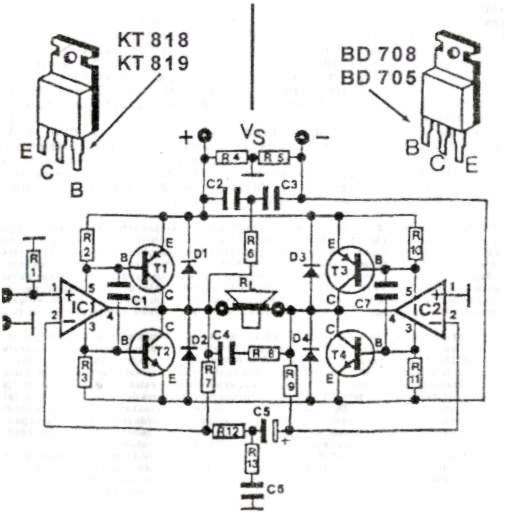
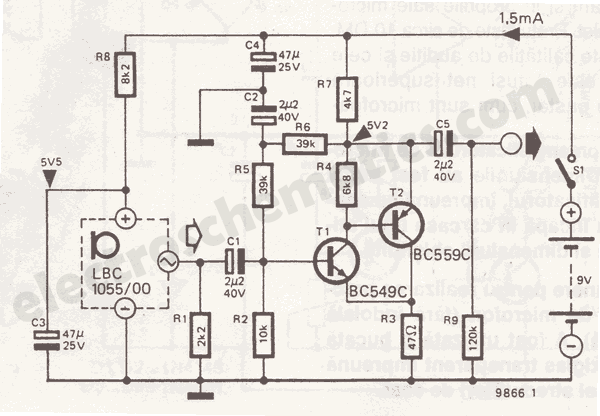
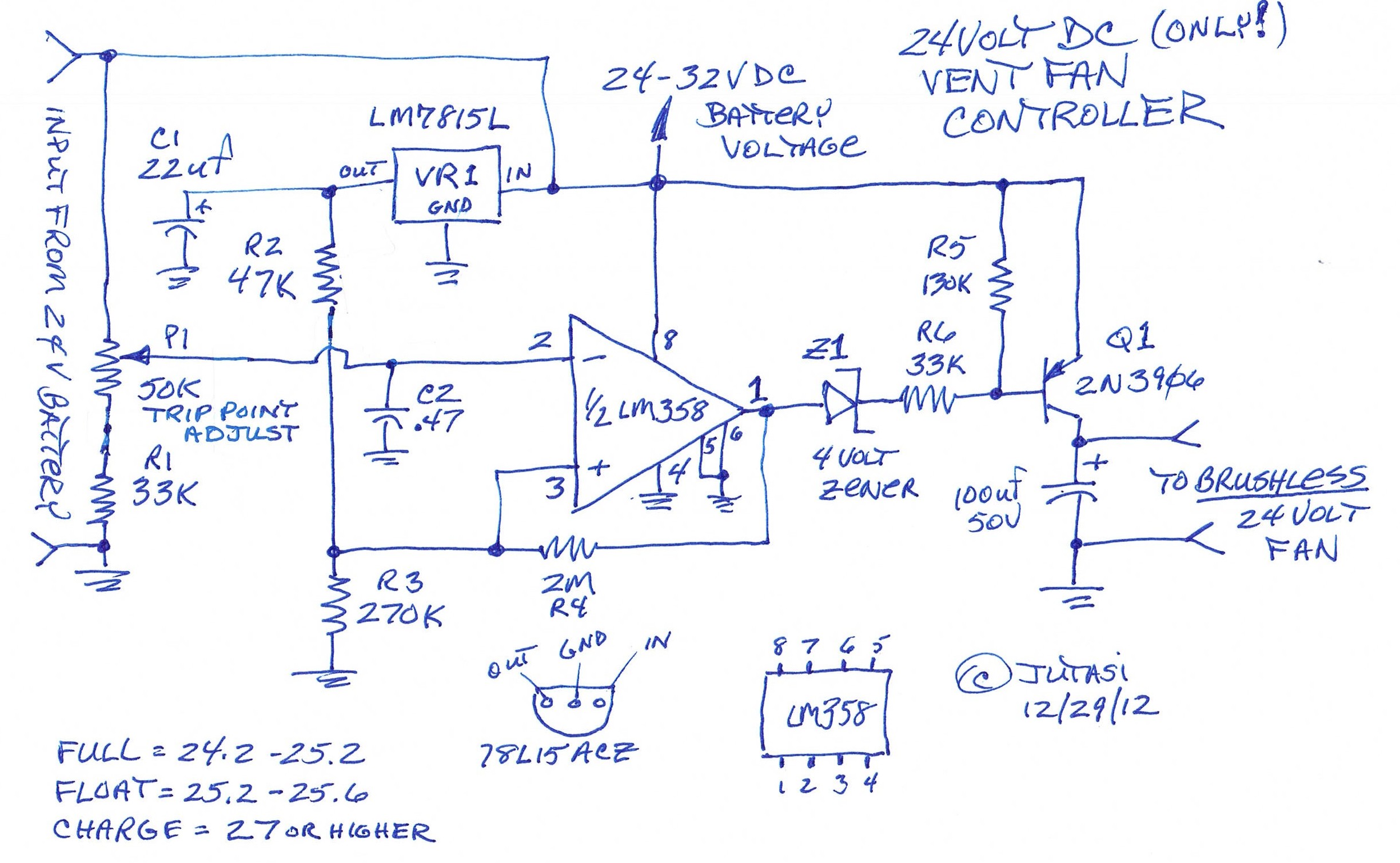
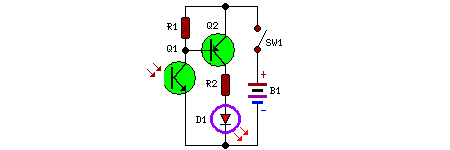
Ballroom synchronous voice switching circuit with music
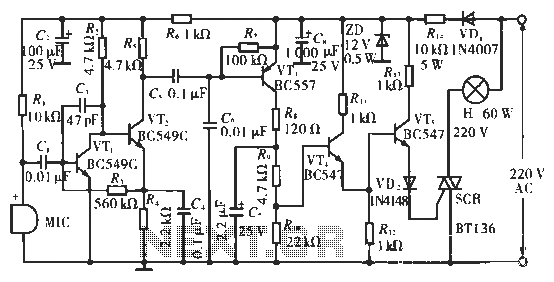
The circuit utilizes condenser microphones to detect sound and convert it into signal variations. This signal is then processed through directly coupled transistors VT1 and VT2, which form an amplification stage before being fed into a switching circuit. The switching circuit is composed of transistors VT3, VT4, and VT5, activating only when the sound signal is present.
The described circuit operates as a sound-activated switch, leveraging the properties of condenser microphones to detect acoustic signals. The condenser microphones are sensitive to sound waves, converting them into electrical signals that vary in amplitude according to the sound intensity. These signals are then routed to a pair of directly coupled transistors, VT1 and VT2, which serve as an amplifier stage. This amplification is crucial for enhancing the weak signals from the microphones to a level suitable for further processing.
Transistors VT1 and VT2 are configured in a common-emitter arrangement, which provides significant voltage gain. The output from this stage is then sent to the switching circuit, which consists of transistors VT3, VT4, and VT5. These transistors are arranged to operate as a relay system, where the presence of a sufficient amplified signal from the microphones triggers the switching action.
The switching circuit is designed to activate only when the input signal exceeds a predetermined threshold, ensuring that background noise does not inadvertently trigger the circuit. This is achieved through careful biasing of the transistors, allowing for precise control over the switching behavior. When the sound signal is detected and amplified, it causes VT3 to conduct, which in turn activates VT4 and VT5, completing the circuit and enabling the connected load.
This configuration allows for a wide range of applications, including automatic lighting systems, sound-activated alarms, and other devices where sound detection is required. The design emphasizes reliability and responsiveness, ensuring that the circuit only activates in response to meaningful sound events, thus minimizing false triggers from ambient noise. Overall, the circuit exemplifies a practical application of sound sensing technology in electronic systems.Circuit works: a circuit with condenser microphones to sense sound and converts it into a signal changes, and then put through directly coupled transistors VT1 and VT2 composed of amplifier amplified to the switching circuit. Switch circuit by the VT3, VT4 and VT5 constitution, only the circuit senses the sound when the signal is turned on.
