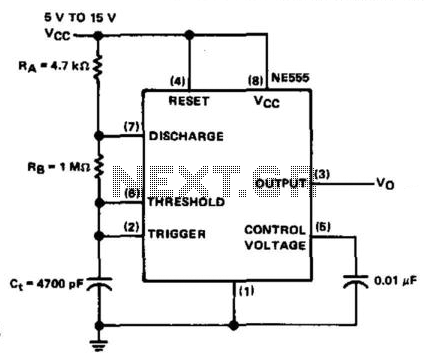
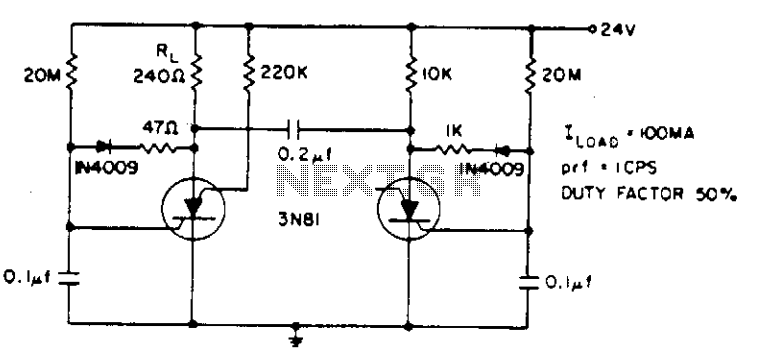
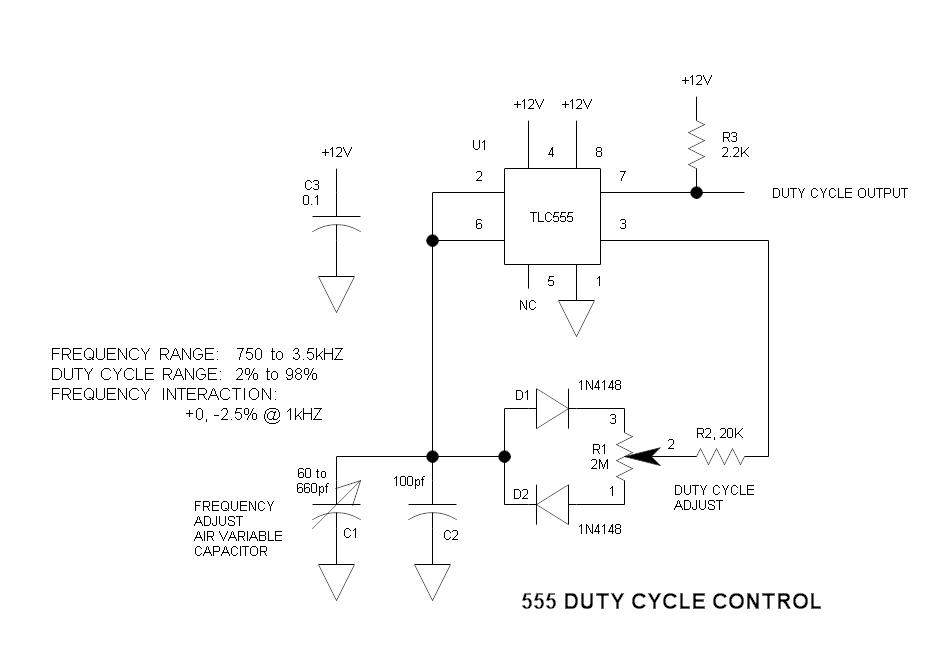
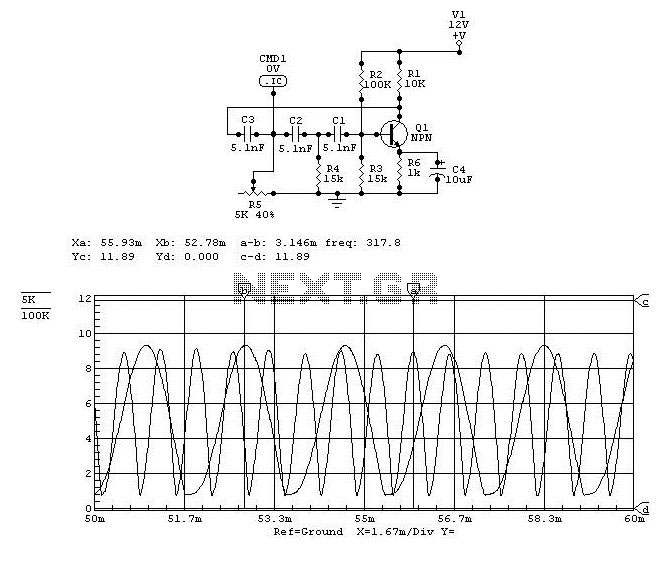
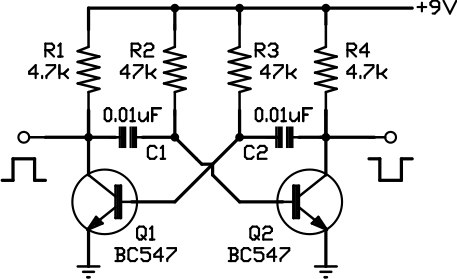
Data control variable frequency oscillator
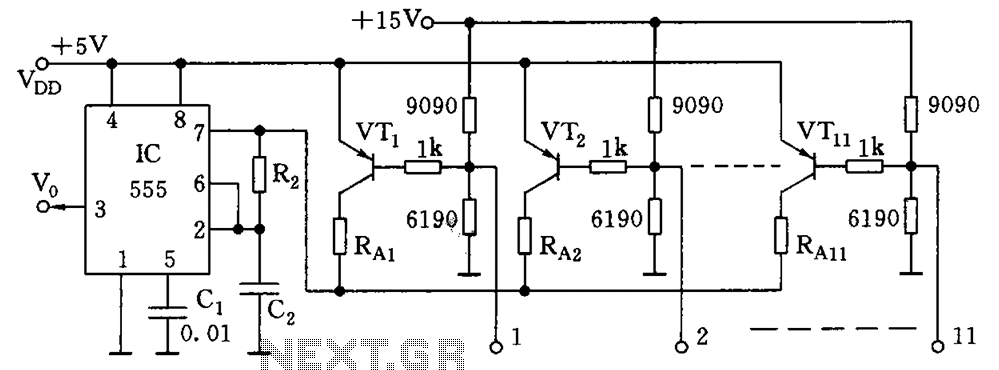
As illustrated in the figure, the base bias circuit for transistors VT1 to VT11 is designed to accept binary data, where a high level represents 1 and a low level represents 0. This configuration allows for 2048 combinations of binary states. When a bit is low, the corresponding transistor VT turns on, leading to the charging of capacitor C2 through resistors RA and R2. Resistor RA serves as the equivalent resistance in this circuit, influencing the oscillation frequency.
The described circuit employs a base biasing technique for a series of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) labeled VT1 through VT11. Each transistor is configured to respond to a binary input signal, facilitating the generation of a corresponding output based on the binary state. The circuit can handle a total of 2048 unique combinations, as indicated by the 11 bits utilized in the configuration.
When a binary input is low (0), the associated transistor (VT) is activated, creating a conductive path that allows current to flow through the circuit. This activation causes capacitor C2 to charge via the resistors RA and R2. The charging process is influenced by the values of these resistors, where RA provides an equivalent resistance that determines the time constant of the charging circuit. The time constant, in turn, plays a critical role in defining the oscillation frequency of the circuit, which is essential for applications requiring precise timing and switching characteristics.
The overall functionality of this circuit is crucial in digital applications where binary data needs to be processed and converted into corresponding analog signals or other digital states. The careful selection of resistor values and capacitor characteristics ensures optimal performance, stability, and reliability in various electronic systems. This design can be implemented in applications such as signal processing, data communication, and control systems where binary state