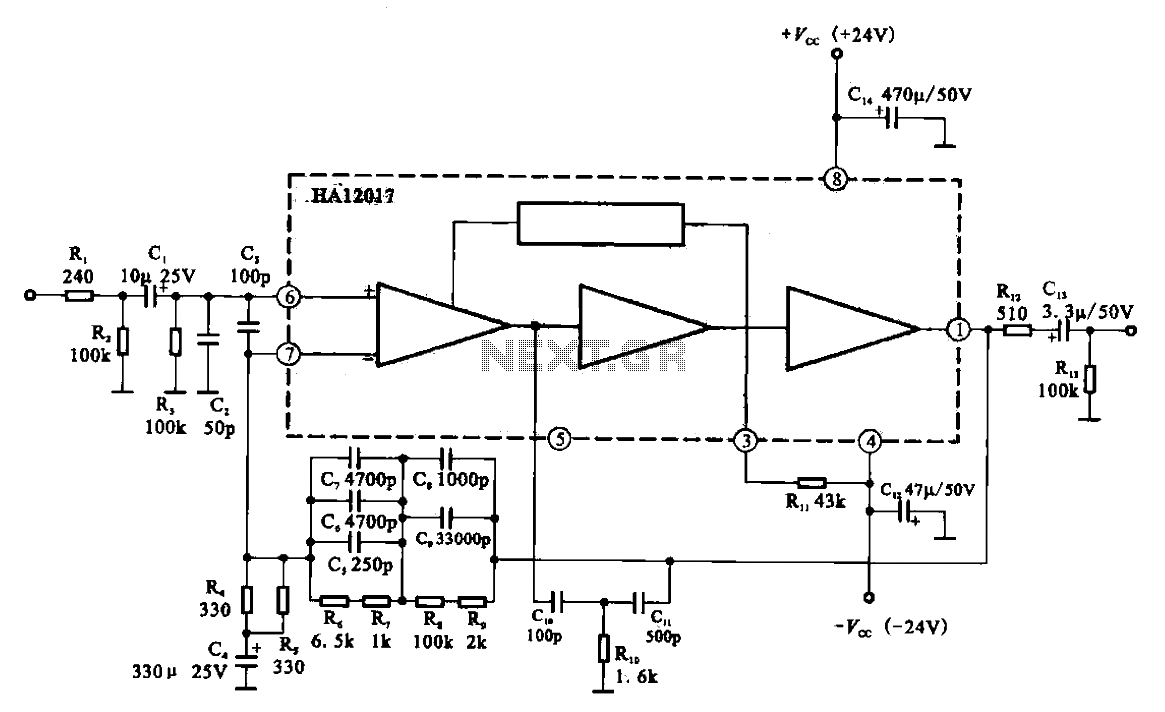
Audio Preamplifier circuit diagram with low distortion
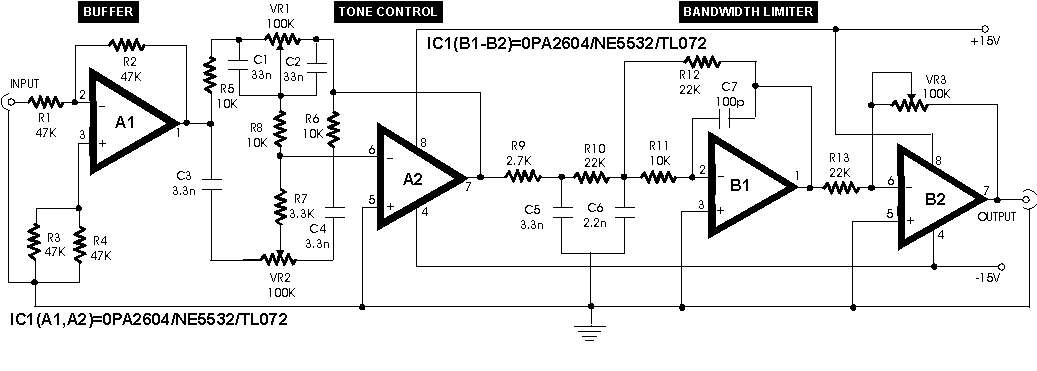
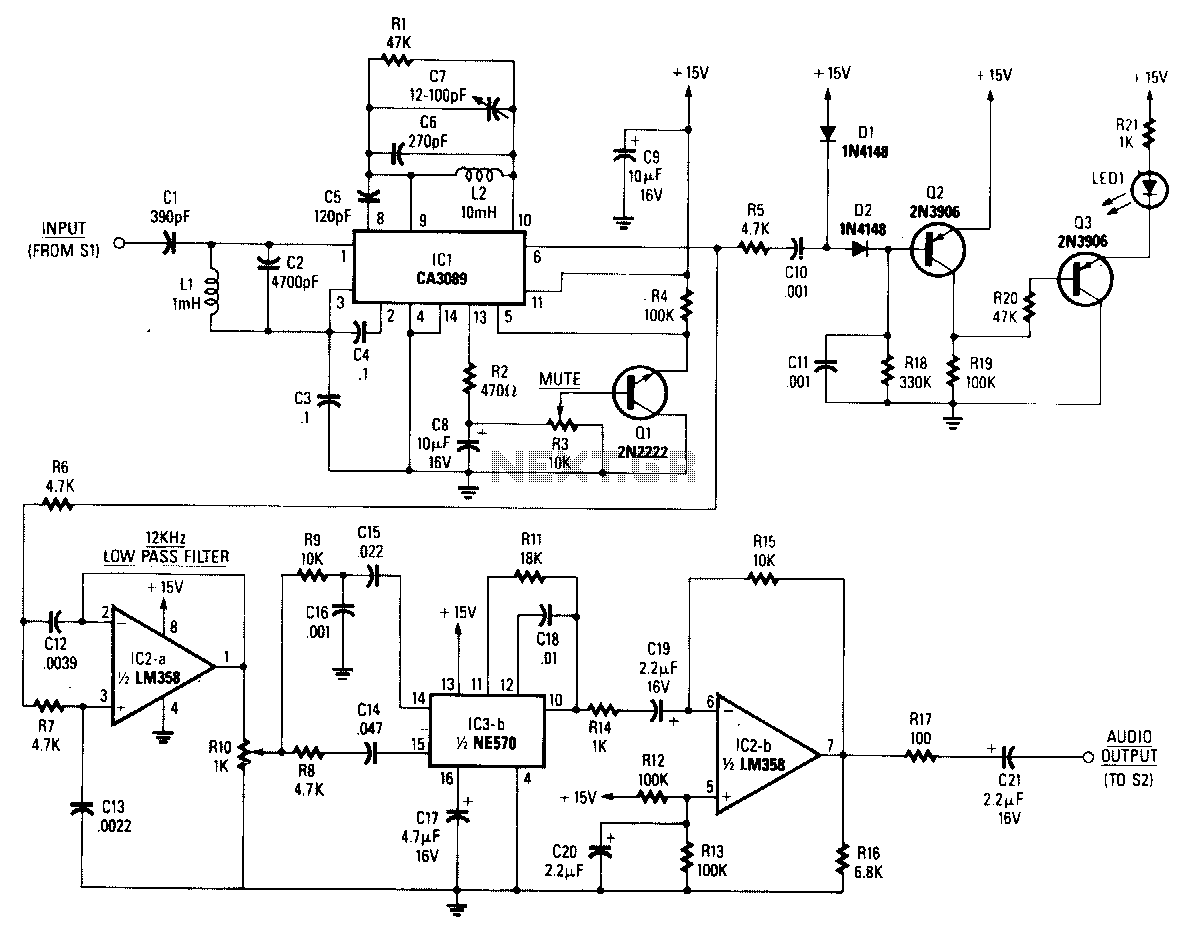
In an audio amplifier, the quality of sound depends on several factors, including the quality of active and passive components, circuit configuration, and layout. The selection of components is influenced by the constructor's budget. Discrete active components like transistors have increasingly been replaced by linear integrated circuits (ICs), simplifying the designer's task. Over time, general-purpose operational amplifiers (op-amps) such as the LM741, previously used in audio and hi-fi circuits, have evolved. The preamplifier circuit presented here is based on a dual precision op-amp for constructing a low distortion, high-quality audio preamplifier. A dual op-amp, OPA2604 from Burr-Brown, is utilized for all stages. The FET input stage op-amp was chosen, although another popular bipolar architecture op-amp, the NE5534A, is noted for its exceptionally low noise figure of 4nV/G–Hz. However, compared to the OPA2604, the NE5534A lacks several specifications. The OPA2604 can operate at higher voltage rails of ±24V (maximum), and its input bias current (100 pA) is significantly lower than that of its bipolar counterpart, resulting in a considerable reduction in noise. The circuit achieves a channel separation of 142 dB. A buffer is essential for the proper functioning of subsequent blocks, providing a nominal input impedance of 47k ohms to prevent overloading of the preamplifier. The tone control employs a Baxandall type filter circuit, while the bandwidth limiter is essentially a low-pass filter with an upper cut-off frequency at the end of the useful audio spectrum. The gain at 10 kHz is approximately 17 dB, and