Blinking LED Emulates Incandescent Bulb
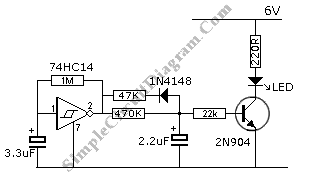
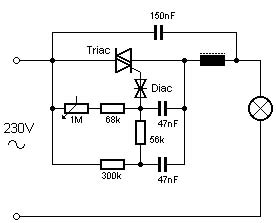
This circuit features a flashing LED that emulates the behavior of an incandescent lamp. The characteristic of an incandescent lamp is that it cannot abruptly change its brightness.
The flashing LED circuit designed to mimic an incandescent lamp operates by simulating the gradual increase and decrease in brightness that is typical of traditional incandescent bulbs. This effect is achieved using a microcontroller or a simple timing circuit that modulates the current flowing through the LED.
The core components of the circuit include an LED, a resistor to limit current, and a timing element, which can be implemented using a capacitor and a transistor or through a microcontroller’s PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) capabilities. The LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to prevent it from drawing excessive current, which could lead to damage.
To create the flashing effect, the circuit utilizes a timing mechanism that controls the on and off states of the LED. When the LED is turned on, the current flows through the resistor, causing the LED to light up. As the timing circuit triggers the LED to turn off, the current ceases, and the LED gradually dims. This dimming effect can be further enhanced by adjusting the timing parameters, allowing for a more realistic simulation of the incandescent lamp's warm glow.
The overall design can be expanded with additional features, such as adjustable brightness levels or varying flash rates, to better suit specific applications or user preferences. This circuit can be effectively used in decorative lighting, automotive applications, or any scenario where a warm, incandescent-like glow is desired from LED technology.This is flashing LED circuit emulate the turning of incandescent lamp. The characteristic of incandescent lamp is that they can`t abruptly change the.. 🔗 External reference
The flashing LED circuit designed to mimic an incandescent lamp operates by simulating the gradual increase and decrease in brightness that is typical of traditional incandescent bulbs. This effect is achieved using a microcontroller or a simple timing circuit that modulates the current flowing through the LED.
The core components of the circuit include an LED, a resistor to limit current, and a timing element, which can be implemented using a capacitor and a transistor or through a microcontroller’s PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) capabilities. The LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to prevent it from drawing excessive current, which could lead to damage.
To create the flashing effect, the circuit utilizes a timing mechanism that controls the on and off states of the LED. When the LED is turned on, the current flows through the resistor, causing the LED to light up. As the timing circuit triggers the LED to turn off, the current ceases, and the LED gradually dims. This dimming effect can be further enhanced by adjusting the timing parameters, allowing for a more realistic simulation of the incandescent lamp's warm glow.
The overall design can be expanded with additional features, such as adjustable brightness levels or varying flash rates, to better suit specific applications or user preferences. This circuit can be effectively used in decorative lighting, automotive applications, or any scenario where a warm, incandescent-like glow is desired from LED technology.This is flashing LED circuit emulate the turning of incandescent lamp. The characteristic of incandescent lamp is that they can`t abruptly change the.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713