The described circuit operates as a sound-activated switch, leveraging the properties of condenser microphones to detect acoustic signals. The condenser microphones are sensitive to sound waves, converting them into electrical signals that vary in amplitude according to the sound intensity. These signals are then routed to a pair of directly coupled transistors, VT1 and VT2, which serve as an amplifier stage. This amplification is crucial for enhancing the weak signals from the microphones to a level suitable for further processing.
Transistors VT1 and VT2 are configured in a common-emitter arrangement, which provides significant voltage gain. The output from this stage is then sent to the switching circuit, which consists of transistors VT3, VT4, and VT5. These transistors are arranged to operate as a relay system, where the presence of a sufficient amplified signal from the microphones triggers the switching action.
The switching circuit is designed to activate only when the input signal exceeds a predetermined threshold, ensuring that background noise does not inadvertently trigger the circuit. This is achieved through careful biasing of the transistors, allowing for precise control over the switching behavior. When the sound signal is detected and amplified, it causes VT3 to conduct, which in turn activates VT4 and VT5, completing the circuit and enabling the connected load.
This configuration allows for a wide range of applications, including automatic lighting systems, sound-activated alarms, and other devices where sound detection is required. The design emphasizes reliability and responsiveness, ensuring that the circuit only activates in response to meaningful sound events, thus minimizing false triggers from ambient noise. Overall, the circuit exemplifies a practical application of sound sensing technology in electronic systems.Circuit works: a circuit with condenser microphones to sense sound and converts it into a signal changes, and then put through directly coupled transistors VT1 and VT2 composed of amplifier amplified to the switching circuit. Switch circuit by the VT3, VT4 and VT5 constitution, only the circuit senses the sound when the signal is turned on.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713