Audio Clipping Indicator
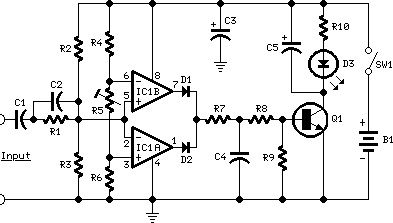
This circuit is designed as a portable unit that signals with an LED when the output waveform of a specific audio stage is "clipping," indicating that it is approaching its maximum permitted peak-to-peak voltage before an overload occurs. This feature assists operators in preventing severe audible distortion through the audio equipment chain. The unit is particularly beneficial for signaling overload in the input stages of mixers, PA systems, or musical instrument amplification chains, and it is also applicable to power amplifiers. A careful adjustment of Trimmer R5 allows the LED to trigger across a wide range of peak-to-peak input voltages to accommodate various requirements. However, setting up this circuit accurately requires an oscilloscope and a sine wave frequency generator. The unit can be integrated into an existing mixer, preamp, or power amplifier, powered by internal supply rails ranging from 9V to 30V. Higher voltage rails can also be utilized with appropriate R/C cells, while SW1 and B1 can be omitted. The core of the circuit is a window comparator, which consists of two op-amps in IC1. This configuration enables precise and symmetrical detection of both the positive and negative peak values of the monitored signal. The outputs of the op-amps are combined through D1 and D2, smoothed by C4, R7, and R8, and then drive the LED driver Q1 with a positive pulse. C5 introduces a slight output delay to detect very short peaks. With the specified values, the circuit can be set up to detect sine wave clipping from less than 1V to 30V peak-to-peak (equivalent to 15W into 8 Ohms). To detect higher output peak-to-peak voltages, the value of R1 must be increased. Conversely, for detecting very low peak-to-peak voltages, it is advisable to decrease the value of R1 to approximately 220K and omit C2, simplifying the adjustment of R5. Utilizing a TL062 chip with a 9V supply results in a stand-by current of about 1.5mA and less than 10mA when the LED is illuminated. For TL072 or TL082 chips, the current draw is approximately 4.5mA and 13mA, respectively.
The circuit operates effectively by implementing a window comparator to monitor audio signals for clipping conditions, which is vital in audio applications where signal integrity is paramount. The window comparator's design allows for accurate detection of both the positive and negative peaks of the audio waveform, ensuring that any distortion caused by clipping is promptly indicated by the LED. This is particularly important in professional audio settings where maintaining sound quality is critical.
In practical applications, the circuit can be integrated into various audio equipment, enhancing its functionality without significant modifications. The ability to adjust the sensitivity through Trimmer R5 provides flexibility, making it suitable for different audio environments and requirements. The power supply versatility allows for adaptation to different systems, ensuring that the circuit can be used in a wide range of scenarios.
The inclusion of additional components such as diodes and capacitors for signal smoothing and delay aids in refining the detection process, allowing the circuit to react to transient signals effectively. The design considerations for current draw also ensure that the circuit remains efficient, making it suitable for long-term use in portable applications. Overall, this circuit serves as a valuable tool for audio professionals, helping to prevent distortion and maintain audio fidelity in various amplification scenarios.This circuit was intended to be used as a separate, portable unit, to signal by means of a LED when the output wave form of a particular audio stage is "clipping" i. e. is reaching the onset of its maximum permitted peak-to-peak voltage value before an overload is occurring.
This will help the operator in preventing severe, audible distortion to be generated through the audio equipment chain. This unit is particularly useful in signaling overload of the input stages in mixers, PA or musical instruments amplification chains, but is also suited to power amplifiers. A careful setting of Trimmer R5 will allow triggering of the LED with a wide range of peak-to-peak input voltages, in order to suit different requirements.
Unfortunately, an oscilloscope and a sine wave frequency generator are required to accurately setup this circuit. Obviously, the unit can be embedded into an existing mixer, preamp or power amplifier, and powered by the internal supply rails in the 9 - 30V range.
