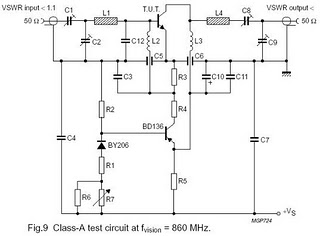
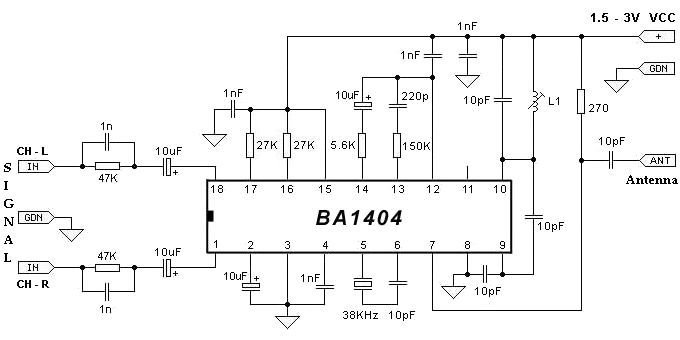
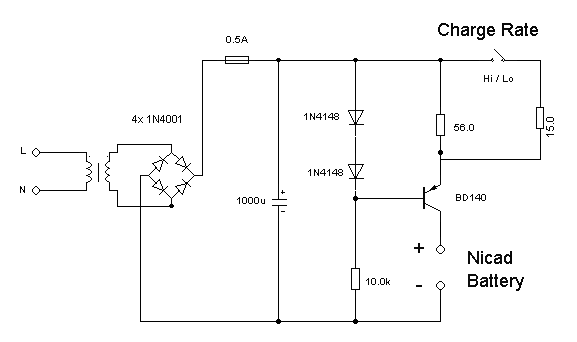
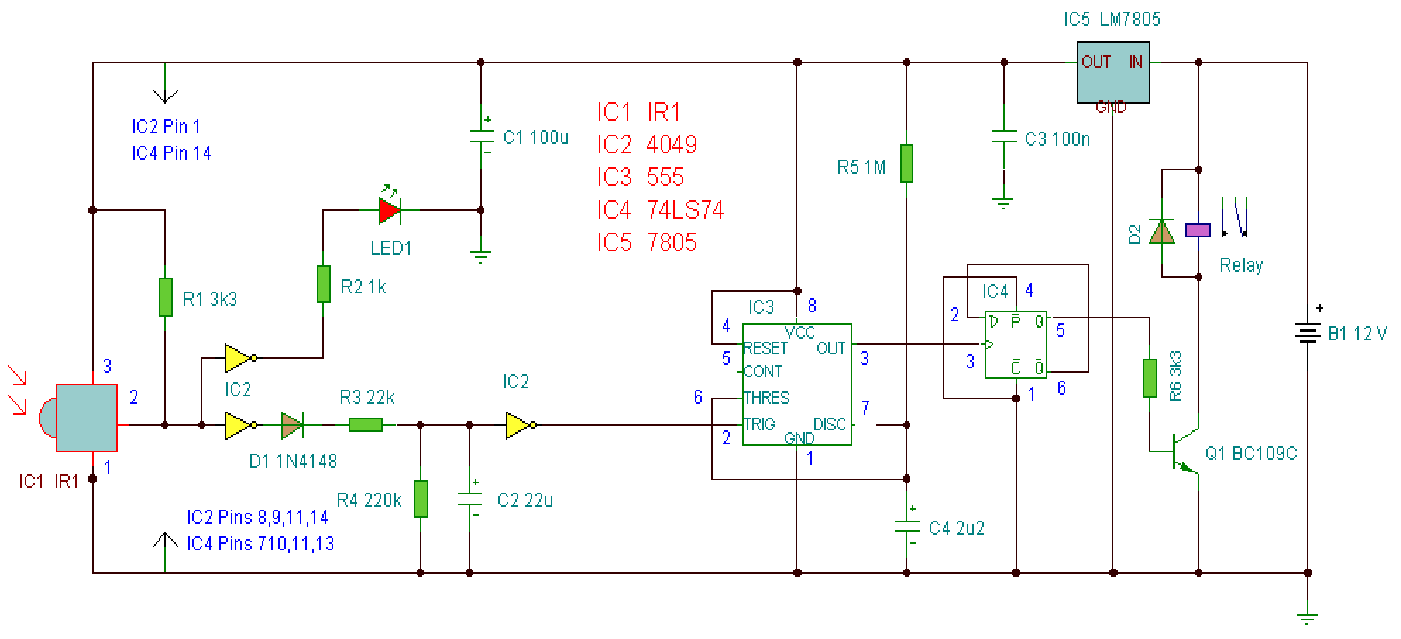
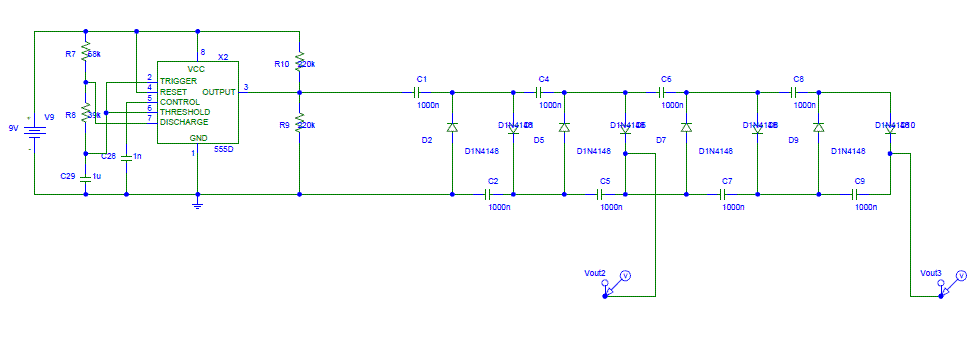
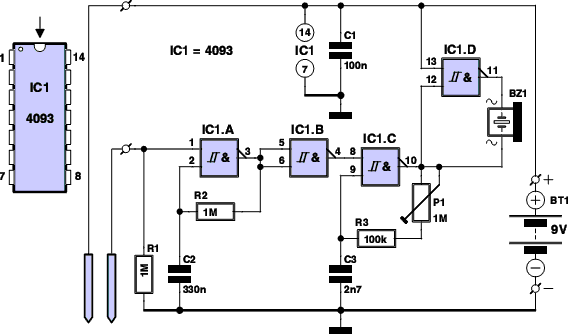
auto battery charger circuit
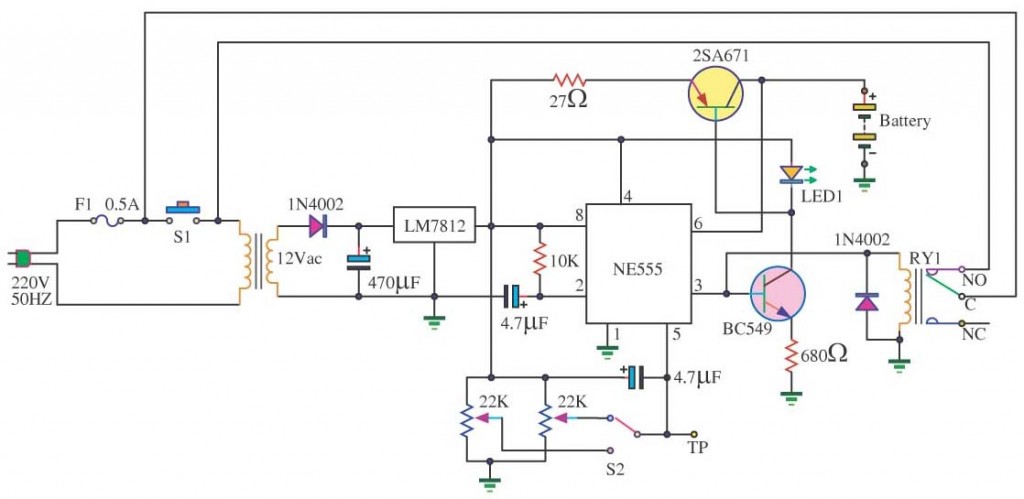
In a lithium-ion cell, a voltage of 3.8V per cell indicates a state of charge of approximately 50%. It is important to note that using voltage as a fuel gauge is not precise, as cells manufactured by different companies exhibit slightly varying voltage profiles. This variation is attributed to the electrochemical properties of the electrodes and electrolyte. Additionally, temperature influences the voltage; as the temperature increases, the voltage tends to decrease.
