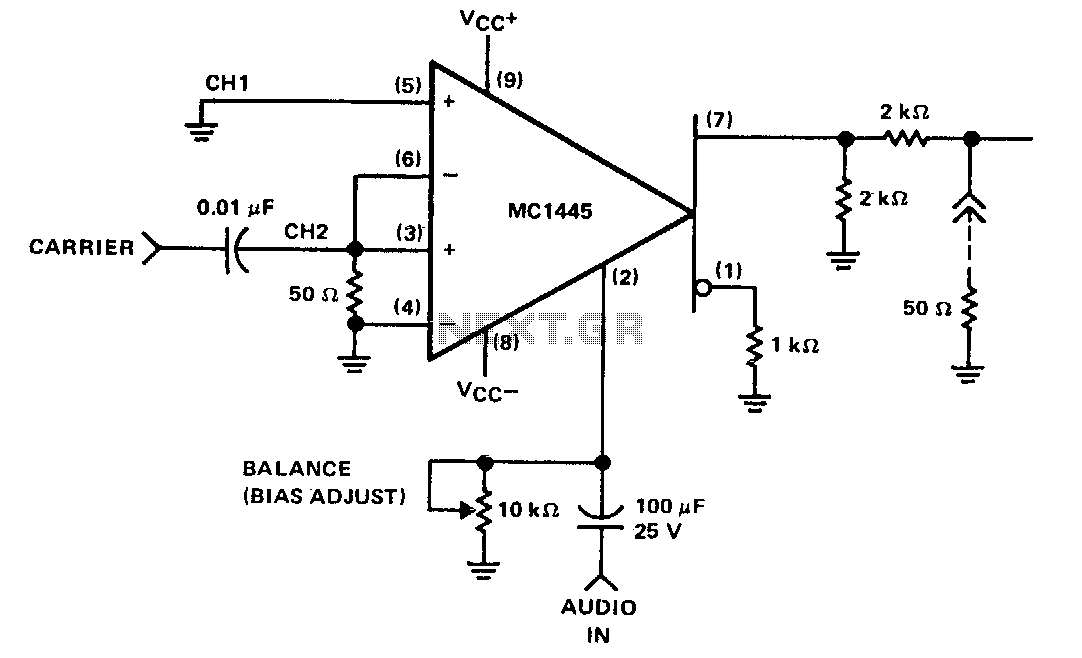
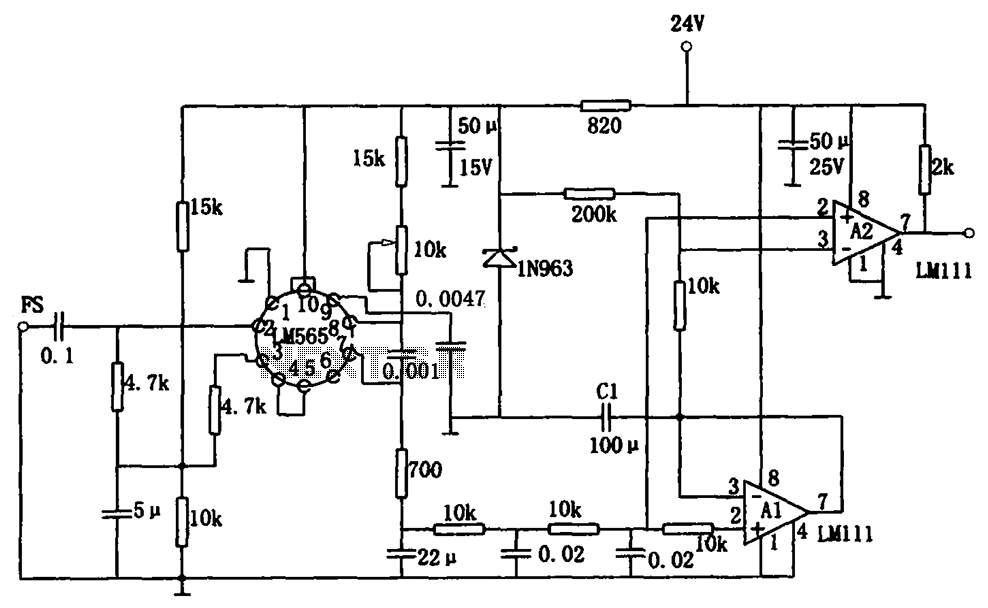
BALANCED MODULATOR DEMODULATOR
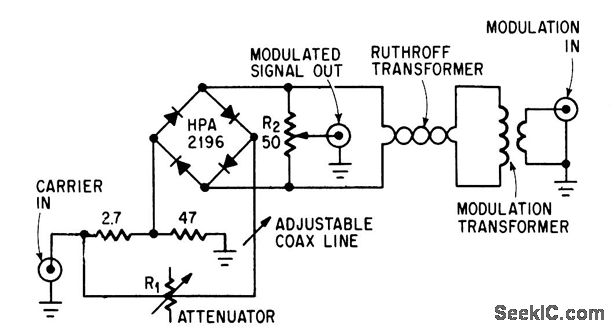
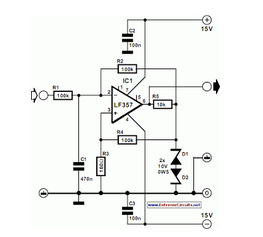
This circuit achieves high carrier and modulation suppression by utilizing closely matched diodes. It includes resistor R1 for amplitude adjustment and a coaxial line for phase adjustment. Resistor R2 allows for slight amplitude adjustments.