The power supply can also be obtained from higher voltage rails provided suitable R/C cells are inserted. SW1 and B1 must obviously be omitted. The heart of the circuit is a window comparator formed by two op-amps packaged into IC1. This technique allows to detect precisely and symmetrically either the positive or negative peak value reached by the monitored signal.
The op-amps outputs are mixed by D1 and D2, smoothed by C4, R7 and R8, and feed the LED driver Q1 with a positive pulse. C5 adds a small output delay in order to allow detection of very short peaks. With the values shown, the circuit can be easily set up to detect sine wave clipping from less than 1V to 30V peak-to-peak (i.
e. 15W into 8 Ohms). If you need to detect higher output peak-to-peak voltages, R1 value must be raised. On the contrary, if the circuit will be used to detect only very low peak-to-peak voltages, it is convenient to lower R1 value to, say, 220K omitting C2. In this way, the adjustment of R5 will be made easier. Using a TL062 chip at 9V supply, stand-by current drawing is about 1. 5mA and less than 10mA when the LED illuminates. With TL072 or TL082 chips, current drawing is about 4. 5mA and 13mA respectively. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates effectively by implementing a window comparator to monitor audio signals for clipping conditions, which is vital in audio applications where signal integrity is paramount. The window comparator's design allows for accurate detection of both the positive and negative peaks of the audio waveform, ensuring that any distortion caused by clipping is promptly indicated by the LED. This is particularly important in professional audio settings where maintaining sound quality is critical.
In practical applications, the circuit can be integrated into various audio equipment, enhancing its functionality without significant modifications. The ability to adjust the sensitivity through Trimmer R5 provides flexibility, making it suitable for different audio environments and requirements. The power supply versatility allows for adaptation to different systems, ensuring that the circuit can be used in a wide range of scenarios.
The inclusion of additional components such as diodes and capacitors for signal smoothing and delay aids in refining the detection process, allowing the circuit to react to transient signals effectively. The design considerations for current draw also ensure that the circuit remains efficient, making it suitable for long-term use in portable applications. Overall, this circuit serves as a valuable tool for audio professionals, helping to prevent distortion and maintain audio fidelity in various amplification scenarios.This circuit was intended to be used as a separate, portable unit, to signal by means of a LED when the output wave form of a particular audio stage is "clipping" i. e. is reaching the onset of its maximum permitted peak-to-peak voltage value before an overload is occurring.
This will help the operator in preventing severe, audible distortion to be generated through the audio equipment chain. This unit is particularly useful in signaling overload of the input stages in mixers, PA or musical instruments amplification chains, but is also suited to power amplifiers. A careful setting of Trimmer R5 will allow triggering of the LED with a wide range of peak-to-peak input voltages, in order to suit different requirements.
Unfortunately, an oscilloscope and a sine wave frequency generator are required to accurately setup this circuit. Obviously, the unit can be embedded into an existing mixer, preamp or power amplifier, and powered by the internal supply rails in the 9 - 30V range.
The power supply can also be obtained from higher voltage rails provided suitable R/C cells are inserted. SW1 and B1 must obviously be omitted. The heart of the circuit is a window comparator formed by two op-amps packaged into IC1. This technique allows to detect precisely and symmetrically either the positive or negative peak value reached by the monitored signal.
The op-amps outputs are mixed by D1 and D2, smoothed by C4, R7 and R8, and feed the LED driver Q1 with a positive pulse. C5 adds a small output delay in order to allow detection of very short peaks. With the values shown, the circuit can be easily set up to detect sine wave clipping from less than 1V to 30V peak-to-peak (i.
e. 15W into 8 Ohms). If you need to detect higher output peak-to-peak voltages, R1 value must be raised. On the contrary, if the circuit will be used to detect only very low peak-to-peak voltages, it is convenient to lower R1 value to, say, 220K omitting C2. In this way, the adjustment of R5 will be made easier. Using a TL062 chip at 9V supply, stand-by current drawing is about 1. 5mA and less than 10mA when the LED illuminates. With TL072 or TL082 chips, current drawing is about 4. 5mA and 13mA respectively. 🔗 External reference