Lithium-ion cells are widely used in various applications due to their high energy density and rechargeability. The voltage of a lithium-ion cell is a critical parameter that can provide insights into the state of charge (SoC), but relying solely on voltage measurements can lead to inaccuracies. This is primarily because the open-circuit voltage (OCV) of lithium-ion cells can vary significantly between different manufacturers and even among different batches from the same manufacturer.
The electrochemical behavior of the electrodes, which typically consist of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) for the positive electrode and graphite for the negative electrode, plays a significant role in determining the voltage profile. The electrolyte, usually a lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent, also contributes to the overall performance and voltage characteristics of the cell. Variations in the composition and quality of these materials can lead to differences in the voltage output.
Furthermore, temperature is a critical factor affecting the performance of lithium-ion cells. As the temperature increases, the internal resistance of the cell decreases, which can lead to a temporary increase in voltage during discharge. However, at elevated temperatures, the degradation of the cell can occur more rapidly, potentially leading to a decrease in overall voltage and capacity over time. Conversely, at lower temperatures, the internal resistance increases, resulting in lower voltage output and reduced performance.
For accurate state-of-charge estimation in lithium-ion batteries, it is recommended to use a combination of methods, including coulomb counting, impedance spectroscopy, and temperature compensation, rather than relying solely on voltage measurements. Implementing a battery management system (BMS) that takes these factors into account can enhance the accuracy of state-of-charge predictions and prolong the lifespan of the battery.On a lithium-ion cell, 3. 8V/cell indicates a state-of-charge of about 50%. It must be noted that utilizing voltage as a fuel gauge function is inaccurate because cells made by different manufacturers produce a slightly different voltage profile. This is due to the electrochemistry of the electrodes and electrolyte. Temperature also affects the voltage. The higher the temperature, the lower the voltage will be Auto 🔗 External reference
Lithium-ion cells are widely used in various applications due to their high energy density and rechargeability. The voltage of a lithium-ion cell is a critical parameter that can provide insights into the state of charge (SoC), but relying solely on voltage measurements can lead to inaccuracies. This is primarily because the open-circuit voltage (OCV) of lithium-ion cells can vary significantly between different manufacturers and even among different batches from the same manufacturer.
The electrochemical behavior of the electrodes, which typically consist of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) for the positive electrode and graphite for the negative electrode, plays a significant role in determining the voltage profile. The electrolyte, usually a lithium salt dissolved in an organic solvent, also contributes to the overall performance and voltage characteristics of the cell. Variations in the composition and quality of these materials can lead to differences in the voltage output.
Furthermore, temperature is a critical factor affecting the performance of lithium-ion cells. As the temperature increases, the internal resistance of the cell decreases, which can lead to a temporary increase in voltage during discharge. However, at elevated temperatures, the degradation of the cell can occur more rapidly, potentially leading to a decrease in overall voltage and capacity over time. Conversely, at lower temperatures, the internal resistance increases, resulting in lower voltage output and reduced performance.
For accurate state-of-charge estimation in lithium-ion batteries, it is recommended to use a combination of methods, including coulomb counting, impedance spectroscopy, and temperature compensation, rather than relying solely on voltage measurements. Implementing a battery management system (BMS) that takes these factors into account can enhance the accuracy of state-of-charge predictions and prolong the lifespan of the battery.On a lithium-ion cell, 3. 8V/cell indicates a state-of-charge of about 50%. It must be noted that utilizing voltage as a fuel gauge function is inaccurate because cells made by different manufacturers produce a slightly different voltage profile. This is due to the electrochemistry of the electrodes and electrolyte. Temperature also affects the voltage. The higher the temperature, the lower the voltage will be Auto 🔗 External reference