Cranial Electrotherapy StimulatorCircuit
Due to the recent launch of Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES) portable devices in Europe, a similar circuit has been designed for hobbyists. CES is a widely used method for electrically enhancing brain function and has been prescribed by medical professionals, particularly in the USA, for therapeutic reasons, including anxiety, depression, insomnia, and chemical dependency. CES units produce an adjustable current ranging from 80 to 600 microamperes, which flows through clips attached to the earlobes. The device's waveform consists of a 400-millisecond positive pulse followed by an equal negative pulse, followed by a 1.2-second pause, with a primary frequency of 0.5 Hz, resulting in a double pulse every two seconds. Some users report that these subtle electrical impulses help achieve a relaxed yet alert state of mind. While no therapeutic effectiveness can be claimed or proven for this device, the circuit is inexpensive and simple enough to construct without risk.
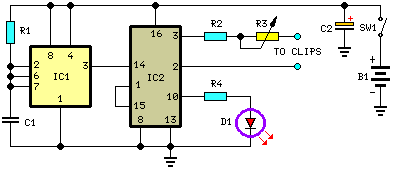
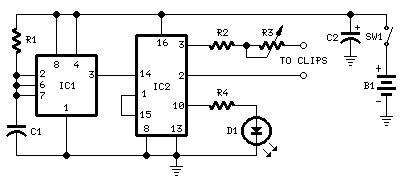
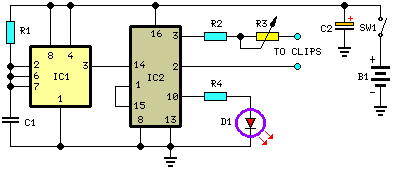
The circuit utilizes IC1 to create a narrow pulse oscillator operating at 2.5 Hz, which feeds into IC2. This integrated circuit generates the various timing sequences for the output pulses. Outputs are taken from pins 2 and 3 to easily obtain negative-going pulses. The current output is limited to 600 µA by resistor R2 and can be adjusted between 80 and 600 µA using resistor R3. An LED flashes every two seconds to indicate proper operation and can also assist with the setting process. If desired, the LED and resistor R4 can be omitted to significantly extend battery life. In this case, a frequency meter should be used to measure 2.5 Hz at pin 3 of IC1, or an oscilloscope can be employed to observe 400-millisecond pulses at pins 2, 3, or 10, while adjusting the added trimmer. Simple ear clips can be fabricated using thin copper foil, approximately 4 cm long and 1.5 cm wide, with rounded corners. The wire end is soldered at the center, and the foil is folded to secure the earlobes. Commercial CES devices often include a built-in timer, with session durations typically ranging from 20 minutes to 1 hour. For timing purposes, circuits such as the Timed Beeper, Bedside Lamp Timer, or Jogging Timer available on this website can be utilized, with timing components adjusted to meet specific requirements.
This circuit design is an accessible project for hobbyists interested in exploring the principles of cranial electrotherapy, providing an opportunity to experiment with low-level electrical stimulation while considering safety and efficacy. Proper construction and adherence to the specifications will ensure reliable operation, allowing users to engage with the technology in a manageable and informative way.Owing to the recent launching in Europe of Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES) portable sets, we have been "Electronically Stimulated" in designing a similar circuit for the sake of hobbyists. CES is the most popular technique for electrically boosting brain power, and has long been prescribed by doctors, mainly in the USA, for therapeutic re
asons, including the treatment of anxiety, depression, insomnia, and chemical dependency. CES units generate an adjustable current (80 to 600 microAmperes) that flows through clips placed on the earlobes. The waveform of this device is a 400 milliseconds positive pulse followed by a negative one of the same duration, then a pause of 1.
2 seconds. The main frequency is 0. 5 Hz, i. e. a double pulse every 2 seconds. Some people report that this kind of minute specialized electrical impulses contributes to achieve a relaxed state that leaves the mind alert. Obviously we can`t claim or prove any therapeutic effectiveness for this device, but if you are interested in trying it, the circuit is so cheap and so simple to build that an attempt can be made with quite no harm.