the design is a 3-pole type with the upper frequency set at 25 kHz. Setting up the unit is straightforward; it is important to check the power leads feeding the IC for symmetrical voltages. High-quality audio output from the line output socket serves as the input signal to this preamplifier. The output of the preamplifier is then fed to the power amplifier. The entire circuit consumes about 10 mA when the aforementioned ICs are used. Power supply requirements are not critical, as the circuit operates on 7.5V to 15V DC.
The audio preamplifier circuit is designed to provide high fidelity sound reproduction and low distortion, making it suitable for both professional and home audio applications. The choice of the OPA2604 op-amp is particularly advantageous due to its low noise characteristics and high performance, which are critical in maintaining audio quality. The FET input stage offers a high input impedance and low bias current, minimizing signal degradation and noise introduction. The Baxandall filter circuit allows for effective tone control, enabling the user to adjust the audio output to their preference while maintaining signal integrity. The low-pass filter function of the bandwidth limiter ensures that only the desired frequency range is amplified, effectively reducing unwanted high-frequency noise.
The power supply design is flexible, accommodating a range of voltage inputs, which enhances the circuit's versatility in various applications. The low current consumption of 10 mA contributes to energy efficiency, making the preamplifier suitable for battery-operated devices as well. The careful consideration of component selection and circuit layout contributes to the overall performance, ensuring that the amplifier meets the demands of high-quality audio reproduction. Proper