C-Bot Article
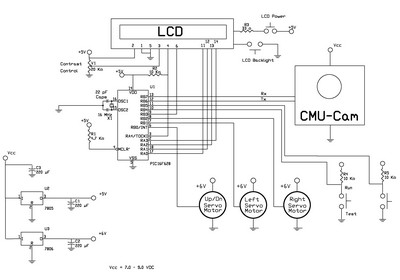
The schematic is illustrated in figure 10. The circuit can be hardwired onto a breadboard, or a printed circuit board (PCB) can be purchased, as shown in figure 11. The LCD display utilized is a 2-line by 16-character display. An LCD module with a Hitachi 44780 controller or an equivalent can be used. These LCDs typically feature a 14 or 16-pin header. Refer to figure 12 for details. A jumper should be placed on jumper position 2 to set the camera baud rate to 38,400. Power is supplied to the two header positions indicated in figure 12, as well as the header positions for the serial transmit and receive lines.
The schematic diagram presented in figure 10 outlines the connections and components necessary for constructing a functional circuit that incorporates a 2-line by 16-character LCD display. This display, compatible with the Hitachi 44780 controller, serves as the primary output interface for the circuit. The use of a breadboard allows for flexibility in prototyping, while a pre-manufactured PCB offers a more permanent solution for the assembly of the circuit.
The LCD module typically features a 14 or 16-pin configuration, which facilitates the connection to the microcontroller or other interfacing hardware. The pin assignments generally include data lines, control lines, and power connections. For optimal operation, it is essential to consult the specific datasheet for the LCD module being utilized, as pin configurations may vary slightly between different manufacturers.
To ensure proper communication between the circuit and the camera module, a jumper must be placed in position 2. This configuration is crucial for setting the camera's baud rate to 38,400 bps, which is a standard rate for serial communication in many electronic applications. The power supply connections are made at the designated header positions shown in figure 12, ensuring that both the LCD and the camera module receive adequate voltage and current for their operation.
Additionally, the schematic includes header positions for serial communication, specifically for transmitting and receiving data. These connections are vital for enabling the microcontroller to send commands to the camera and receive feedback or data from it. Proper attention to these connections will ensure reliable operation and communication within the system.The schematic is shown in figure 10. The circuit can be hardwire onto a breadboard or you can purchase a pc board, see figure 11. The LCD display used is a 2 line by 16 character display. You can use an LCD module with a Hitachi 44780 controller or equivalent. These LCD`s usually have a 14 or 16 pin header. Look at figure 12. Place a jumper on jum per position 2. This sets the camera baud rate to 38, 400. The power is supplied to the two header positions shown on figure 12, as well as the header positions for the serial transmit and receiver lines. 🔗 External reference
The schematic diagram presented in figure 10 outlines the connections and components necessary for constructing a functional circuit that incorporates a 2-line by 16-character LCD display. This display, compatible with the Hitachi 44780 controller, serves as the primary output interface for the circuit. The use of a breadboard allows for flexibility in prototyping, while a pre-manufactured PCB offers a more permanent solution for the assembly of the circuit.
The LCD module typically features a 14 or 16-pin configuration, which facilitates the connection to the microcontroller or other interfacing hardware. The pin assignments generally include data lines, control lines, and power connections. For optimal operation, it is essential to consult the specific datasheet for the LCD module being utilized, as pin configurations may vary slightly between different manufacturers.
To ensure proper communication between the circuit and the camera module, a jumper must be placed in position 2. This configuration is crucial for setting the camera's baud rate to 38,400 bps, which is a standard rate for serial communication in many electronic applications. The power supply connections are made at the designated header positions shown in figure 12, ensuring that both the LCD and the camera module receive adequate voltage and current for their operation.
Additionally, the schematic includes header positions for serial communication, specifically for transmitting and receiving data. These connections are vital for enabling the microcontroller to send commands to the camera and receive feedback or data from it. Proper attention to these connections will ensure reliable operation and communication within the system.The schematic is shown in figure 10. The circuit can be hardwire onto a breadboard or you can purchase a pc board, see figure 11. The LCD display used is a 2 line by 16 character display. You can use an LCD module with a Hitachi 44780 controller or equivalent. These LCD`s usually have a 14 or 16 pin header. Look at figure 12. Place a jumper on jum per position 2. This sets the camera baud rate to 38, 400. The power is supplied to the two header positions shown on figure 12, as well as the header positions for the serial transmit and receiver lines. 🔗 External reference