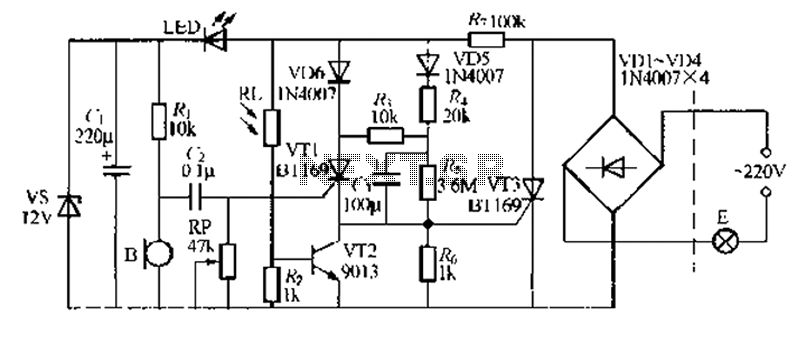
Dc static switch
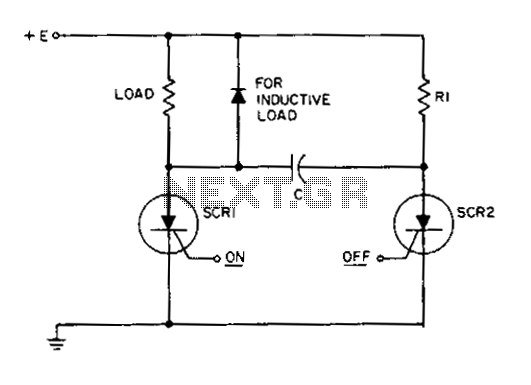
This circuit is a static SCR switch designed for use in a DC circuit. When a low-power signal is applied to the gate of SCR1, this SCR is triggered, allowing voltage to be applied to the load. The right plate of capacitor C charges positively with respect to the left plate through resistor R1. When SCR2 is triggered, capacitor C is connected across SCR1, momentarily reverse biasing this SCR between its anode and cathode. This reverse voltage turns off SCR1, provided that the gate signal is not simultaneously applied to both gates. The current through the load decreases to zero in an exponential manner as capacitor C becomes charged.
This static SCR switch circuit utilizes two silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) to control the flow of current in a DC circuit. The primary operational mechanism relies on the gate control of SCR1, which allows for the initiation of current flow to the load when a low-power signal is applied. The triggering of SCR1 is crucial for the circuit's operation, as it enables the load to receive voltage.
Once SCR1 is activated, capacitor C begins to charge through resistor R1. The charging process causes the voltage across capacitor C to increase, resulting in a positive charge on the right plate relative to the left plate. The charging time constant is determined by the resistance value of R1 and the capacitance of C, influencing the rate at which the capacitor charges.
The role of SCR2 becomes significant when it is triggered. Upon activation, SCR2 connects capacitor C across SCR1, creating a reverse voltage condition. This reverse biasing momentarily disrupts the conduction path of SCR1, effectively turning it off. This action is contingent upon the condition that the gate signals are not applied to both SCRs simultaneously, which would otherwise maintain SCR1 in a conductive state.
As capacitor C charges, the current flowing through the load decreases exponentially. This behavior is characteristic of RC charging circuits, where the current diminishes as the capacitor approaches its maximum charge. The gradual reduction in current ensures a smooth transition to zero load current, which can be beneficial in applications where abrupt changes in current could cause issues.
Overall, this circuit provides a reliable means of controlling DC loads through the use of SCR technology, allowing for efficient switching and current management. Proper selection of component values for R1 and C is essential to achieve the desired timing and performance characteristics of the circuit.This circuit is a static SCR switch for use in a dc circuit. When a low power signal is applied to the gate of SCR1, this SCR is triggered and voltage is applied to the load. The right hand plate of C charges positively with respect to the left hand plate through Rl. When SCR2 is triggered on, capacitor C is connected across SCR1, so that this SCR is momentarily reverse biased between anode and cathode.
This reverse voltage turns SCR1 off provided the gate signal is not applied simultaneously to both gates. The current through the load will decrease to zero in an exponential fashion as C becomes charged. 🔗 External reference
This static SCR switch circuit utilizes two silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) to control the flow of current in a DC circuit. The primary operational mechanism relies on the gate control of SCR1, which allows for the initiation of current flow to the load when a low-power signal is applied. The triggering of SCR1 is crucial for the circuit's operation, as it enables the load to receive voltage.
Once SCR1 is activated, capacitor C begins to charge through resistor R1. The charging process causes the voltage across capacitor C to increase, resulting in a positive charge on the right plate relative to the left plate. The charging time constant is determined by the resistance value of R1 and the capacitance of C, influencing the rate at which the capacitor charges.
The role of SCR2 becomes significant when it is triggered. Upon activation, SCR2 connects capacitor C across SCR1, creating a reverse voltage condition. This reverse biasing momentarily disrupts the conduction path of SCR1, effectively turning it off. This action is contingent upon the condition that the gate signals are not applied to both SCRs simultaneously, which would otherwise maintain SCR1 in a conductive state.
As capacitor C charges, the current flowing through the load decreases exponentially. This behavior is characteristic of RC charging circuits, where the current diminishes as the capacitor approaches its maximum charge. The gradual reduction in current ensures a smooth transition to zero load current, which can be beneficial in applications where abrupt changes in current could cause issues.
Overall, this circuit provides a reliable means of controlling DC loads through the use of SCR technology, allowing for efficient switching and current management. Proper selection of component values for R1 and C is essential to achieve the desired timing and performance characteristics of the circuit.This circuit is a static SCR switch for use in a dc circuit. When a low power signal is applied to the gate of SCR1, this SCR is triggered and voltage is applied to the load. The right hand plate of C charges positively with respect to the left hand plate through Rl. When SCR2 is triggered on, capacitor C is connected across SCR1, so that this SCR is momentarily reverse biased between anode and cathode.
This reverse voltage turns SCR1 off provided the gate signal is not applied simultaneously to both gates. The current through the load will decrease to zero in an exponential fashion as C becomes charged. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713