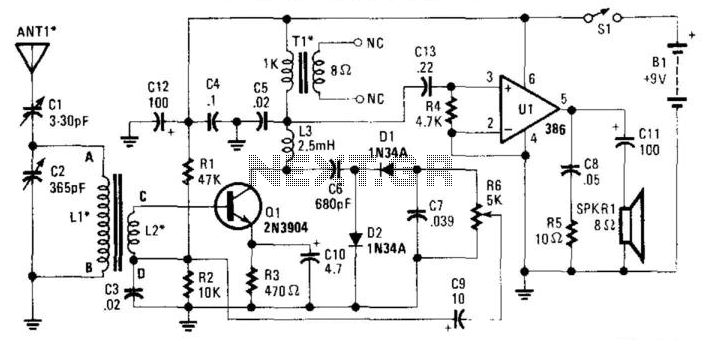
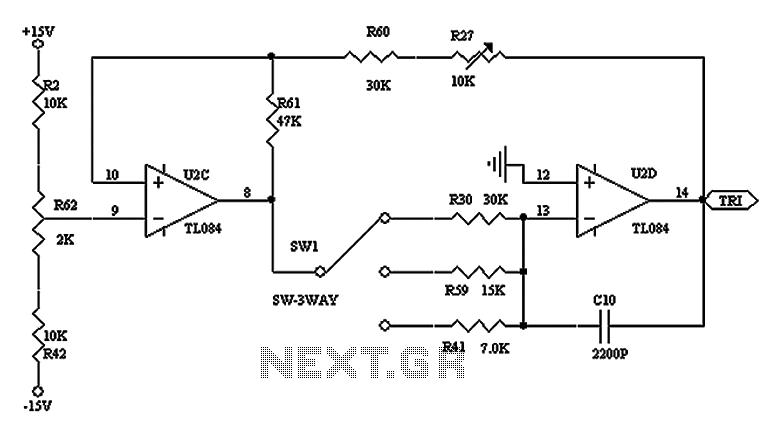
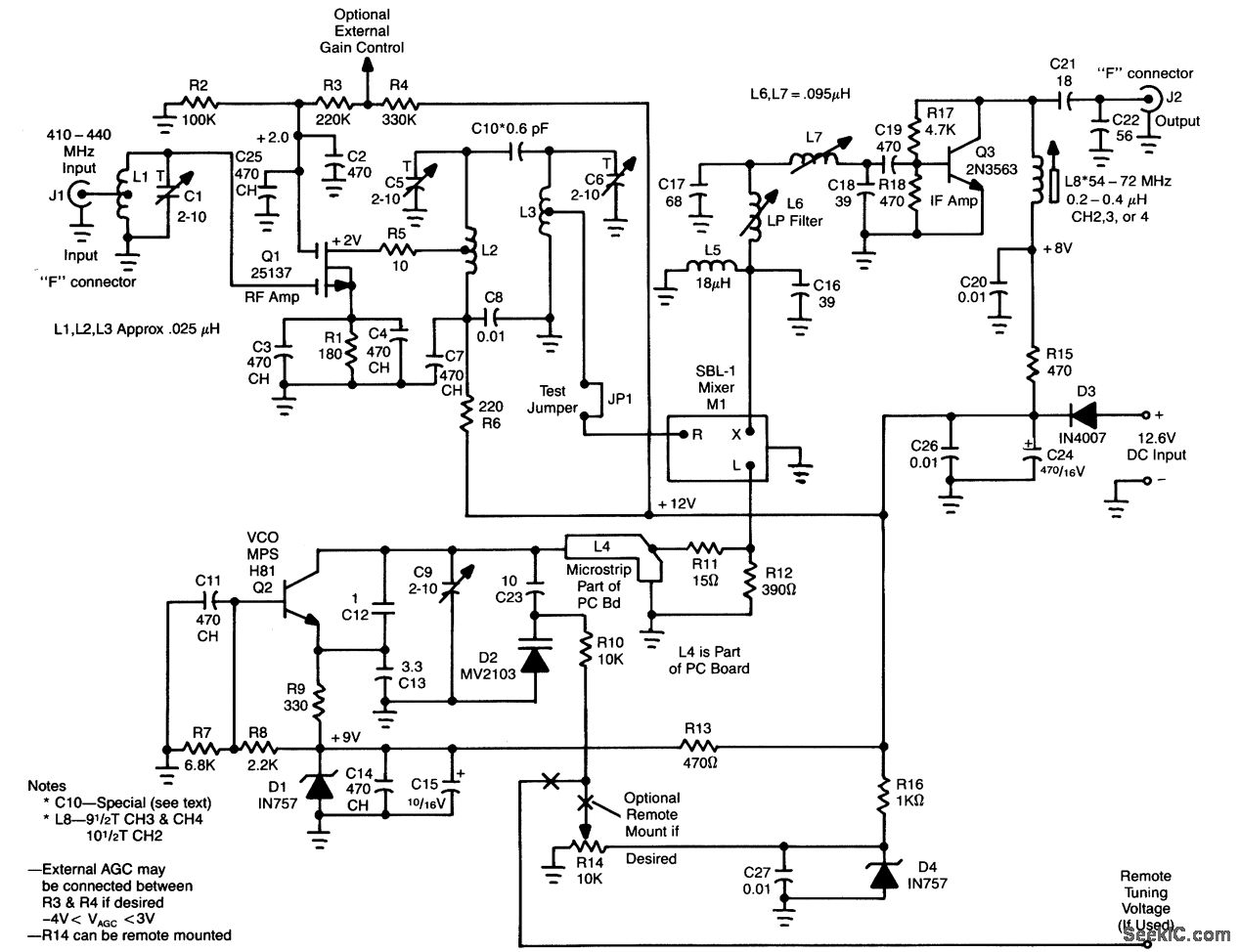
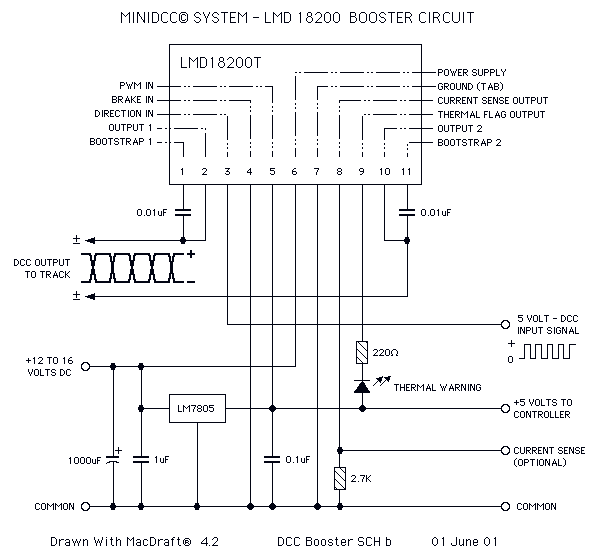
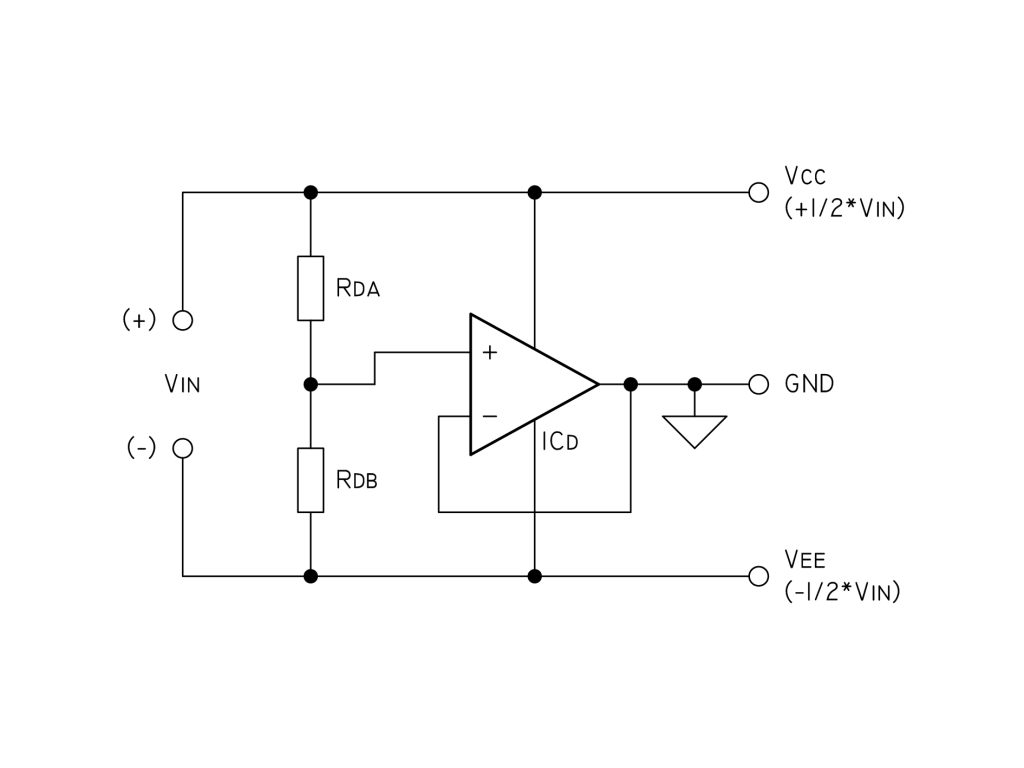
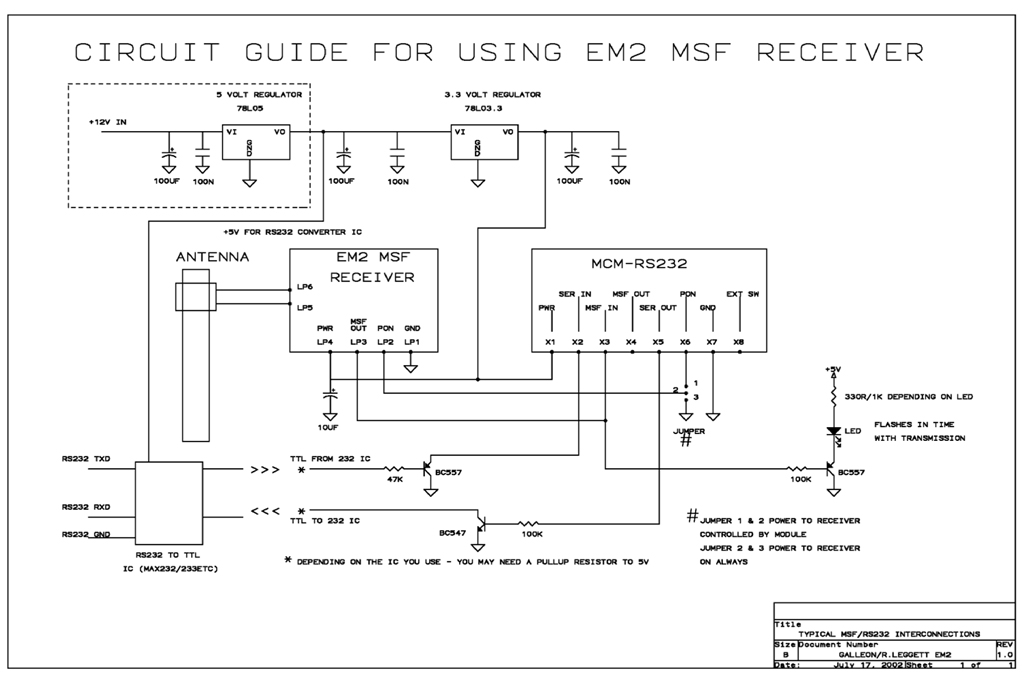
Carrier current receiver
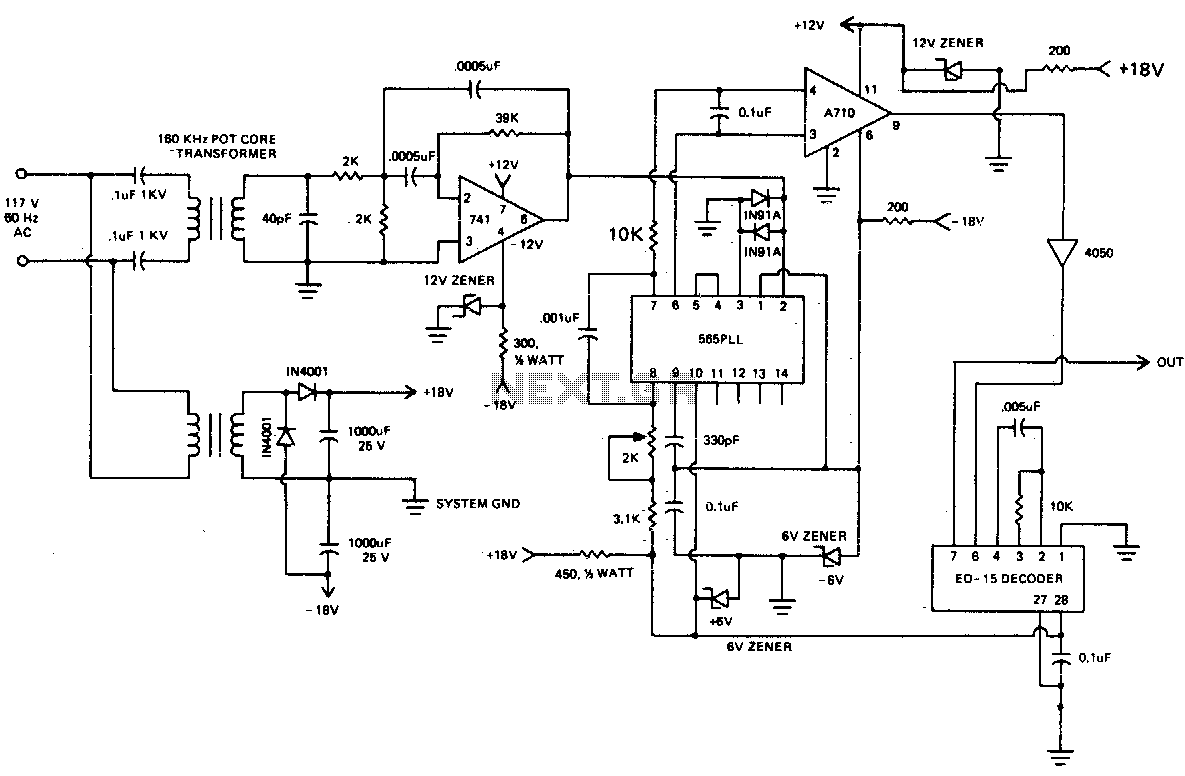
A 60 kHz transformer is constructed using an 18 x 11 mm ungapped pot core (such as those from Siemens or Fer-rocube). It employs magnetics of type "F" material and is wound with SOV2 turns of No. 5 wire for the secondary winding and additional turns for the primary winding. This configuration results in a turns ratio of approximately 15:1.
The 60 kHz transformer is designed for efficient energy transfer at high frequencies, making it suitable for applications in power electronics, signal processing, and RF circuits. The choice of an ungapped pot core allows for improved magnetic coupling and reduced losses, which is critical in high-frequency operations. The use of type "F" magnetic