setup and configuration are essential to achieving optimal performance, emphasizing the importance of checking voltage symmetry and the integrity of connections throughout the circuit.In an audio amplifier the quality of sound depends upon a number of factors, e. g. quality of active and passive components, circuit configuration, and layout. To an extent, the selection of components depends on the constructor`s budget. The discrete active components like transistors have been increasingly replaced by linear ICs, making the task of designer easier. With the passage of time, the general-purpose op-amps like LM741, which were being used in audio/hi-fi circuits, have become The preamplifier circuit presented here is based on a dual precision op-amp for the construction of a low distortion, high quality audio preamplifier. A dual op-amp OPA2604 from Burr-Brown is used for all the stages. The FET input stage op-amp was chosen in this context it is worthwile to mention another popular bi-polar architecture op-amp, the NE5534A.
It has, no doubt, an exceptionally low noise figure of 4nV/G–Hz but rest of the specifications compared to OPA2604 are virtually absent in this IC. Also This IC is also capable of operating at higher voltage rails of ± 24V (max. ). Also its input bias current (100 pA) is many orders lower than its bipolar counterpart`s. This ensures a multifold reduction in noise. A channel seperation of 142 dB exists between In the circuit, buffer is essential for the proper working of the subsequent blocks.
A nominal input impedance of 47k is offered by this stage which prevents overloading of the preamplifier. The tone control is a baxandall type filter circuit. The bandwidth limiter is basically a low-pass filter with an upper cut-off ceiling at the end of the useful audio spectrum.
