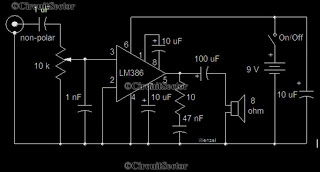
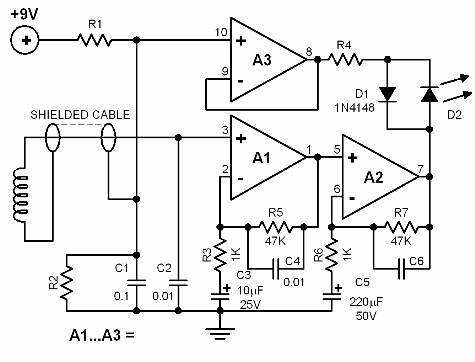
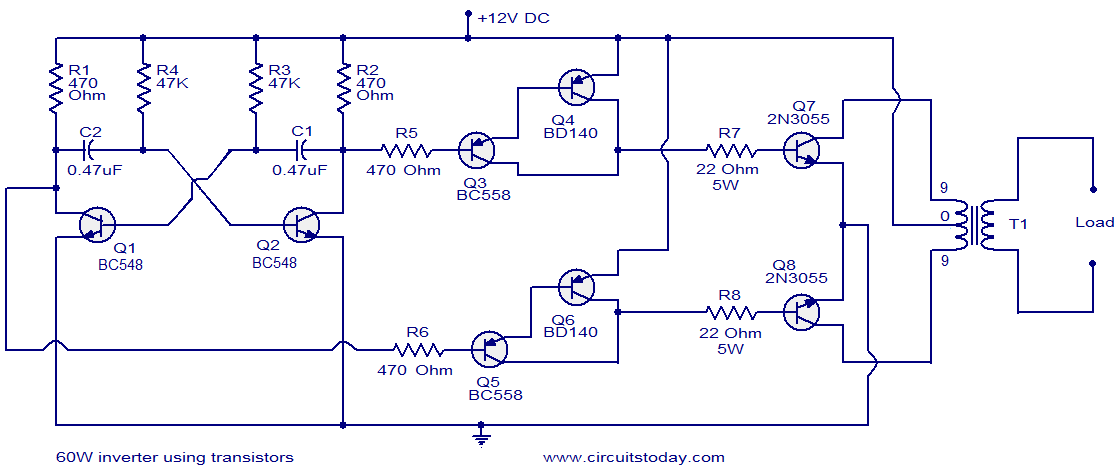
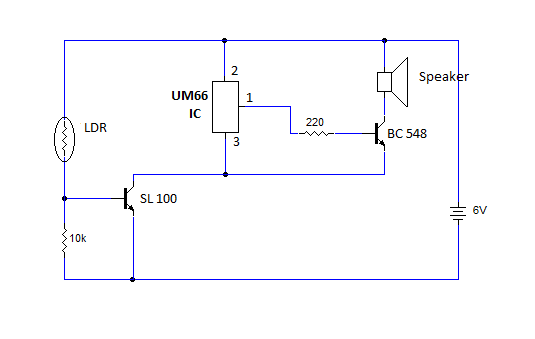
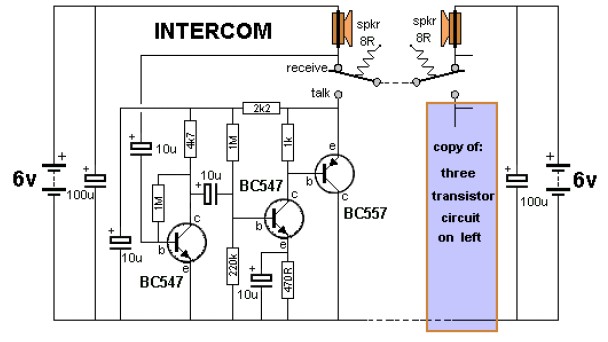
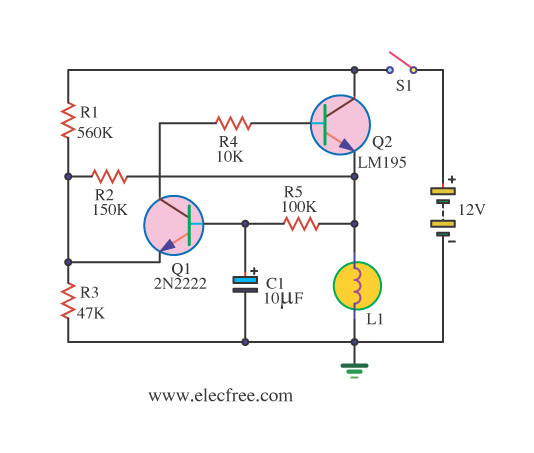
darklight sensor using transistor
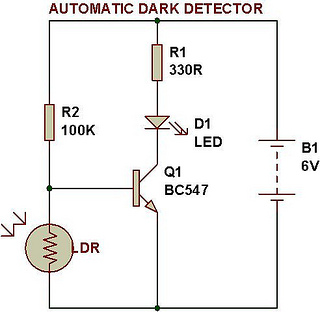
An automatic dark detector senses darkness. As the light level decreases and the light-dependent resistor (LDR) reaches the maximum threshold resistance, the circuit automatically activates the LED D1. Conversely, a light detector senses light, and when the light level increases to meet the lowest threshold resistance of the LDR, the circuit automatically turns on LED D1. The sensitivity of the circuit can be adjusted using the preset variable resistor VR1-10K.
This circuit operates based on the principle of light-dependent resistors (LDRs), which change their resistance according to the ambient light level. In bright conditions, the resistance of the LDR decreases, allowing current to flow through the circuit. When the light level drops below a certain threshold, the resistance increases, triggering the activation of LED D1.
The circuit comprises an LDR connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor. The output from this configuration is fed into a comparator circuit, which compares the voltage across the LDR with a reference voltage set by a potentiometer. When the voltage across the LDR exceeds the reference voltage, the comparator output changes state, activating the LED.
To enhance functionality, the circuit includes a variable resistor (VR1-10K), which allows for fine-tuning of the sensitivity. By adjusting this resistor, users can set the desired light level at which the LED will turn on or off. This feature makes the circuit versatile for various applications, such as automatic street lighting or garden lights that activate at dusk and deactivate at dawn.
