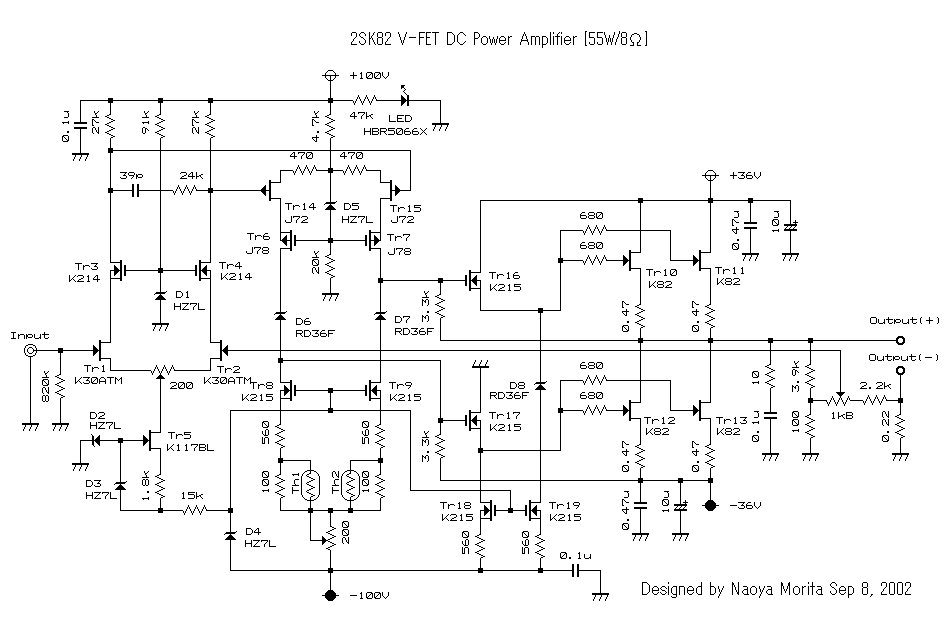
2N6766 FET Derating Curve
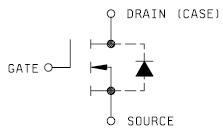
When the case temperature reaches 250°C, the device must be derated to maintain a maximum case temperature of 1500°C, ensuring that the junction temperature remains below the maximum permissible limit. This pertains to MIL-PRF-19500/543; Semiconductor Device, Transistor, Field Effect, N-Channel, Silicon, Repetitive Avalanche Types 2N6764, 2N6764T1, 2N6766, 2N6766T1, 2N6768, 2N6768T1, 2N6770, and 2N6770T1, including JAN, JANTX, JANTXV, JANS, JANHC, and JANKC. The device is packaged in a TO-204AE configuration, which is a flange mount type that allows for the attachment of the semiconductor device's surface to a heat dissipater, facilitating effective thermal management of the case temperature. The drain is electrically connected to the case for this device. The junction-to-case thermal resistance for the TO-3 case is 0.83 °C/W.
The proper thermal management of semiconductor devices is critical for their reliable operation, particularly in high-performance applications. The specified derating process is essential for maintaining device integrity under elevated temperatures. The maximum case temperature of 1500°C indicates the upper limit for safe operation, while the initial threshold of 250°C serves as a warning point for users to begin the derating process.
The TO-204AE package design, which is equivalent to the JEDEC TO-3 package, is specifically engineered for effective heat dissipation. This design includes a flange that allows for direct mounting to a heat sink, ensuring that heat generated during operation is efficiently transferred away from the semiconductor junction. The electrical connection of the drain to the case is a significant feature, as it facilitates the removal of heat directly from the active region of the transistor.
The junction-to-case thermal resistance value of 0.83 °C/W is a critical parameter, as it quantifies the thermal performance of the device. A lower thermal resistance indicates better thermal conductivity and heat dissipation capabilities, which are vital for maintaining junction temperatures within safe operating limits. This parameter is particularly important in applications requiring high power handling, where excessive heat can lead to device failure.
In summary, the operational guidelines, thermal management features, and packaging specifications provided for these N-channel silicon field-effect transistors are crucial for ensuring their reliability and performance in various electronic applications. Proper understanding and adherence to these specifications can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of the devices in practical use.Once the case temperature reaches 250C the device must be derated up to a maximum case temperature of 1500C, insuring the junction temperature remains below the maximum permissible temperature. MIL-PRF-19500/543; Semiconductor Device, Transistor, Field Effect, N-Channel, Silicon, Repetitive Avalanche Types 2N6764, 2N6764T1, 2N6766, 2N6766T1, 2N6768, 2N6768T1, 2N6770,
and 2N6770T1, JAN, JANTX, JANTXV, JANS, JANHC, and JANKC [ TO-204AE ; formerly the JEDEC TO-3 package designation ] TO-204 Flange mount. Is a type of package which provides a method of attaching a surface of the semiconductor device, the flange in this case, to a heat dissipater [a component that acts as a heat sink] to achieve thermal management of the case temperature.
The Drain is electrically connected to the case [for this device]. The Junction to Case Thermal Resistance for the TO-3 case is 0. 83 0C/W. 🔗 External reference
The proper thermal management of semiconductor devices is critical for their reliable operation, particularly in high-performance applications. The specified derating process is essential for maintaining device integrity under elevated temperatures. The maximum case temperature of 1500°C indicates the upper limit for safe operation, while the initial threshold of 250°C serves as a warning point for users to begin the derating process.
The TO-204AE package design, which is equivalent to the JEDEC TO-3 package, is specifically engineered for effective heat dissipation. This design includes a flange that allows for direct mounting to a heat sink, ensuring that heat generated during operation is efficiently transferred away from the semiconductor junction. The electrical connection of the drain to the case is a significant feature, as it facilitates the removal of heat directly from the active region of the transistor.
The junction-to-case thermal resistance value of 0.83 °C/W is a critical parameter, as it quantifies the thermal performance of the device. A lower thermal resistance indicates better thermal conductivity and heat dissipation capabilities, which are vital for maintaining junction temperatures within safe operating limits. This parameter is particularly important in applications requiring high power handling, where excessive heat can lead to device failure.
In summary, the operational guidelines, thermal management features, and packaging specifications provided for these N-channel silicon field-effect transistors are crucial for ensuring their reliability and performance in various electronic applications. Proper understanding and adherence to these specifications can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of the devices in practical use.Once the case temperature reaches 250C the device must be derated up to a maximum case temperature of 1500C, insuring the junction temperature remains below the maximum permissible temperature. MIL-PRF-19500/543; Semiconductor Device, Transistor, Field Effect, N-Channel, Silicon, Repetitive Avalanche Types 2N6764, 2N6764T1, 2N6766, 2N6766T1, 2N6768, 2N6768T1, 2N6770,
and 2N6770T1, JAN, JANTX, JANTXV, JANS, JANHC, and JANKC [ TO-204AE ; formerly the JEDEC TO-3 package designation ] TO-204 Flange mount. Is a type of package which provides a method of attaching a surface of the semiconductor device, the flange in this case, to a heat dissipater [a component that acts as a heat sink] to achieve thermal management of the case temperature.
The Drain is electrically connected to the case [for this device]. The Junction to Case Thermal Resistance for the TO-3 case is 0. 83 0C/W. 🔗 External reference