The gain at 10 kHz is approximately 17 dB. The design is essentially 3-pole type and the upper frequency is set at 25 kHz. This lSetting the unit is fairly simple. Check the power leads feeding the IC for symmetrical voltages. High quality audio output from the line output socket is to be fed as the input signal to this preamplifier. Output of the preamplifier is fed to the power a The whole circuit consumes about 10 mA when the above-mentioned ICs are used.
Power supply requirements are not critical as the circuit works on 7. 5V to 15V DC. Disclaimer: All the information present on this site are for personal use only. No commercial use is permitted without the prior permission from authors of this website. All content on this site is provided as is and without any guarantee on any kind, implied or otherwise. We cannot be held responsible for any errors, omissions, or damages arising out of use of information available on this web site.
The content in this site may contain COPYRIGHTED information and should not be reproduced in any way without prior permission from the authors. 🔗 External reference
The audio preamplifier circuit is designed to provide high fidelity sound reproduction and low distortion, making it suitable for both professional and home audio applications. The choice of the OPA2604 op-amp is particularly advantageous due to its low noise characteristics and high performance, which are critical in maintaining audio quality. The FET input stage offers a high input impedance and low bias current, minimizing signal degradation and noise introduction. The Baxandall filter circuit allows for effective tone control, enabling the user to adjust the audio output to their preference while maintaining signal integrity. The low-pass filter function of the bandwidth limiter ensures that only the desired frequency range is amplified, effectively reducing unwanted high-frequency noise.
The power supply design is flexible, accommodating a range of voltage inputs, which enhances the circuit's versatility in various applications. The low current consumption of 10 mA contributes to energy efficiency, making the preamplifier suitable for battery-operated devices as well. The careful consideration of component selection and circuit layout contributes to the overall performance, ensuring that the amplifier meets the demands of high-quality audio reproduction. Proper setup and configuration are essential to achieving optimal performance, emphasizing the importance of checking voltage symmetry and the integrity of connections throughout the circuit.In an audio amplifier the quality of sound depends upon a number of factors, e. g. quality of active and passive components, circuit configuration, and layout. To an extent, the selection of components depends on the constructor`s budget. The discrete active components like transistors have been increasingly replaced by linear ICs, making the task of designer easier. With the passage of time, the general-purpose op-amps like LM741, which were being used in audio/hi-fi circuits, have become The preamplifier circuit presented here is based on a dual precision op-amp for the construction of a low distortion, high quality audio preamplifier. A dual op-amp OPA2604 from Burr-Brown is used for all the stages. The FET input stage op-amp was chosen in this context it is worthwile to mention another popular bi-polar architecture op-amp, the NE5534A.
It has, no doubt, an exceptionally low noise figure of 4nV/G–Hz but rest of the specifications compared to OPA2604 are virtually absent in this IC. Also This IC is also capable of operating at higher voltage rails of ± 24V (max. ). Also its input bias current (100 pA) is many orders lower than its bipolar counterpart`s. This ensures a multifold reduction in noise. A channel seperation of 142 dB exists between In the circuit, buffer is essential for the proper working of the subsequent blocks.
A nominal input impedance of 47k is offered by this stage which prevents overloading of the preamplifier. The tone control is a baxandall type filter circuit. The bandwidth limiter is basically a low-pass filter with an upper cut-off ceiling at the end of the useful audio spectrum.
The gain at 10 kHz is approximately 17 dB. The design is essentially 3-pole type and the upper frequency is set at 25 kHz. This lSetting the unit is fairly simple. Check the power leads feeding the IC for symmetrical voltages. High quality audio output from the line output socket is to be fed as the input signal to this preamplifier. Output of the preamplifier is fed to the power a The whole circuit consumes about 10 mA when the above-mentioned ICs are used.
Power supply requirements are not critical as the circuit works on 7. 5V to 15V DC. Disclaimer: All the information present on this site are for personal use only. No commercial use is permitted without the prior permission from authors of this website. All content on this site is provided as is and without any guarantee on any kind, implied or otherwise. We cannot be held responsible for any errors, omissions, or damages arising out of use of information available on this web site.
The content in this site may contain COPYRIGHTED information and should not be reproduced in any way without prior permission from the authors. 🔗 External reference