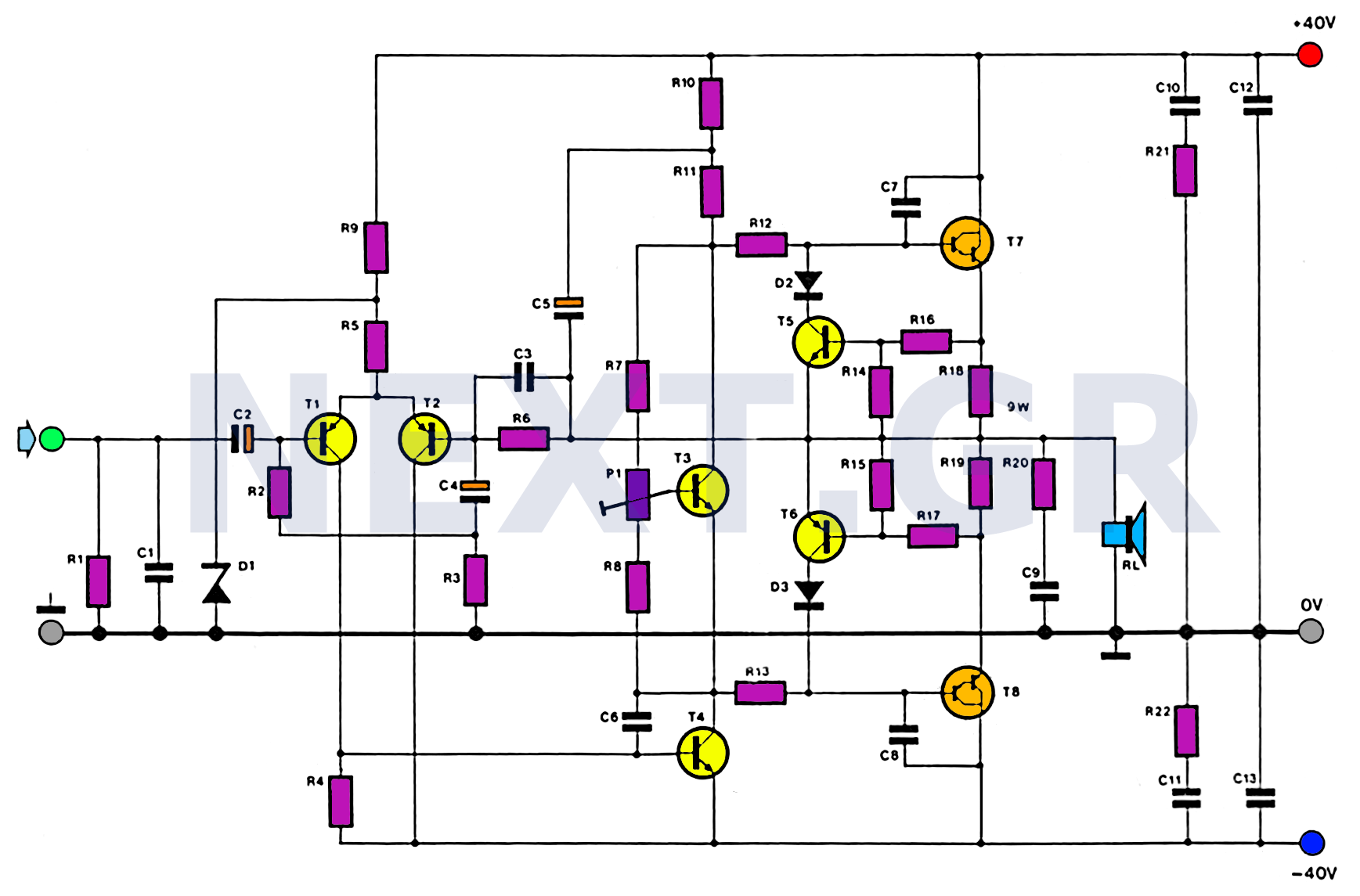
Audio Booster
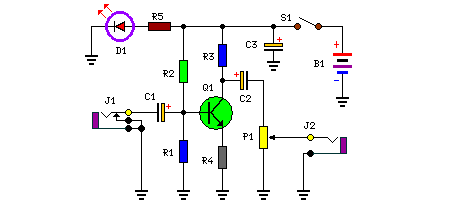
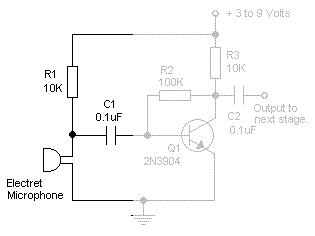
This is a compact and portable unit that can be constructed on a veroboard. The amplifier's gain is nominally set at 20 dB, and its frequency response is primarily dictated by the component values used.
The design of the amplifier circuit focuses on achieving a gain of 20 dB, which indicates that the output signal will be 10 times the amplitude of the input signal. This gain is suitable for various applications, including audio signal amplification and sensor signal conditioning.
The choice of components is critical in defining the frequency response of the amplifier. Typically, resistors and capacitors are selected based on desired cutoff frequencies, which determine the bandwidth of the amplifier. For instance, using a capacitor in the feedback loop can create a high-pass filter effect, allowing signals above a certain frequency to pass while attenuating lower frequencies. Conversely, a capacitor placed at the input can create a low-pass filter, blocking high-frequency signals.
The construction on a veroboard allows for a straightforward assembly process, where components can be easily placed and soldered in a compact layout. This method also facilitates modifications and troubleshooting, as connections can be adjusted without the need for a custom printed circuit board (PCB).
Power supply considerations are also essential; the amplifier should be powered by a stable voltage source to ensure consistent performance. Bypass capacitors may be employed to filter out noise from the power supply, enhancing the overall signal integrity.
Overall, this small and portable amplifier unit is designed for versatility and ease of construction, making it an excellent choice for hobbyists and professionals alike looking to amplify low-level signals in a variety of applications.Small and portable unit, Can be built on a veroboard The amplifier s gain is nominally 20 dB. Its frequency response is determined primarily by the value.. 🔗 External reference
The design of the amplifier circuit focuses on achieving a gain of 20 dB, which indicates that the output signal will be 10 times the amplitude of the input signal. This gain is suitable for various applications, including audio signal amplification and sensor signal conditioning.
The choice of components is critical in defining the frequency response of the amplifier. Typically, resistors and capacitors are selected based on desired cutoff frequencies, which determine the bandwidth of the amplifier. For instance, using a capacitor in the feedback loop can create a high-pass filter effect, allowing signals above a certain frequency to pass while attenuating lower frequencies. Conversely, a capacitor placed at the input can create a low-pass filter, blocking high-frequency signals.
The construction on a veroboard allows for a straightforward assembly process, where components can be easily placed and soldered in a compact layout. This method also facilitates modifications and troubleshooting, as connections can be adjusted without the need for a custom printed circuit board (PCB).
Power supply considerations are also essential; the amplifier should be powered by a stable voltage source to ensure consistent performance. Bypass capacitors may be employed to filter out noise from the power supply, enhancing the overall signal integrity.
Overall, this small and portable amplifier unit is designed for versatility and ease of construction, making it an excellent choice for hobbyists and professionals alike looking to amplify low-level signals in a variety of applications.Small and portable unit, Can be built on a veroboard The amplifier s gain is nominally 20 dB. Its frequency response is determined primarily by the value.. 🔗 External reference