In summary, this automatic dark detector and light detector circuit is a practical implementation of light sensing technology, providing an efficient solution for automatic lighting control based on ambient light conditions.Automatic dark detector senses darkness. As the light level decreases and LDR meets the maximum threshold resistance, the circuit automatically switches on the LED D1. A light detector senses light. As the light level increases and LDR meets the lowest threshold resistance, the circuit automatically turns on the LED D1.
We can adjust the sensitivi ty using the preset VR1-10K. 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates based on the principle of light-dependent resistors (LDRs), which change their resistance according to the ambient light level. In bright conditions, the resistance of the LDR decreases, allowing current to flow through the circuit. When the light level drops below a certain threshold, the resistance increases, triggering the activation of LED D1.
The circuit comprises an LDR connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor. The output from this configuration is fed into a comparator circuit, which compares the voltage across the LDR with a reference voltage set by a potentiometer. When the voltage across the LDR exceeds the reference voltage, the comparator output changes state, activating the LED.
To enhance functionality, the circuit includes a variable resistor (VR1-10K), which allows for fine-tuning of the sensitivity. By adjusting this resistor, users can set the desired light level at which the LED will turn on or off. This feature makes the circuit versatile for various applications, such as automatic street lighting or garden lights that activate at dusk and deactivate at dawn.
In summary, this automatic dark detector and light detector circuit is a practical implementation of light sensing technology, providing an efficient solution for automatic lighting control based on ambient light conditions.Automatic dark detector senses darkness. As the light level decreases and LDR meets the maximum threshold resistance, the circuit automatically switches on the LED D1. A light detector senses light. As the light level increases and LDR meets the lowest threshold resistance, the circuit automatically turns on the LED D1.
We can adjust the sensitivi ty using the preset VR1-10K. 🔗 External reference