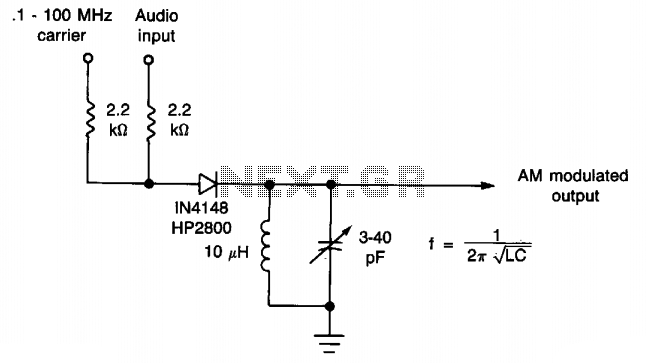
The described circuit is a diode quad modulator designed to effectively suppress carrier signals by 65 dB, as indicated in the reference by W. H. Ellis. This suppression is critical in applications where signal fidelity is paramount, such as in communication systems. The use of closely matched diodes is essential for maintaining consistent performance across the modulation spectrum.
In this configuration, R1 serves as the primary amplitude adjustment component, allowing the user to fine-tune the output signal's amplitude to meet specific requirements. The coaxial line, which is integral to the circuit, is used for precise phase adjustment, ensuring that the modulation is aligned correctly with the carrier signal. This alignment is crucial for minimizing distortion and maximizing the quality of the output signal.
R2, while providing a more minor adjustment, plays a significant role in refining the overall performance of the circuit. By allowing slight variations in amplitude, R2 aids in achieving optimal signal characteristics, which can be particularly beneficial in systems where signal levels may fluctuate due to varying operational conditions.
The overall design emphasizes the importance of component matching and careful adjustment to achieve high levels of suppression, making this circuit suitable for advanced communication applications where clarity and precision are required.Achieves high carrier and modulation suppression by using closely matched diodes and providing R1 for amplitude adjustment and coaxial line for phase adjustment. R2 provides slight amplitude adjustment. -W. H. Ellis, Diode Quad Modulator Suppresses Carrier 65 Db, Electronics, 39:8, p 97. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a diode quad modulator designed to effectively suppress carrier signals by 65 dB, as indicated in the reference by W. H. Ellis. This suppression is critical in applications where signal fidelity is paramount, such as in communication systems. The use of closely matched diodes is essential for maintaining consistent performance across the modulation spectrum.
In this configuration, R1 serves as the primary amplitude adjustment component, allowing the user to fine-tune the output signal's amplitude to meet specific requirements. The coaxial line, which is integral to the circuit, is used for precise phase adjustment, ensuring that the modulation is aligned correctly with the carrier signal. This alignment is crucial for minimizing distortion and maximizing the quality of the output signal.
R2, while providing a more minor adjustment, plays a significant role in refining the overall performance of the circuit. By allowing slight variations in amplitude, R2 aids in achieving optimal signal characteristics, which can be particularly beneficial in systems where signal levels may fluctuate due to varying operational conditions.
The overall design emphasizes the importance of component matching and careful adjustment to achieve high levels of suppression, making this circuit suitable for advanced communication applications where clarity and precision are required.Achieves high carrier and modulation suppression by using closely matched diodes and providing R1 for amplitude adjustment and coaxial line for phase adjustment. R2 provides slight amplitude adjustment. -W. H. Ellis, Diode Quad Modulator Suppresses Carrier 65 Db, Electronics, 39:8, p 97. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713