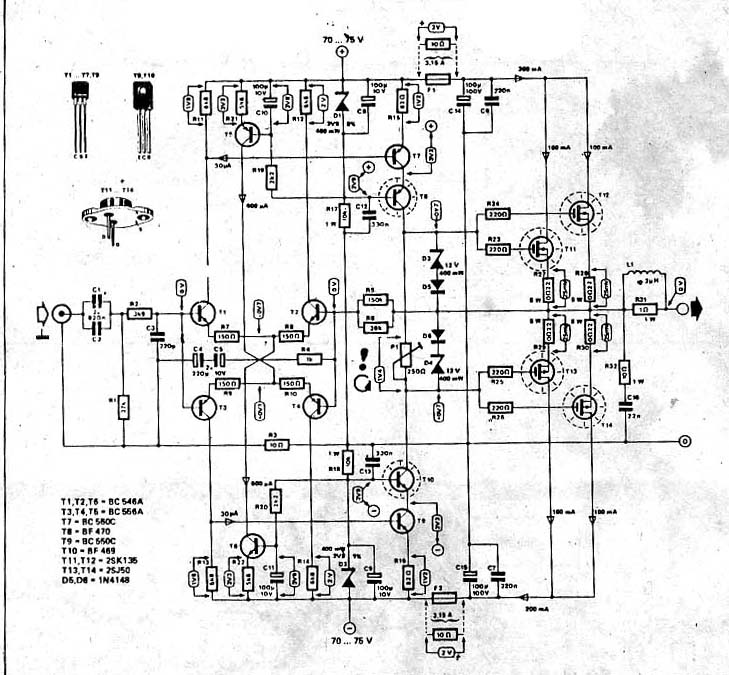
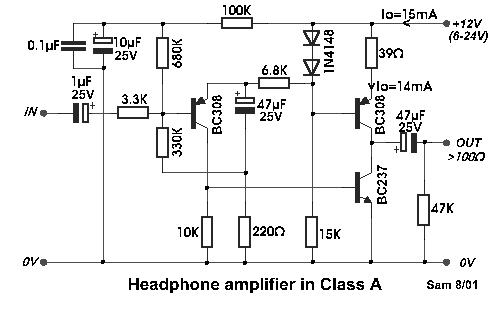
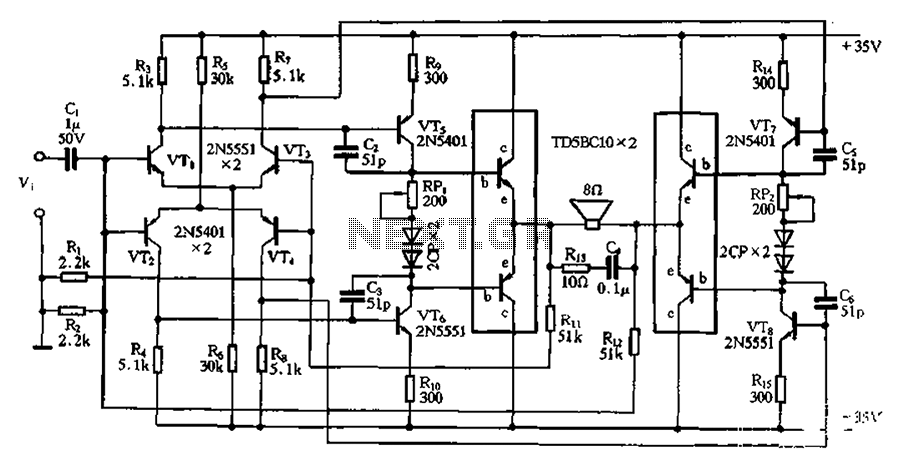
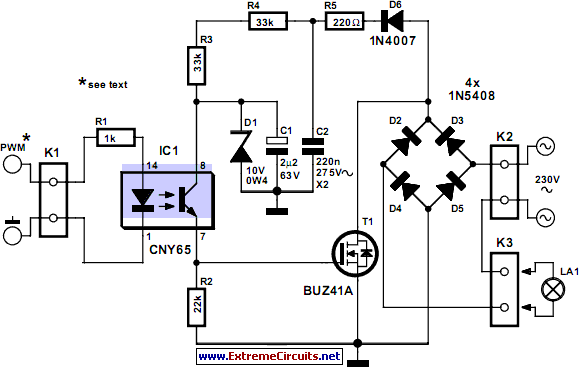
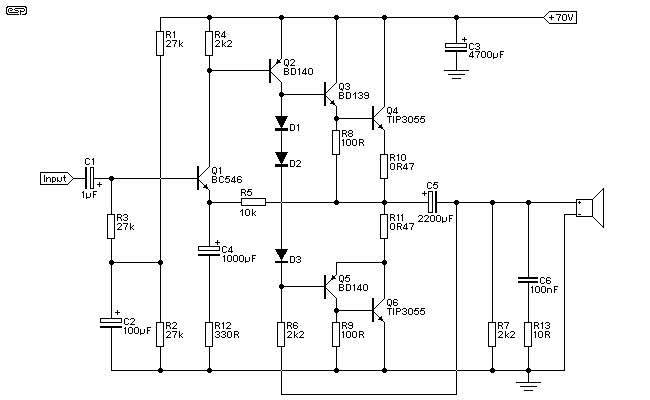
Class A Mosfet Headphone Amplifier
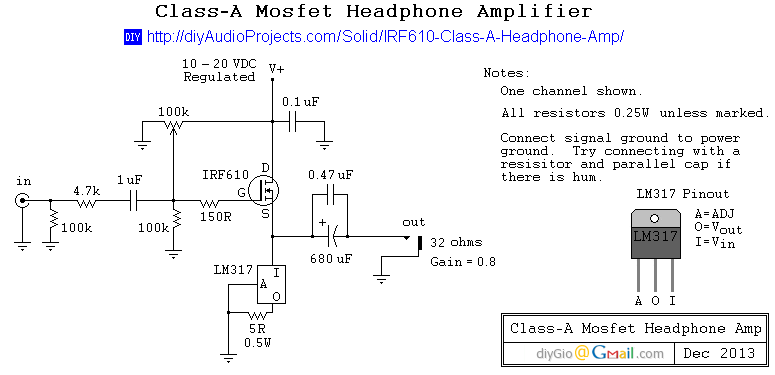
This is a simple and low-cost desktop headphone amplifier designed for office use. The amplifier concept is straightforward and adheres to a typical single-ended Class A circuit.
The desktop headphone amplifier utilizes a single-ended Class A design, which is known for its linearity and low distortion characteristics. This type of amplifier operates with a single transistor or a pair of transistors in a push-pull configuration, ensuring that the audio signal is amplified without significant clipping or distortion, even at higher volumes.
The circuit typically includes a power supply section that converts AC voltage to a suitable DC voltage for the amplifier. It may use a simple rectifier followed by a filtering capacitor to smooth out the output, providing a stable voltage for the amplifier's operation.
Input signals are usually received through a 3.5mm jack or RCA connectors, which are then fed into a volume control potentiometer. This component allows the user to adjust the output level before it is amplified. The signal is then passed to the amplifier stage, where the transistors are biased to operate in the Class A region, ensuring that the output remains faithful to the input signal.
Output coupling capacitors may be employed to block any DC offset from reaching the headphones, protecting them from potential damage. The output stage is designed to drive headphones with a specific impedance, typically ranging from 16 to 32 ohms, ensuring compatibility with most consumer headphones.
To enhance the performance, bypass capacitors may be added near the power supply pins of the amplifier to reduce noise and improve transient response. Additionally, a heat sink may be integrated to dissipate heat generated by the transistors during operation, maintaining optimal performance and reliability.
