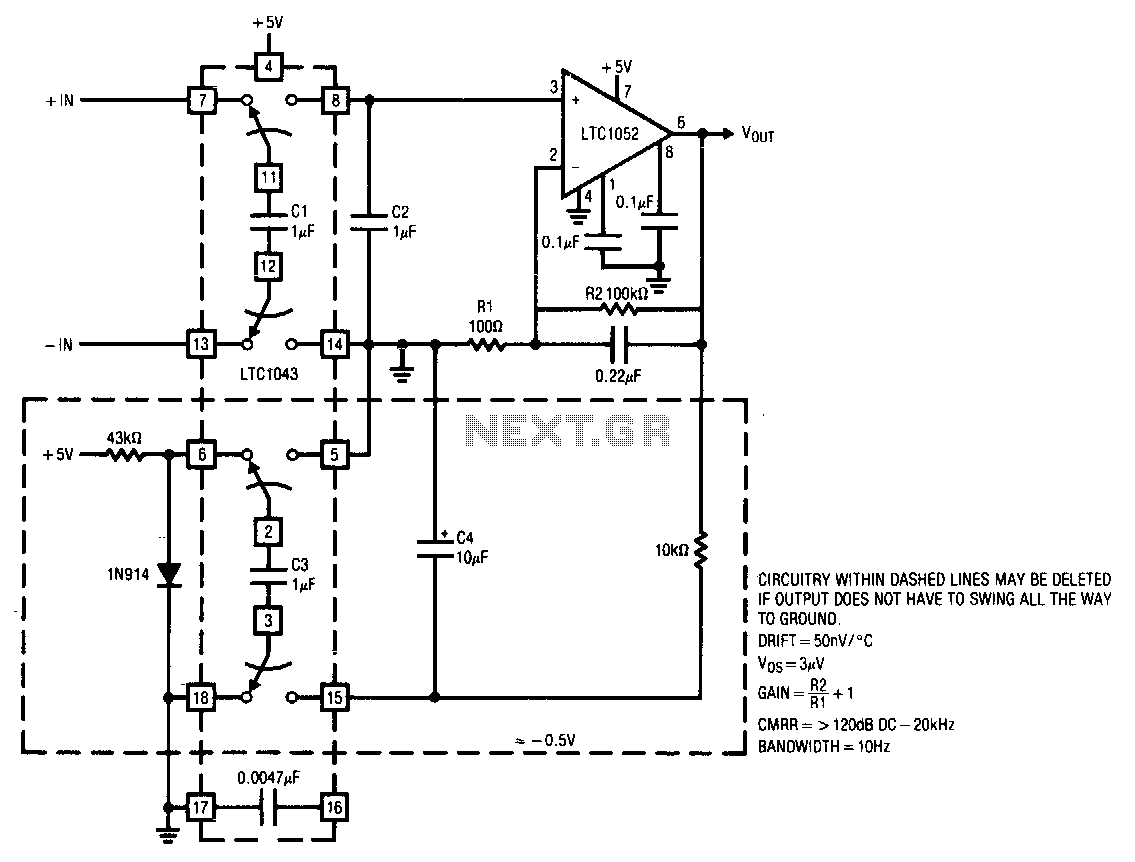
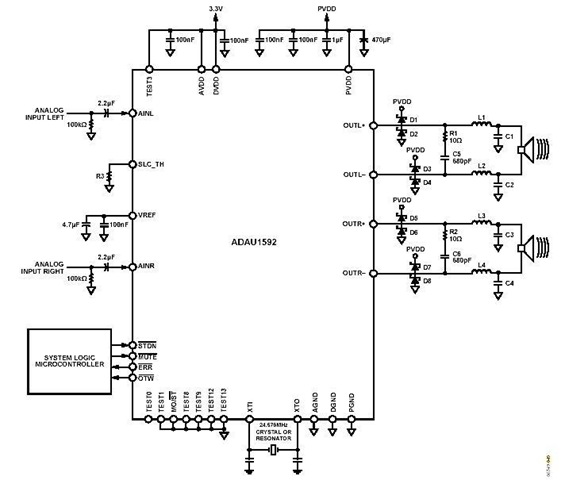
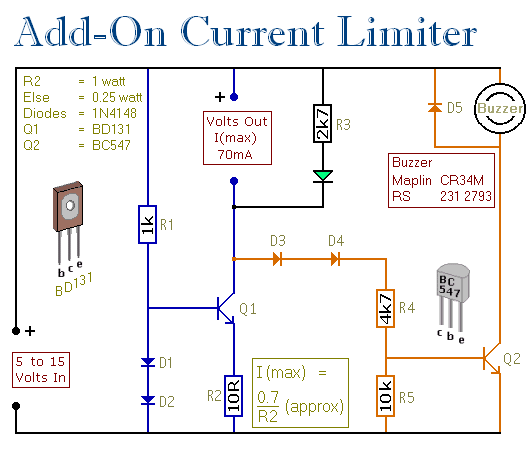
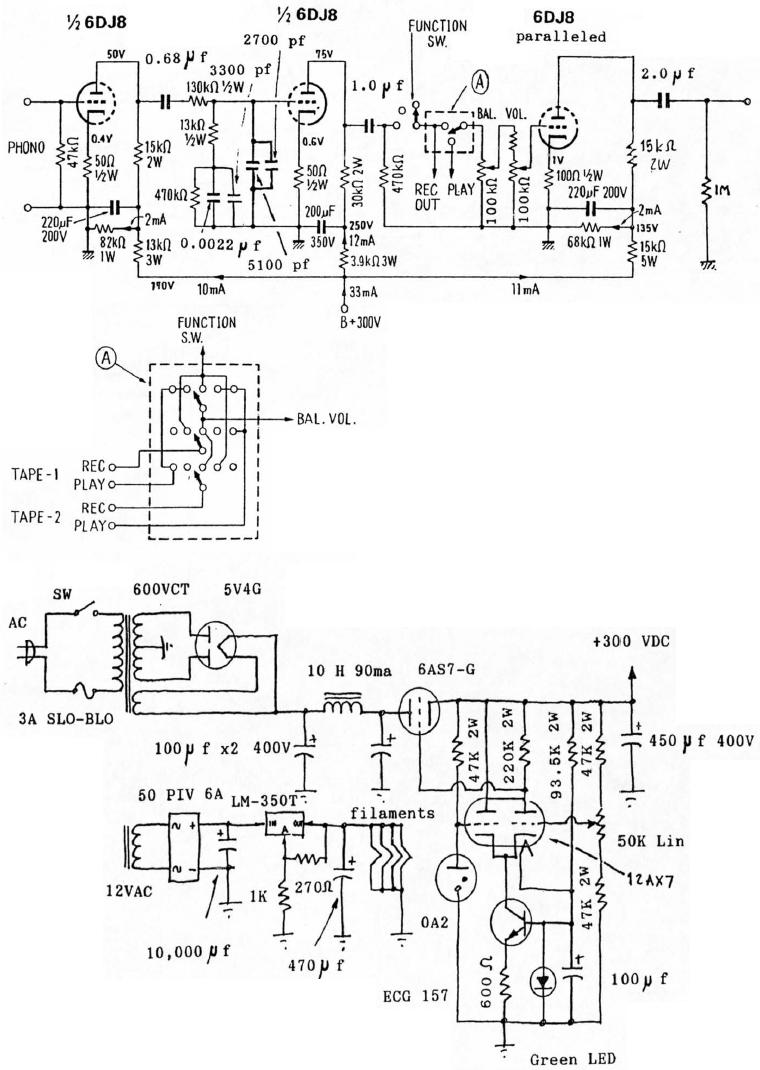
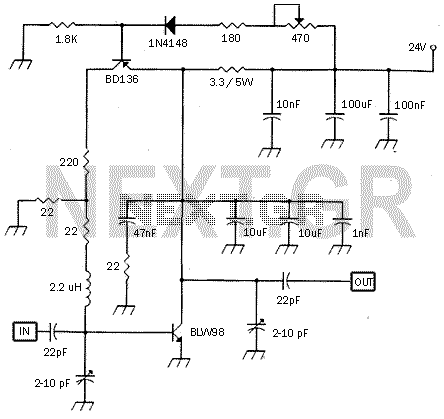
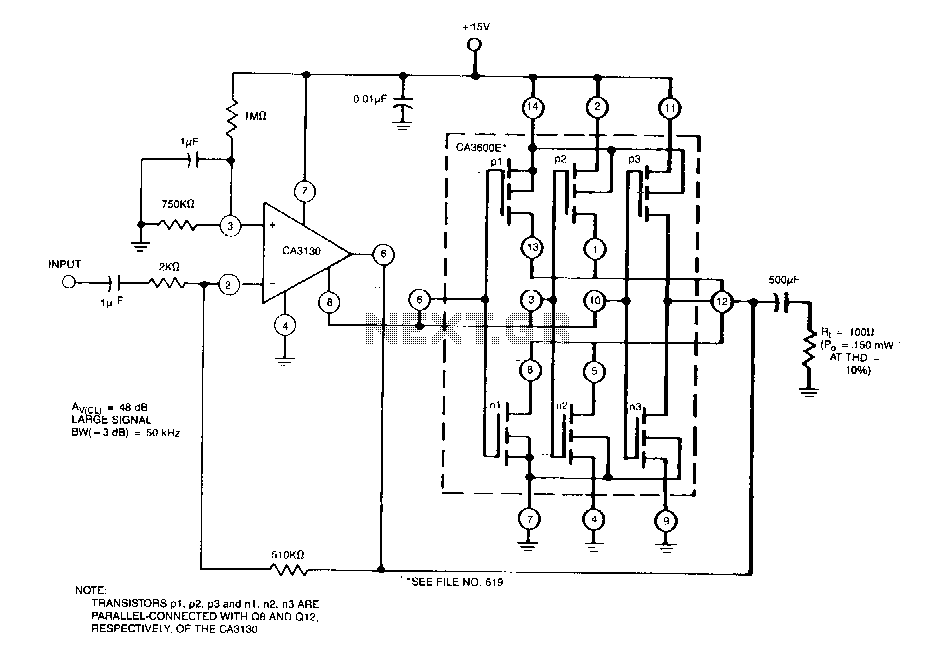
Audio Power Meter: Shows Your Audio Amplifier
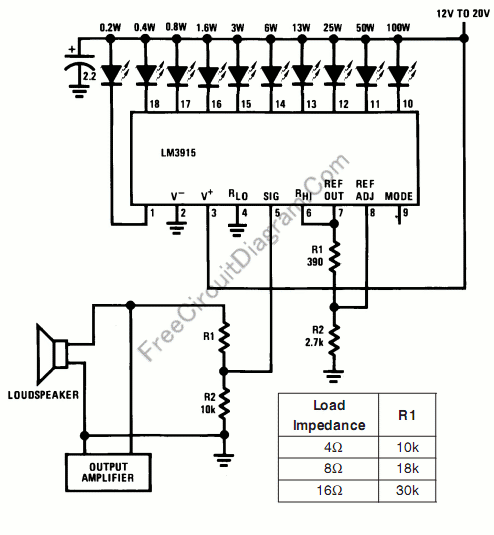
This circuit allows for the measurement of the actual output power of an amplifier. It can be housed in a box to function as a measurement instrument.
The circuit for measuring amplifier output power typically includes a few essential components: a resistive load, a voltage divider, and a microcontroller or analog meter for display purposes.
To construct the circuit, first, select an appropriate resistive load that matches the impedance of the amplifier output, usually 4 or 8 ohms for audio applications. This load will dissipate the power generated by the amplifier, allowing for accurate measurement.
Next, a voltage divider can be employed to scale down the voltage across the load resistor to a level suitable for measurement. The voltage divider consists of two resistors; the values should be chosen based on the maximum expected output voltage from the amplifier to ensure that the scaled voltage does not exceed the input range of the measuring device.
The output from the voltage divider can be fed into either an analog voltmeter or an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) connected to a microcontroller. If using a microcontroller, the measured voltage can be processed to calculate the output power using the formula:
Power (P) = (V^2) / R
where V is the voltage across the load, and R is the resistance of the load. The microcontroller can then display the calculated power on an LCD or LED display for easy reading.
For enhanced functionality, the circuit can be designed with additional features such as peak hold, averaging, or even wireless transmission of the measurement data. Proper calibration of the circuit is essential to ensure accurate readings, which may involve using known reference signals or adjusting the voltage divider based on the specific characteristics of the amplifier being tested.
Overall, this circuit serves as a valuable tool for audio engineers and hobbyists alike, providing real-time feedback on amplifier performance and enabling optimization of audio systems.Using this circuit, you can measure the actual output power of your amplifier.? You can put this circuit in a box as a measurement instrument, or you can. 🔗 External reference
The circuit for measuring amplifier output power typically includes a few essential components: a resistive load, a voltage divider, and a microcontroller or analog meter for display purposes.
To construct the circuit, first, select an appropriate resistive load that matches the impedance of the amplifier output, usually 4 or 8 ohms for audio applications. This load will dissipate the power generated by the amplifier, allowing for accurate measurement.
Next, a voltage divider can be employed to scale down the voltage across the load resistor to a level suitable for measurement. The voltage divider consists of two resistors; the values should be chosen based on the maximum expected output voltage from the amplifier to ensure that the scaled voltage does not exceed the input range of the measuring device.
The output from the voltage divider can be fed into either an analog voltmeter or an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) connected to a microcontroller. If using a microcontroller, the measured voltage can be processed to calculate the output power using the formula:
Power (P) = (V^2) / R
where V is the voltage across the load, and R is the resistance of the load. The microcontroller can then display the calculated power on an LCD or LED display for easy reading.
For enhanced functionality, the circuit can be designed with additional features such as peak hold, averaging, or even wireless transmission of the measurement data. Proper calibration of the circuit is essential to ensure accurate readings, which may involve using known reference signals or adjusting the voltage divider based on the specific characteristics of the amplifier being tested.
Overall, this circuit serves as a valuable tool for audio engineers and hobbyists alike, providing real-time feedback on amplifier performance and enabling optimization of audio systems.Using this circuit, you can measure the actual output power of your amplifier.? You can put this circuit in a box as a measurement instrument, or you can. 🔗 External reference