representation and manipulation are fundamental. As shown in FIG, VT1 ~ VT11 base bias circuit 11 added to the binary data (high level 1 to low level 0 ), there are 211 2048 combinations. When a bit is low, the corresponding VT turns on, the C2 by RA + R2 charging it, RA conducting pipe for the equivalent resistance of the resistor, the oscillation frequency
The described circuit employs a base biasing technique for a series of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) labeled VT1 through VT11. Each transistor is configured to respond to a binary input signal, facilitating the generation of a corresponding output based on the binary state. The circuit can handle a total of 2048 unique combinations, as indicated by the 11 bits utilized in the configuration.
When a binary input is low (0), the associated transistor (VT) is activated, creating a conductive path that allows current to flow through the circuit. This activation causes capacitor C2 to charge via the resistors RA and R2. The charging process is influenced by the values of these resistors, where RA provides an equivalent resistance that determines the time constant of the charging circuit. The time constant, in turn, plays a critical role in defining the oscillation frequency of the circuit, which is essential for applications requiring precise timing and switching characteristics.
The overall functionality of this circuit is crucial in digital applications where binary data needs to be processed and converted into corresponding analog signals or other digital states. The careful selection of resistor values and capacitor characteristics ensures optimal performance, stability, and reliability in various electronic systems. This design can be implemented in applications such as signal processing, data communication, and control systems where binary state representation and manipulation are fundamental. As shown in FIG, VT1 ~ VT11 base bias circuit 11 added to the binary data (high level 1 to low level 0 ), there are 211 2048 combinations. When a bit is low, the corresponding VT turns on, the C2 by RA + R2 charging it, RA conducting pipe for the equivalent resistance of the resistor, the oscillation frequency
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713