IC1 forms a narrow pulse, 2. 5Hz oscillator feeding IC2. This chip generates the various timings for the output pulses. Output is taken at pins 2 & 3 to easily obtain negative going pulses also. Current output is limited to 600 µA by R2 and can be regulated from 80 to 600 µA by means of R3. The LED flashes every 2 seconds signaling proper operation and can also be used for setting purposes. It can be omitted together with R4, greatly increasing battery life. In this case use a frequency meter to read 2. 5Hz at pin 3 of IC1, or an oscilloscope to read 400msec pulses at pins 2, 3 or 10, adjusting the added trimmer.
Ultra-simple earclips can be made using a thin copper foil with rounded corners 4 cm. long and 1. 5 cm. wide, soldering the wire end in the center, and then folding the foil in two parts holding the earlobes. Commercial sets have frequently a built-in timer. Timing sessions last usually 20 minutes to 1 hour. For this purpose you can use the Timed Beeper the Bedside Lamp Timer or the Jogging Timer circuits available on this website, adjusting the timing components in order to suit your needs.
🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes IC1 to create a narrow pulse oscillator operating at 2.5 Hz, which feeds into IC2. This integrated circuit generates the various timing sequences for the output pulses. Outputs are taken from pins 2 and 3 to easily obtain negative-going pulses. The current output is limited to 600 µA by resistor R2 and can be adjusted between 80 and 600 µA using resistor R3. An LED flashes every two seconds to indicate proper operation and can also assist with the setting process. If desired, the LED and resistor R4 can be omitted to significantly extend battery life. In this case, a frequency meter should be used to measure 2.5 Hz at pin 3 of IC1, or an oscilloscope can be employed to observe 400-millisecond pulses at pins 2, 3, or 10, while adjusting the added trimmer. Simple ear clips can be fabricated using thin copper foil, approximately 4 cm long and 1.5 cm wide, with rounded corners. The wire end is soldered at the center, and the foil is folded to secure the earlobes. Commercial CES devices often include a built-in timer, with session durations typically ranging from 20 minutes to 1 hour. For timing purposes, circuits such as the Timed Beeper, Bedside Lamp Timer, or Jogging Timer available on this website can be utilized, with timing components adjusted to meet specific requirements.
This circuit design is an accessible project for hobbyists interested in exploring the principles of cranial electrotherapy, providing an opportunity to experiment with low-level electrical stimulation while considering safety and efficacy. Proper construction and adherence to the specifications will ensure reliable operation, allowing users to engage with the technology in a manageable and informative way.Owing to the recent launching in Europe of Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES) portable sets, we have been "Electronically Stimulated" in designing a similar circuit for the sake of hobbyists. CES is the most popular technique for electrically boosting brain power, and has long been prescribed by doctors, mainly in the USA, for therapeutic re
asons, including the treatment of anxiety, depression, insomnia, and chemical dependency. CES units generate an adjustable current (80 to 600 microAmperes) that flows through clips placed on the earlobes. The waveform of this device is a 400 milliseconds positive pulse followed by a negative one of the same duration, then a pause of 1.
2 seconds. The main frequency is 0. 5 Hz, i. e. a double pulse every 2 seconds. Some people report that this kind of minute specialized electrical impulses contributes to achieve a relaxed state that leaves the mind alert. Obviously we can`t claim or prove any therapeutic effectiveness for this device, but if you are interested in trying it, the circuit is so cheap and so simple to build that an attempt can be made with quite no harm.
IC1 forms a narrow pulse, 2. 5Hz oscillator feeding IC2. This chip generates the various timings for the output pulses. Output is taken at pins 2 & 3 to easily obtain negative going pulses also. Current output is limited to 600 µA by R2 and can be regulated from 80 to 600 µA by means of R3. The LED flashes every 2 seconds signaling proper operation and can also be used for setting purposes. It can be omitted together with R4, greatly increasing battery life. In this case use a frequency meter to read 2. 5Hz at pin 3 of IC1, or an oscilloscope to read 400msec pulses at pins 2, 3 or 10, adjusting the added trimmer.
Ultra-simple earclips can be made using a thin copper foil with rounded corners 4 cm. long and 1. 5 cm. wide, soldering the wire end in the center, and then folding the foil in two parts holding the earlobes. Commercial sets have frequently a built-in timer. Timing sessions last usually 20 minutes to 1 hour. For this purpose you can use the Timed Beeper the Bedside Lamp Timer or the Jogging Timer circuits available on this website, adjusting the timing components in order to suit your needs.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713