Overall, this desktop headphone amplifier offers a cost-effective solution for enhancing audio quality in an office environment, providing users with an improved listening experience without the complexities of more advanced amplifier designs.This is a simple and low cost desktop headphone amplifier for the office. The amplifier concept is simple and follows a typical single-ended class A circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The desktop headphone amplifier utilizes a single-ended Class A design, which is known for its linearity and low distortion characteristics. This type of amplifier operates with a single transistor or a pair of transistors in a push-pull configuration, ensuring that the audio signal is amplified without significant clipping or distortion, even at higher volumes.
The circuit typically includes a power supply section that converts AC voltage to a suitable DC voltage for the amplifier. It may use a simple rectifier followed by a filtering capacitor to smooth out the output, providing a stable voltage for the amplifier's operation.
Input signals are usually received through a 3.5mm jack or RCA connectors, which are then fed into a volume control potentiometer. This component allows the user to adjust the output level before it is amplified. The signal is then passed to the amplifier stage, where the transistors are biased to operate in the Class A region, ensuring that the output remains faithful to the input signal.
Output coupling capacitors may be employed to block any DC offset from reaching the headphones, protecting them from potential damage. The output stage is designed to drive headphones with a specific impedance, typically ranging from 16 to 32 ohms, ensuring compatibility with most consumer headphones.
To enhance the performance, bypass capacitors may be added near the power supply pins of the amplifier to reduce noise and improve transient response. Additionally, a heat sink may be integrated to dissipate heat generated by the transistors during operation, maintaining optimal performance and reliability.
Overall, this desktop headphone amplifier offers a cost-effective solution for enhancing audio quality in an office environment, providing users with an improved listening experience without the complexities of more advanced amplifier designs.This is a simple and low cost desktop headphone amplifier for the office. The amplifier concept is simple and follows a typical single-ended class A circuit.. 🔗 External reference