material enhances the core's performance by providing low core losses and high saturation flux density, ensuring reliable operation within the specified frequency range.
The winding configuration, with SOV2 turns for the secondary and a calculated number of turns for the primary, is essential for achieving the desired voltage transformation. The turns ratio of approximately 15:1 indicates that the primary winding has 15 times more turns than the secondary winding, which allows for stepping down the voltage efficiently. This transformer can be used in various applications, including power supplies, inverters, and signal isolation, where voltage transformation and impedance matching are required.
In designing the circuit around this transformer, attention must be given to the selection of components that can handle the operating frequency and the corresponding power levels. Proper insulation and thermal management should also be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the transformer in its intended application.60 kHz transformer consists of a 18 x 11mm ungapped pot core (Siemens, Fer-rocube, etc), utilizing magnetics incorporated type "F" material wound with SOV2 turns of No5 wire for the secondary and turns for the primary This gives a turns ratio of approximately 15 to 1. 🔗 External reference
The 60 kHz transformer is designed for efficient energy transfer at high frequencies, making it suitable for applications in power electronics, signal processing, and RF circuits. The choice of an ungapped pot core allows for improved magnetic coupling and reduced losses, which is critical in high-frequency operations. The use of type "F" magnetic material enhances the core's performance by providing low core losses and high saturation flux density, ensuring reliable operation within the specified frequency range.
The winding configuration, with SOV2 turns for the secondary and a calculated number of turns for the primary, is essential for achieving the desired voltage transformation. The turns ratio of approximately 15:1 indicates that the primary winding has 15 times more turns than the secondary winding, which allows for stepping down the voltage efficiently. This transformer can be used in various applications, including power supplies, inverters, and signal isolation, where voltage transformation and impedance matching are required.
In designing the circuit around this transformer, attention must be given to the selection of components that can handle the operating frequency and the corresponding power levels. Proper insulation and thermal management should also be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the transformer in its intended application.60 kHz transformer consists of a 18 x 11mm ungapped pot core (Siemens, Fer-rocube, etc), utilizing magnetics incorporated type "F" material wound with SOV2 turns of No5 wire for the secondary and turns for the primary This gives a turns ratio of approximately 15 to 1. 🔗 External reference