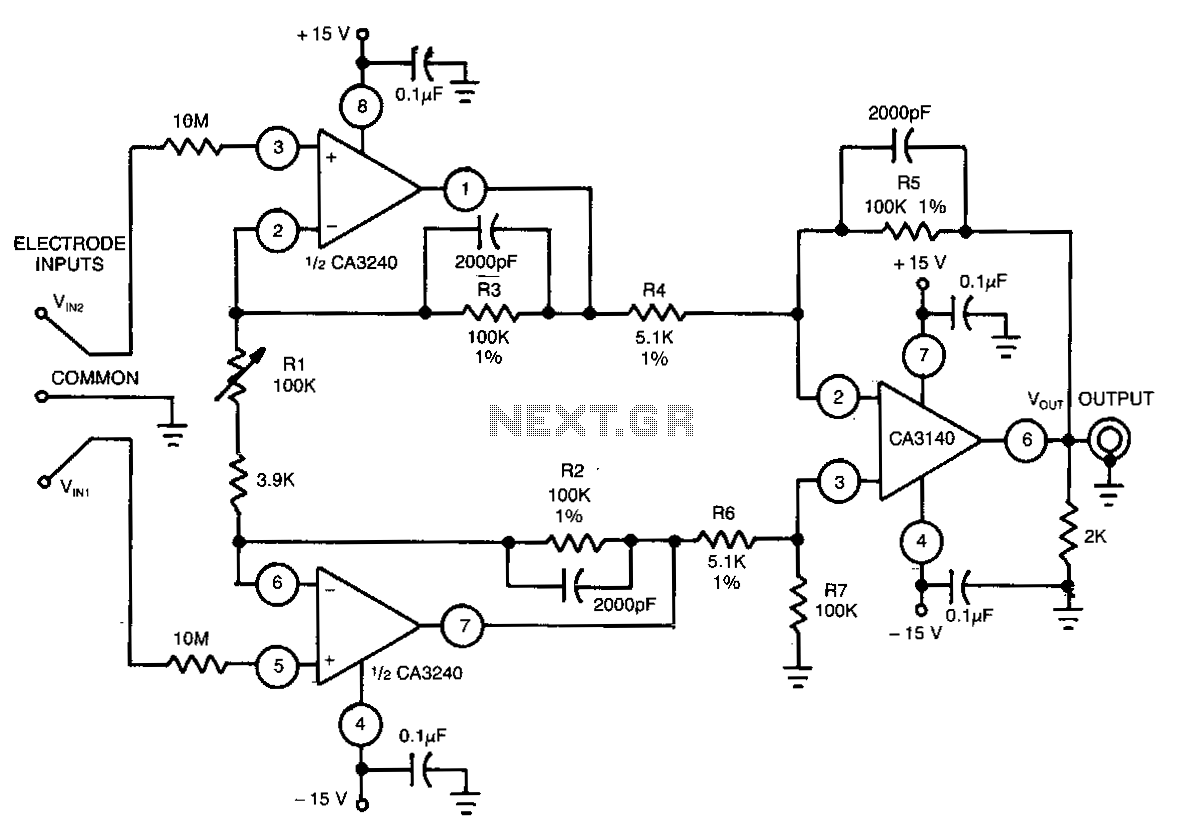
Differential-amplifier
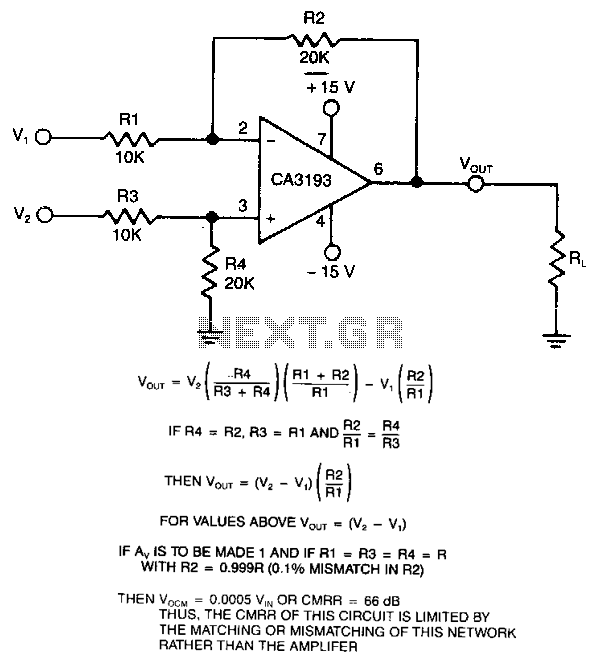
This differential amplifier utilizes a CA3193 BiMOS operational amplifier. It serves as a classical differential input-to-signal-ended output converter, which, when paired with a low-resistance signal source, will sustain a high common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), provided that R1 equals R3 plus R4.
The described differential amplifier configuration employs the CA3193 BiMOS op-amp, known for its high performance in analog signal processing. The differential amplifier is designed to amplify the difference between two input signals while rejecting any signals that are common to both inputs, thus enhancing the signal integrity.
In this circuit, the operational amplifier is configured with feedback and input resistors that establish the desired gain and input impedance characteristics. The relationship specified, where R1 equals R3 plus R4, is crucial for maintaining optimal common-mode rejection. This ensures that variations in the common-mode voltage, which can arise from noise or interference, do not affect the output significantly.
The CA3193 op-amp features a high input impedance, which is beneficial for interfacing with low-resistance signal sources, minimizing the loading effect on the signal source and preserving the original signal's integrity. The BiMOS technology combines the advantages of both bipolar and CMOS transistors, providing low noise and high speed.
In practical applications, this differential amplifier can be employed in instrumentation, audio processing, and sensor signal conditioning, where accurate signal amplification is required. Proper selection of resistor values and maintaining the specified relationship between them are essential for achieving the desired performance metrics, including bandwidth, gain stability, and CMRR.This differential amplifier uses a CA3193 BiMOS op amp. This classical, differential input-tosignal- ended output converter when used with lowresistance signal source will maintain level of CMRR, if R1 = R3 + R4. 🔗 External reference
The described differential amplifier configuration employs the CA3193 BiMOS op-amp, known for its high performance in analog signal processing. The differential amplifier is designed to amplify the difference between two input signals while rejecting any signals that are common to both inputs, thus enhancing the signal integrity.
In this circuit, the operational amplifier is configured with feedback and input resistors that establish the desired gain and input impedance characteristics. The relationship specified, where R1 equals R3 plus R4, is crucial for maintaining optimal common-mode rejection. This ensures that variations in the common-mode voltage, which can arise from noise or interference, do not affect the output significantly.
The CA3193 op-amp features a high input impedance, which is beneficial for interfacing with low-resistance signal sources, minimizing the loading effect on the signal source and preserving the original signal's integrity. The BiMOS technology combines the advantages of both bipolar and CMOS transistors, providing low noise and high speed.
In practical applications, this differential amplifier can be employed in instrumentation, audio processing, and sensor signal conditioning, where accurate signal amplification is required. Proper selection of resistor values and maintaining the specified relationship between them are essential for achieving the desired performance metrics, including bandwidth, gain stability, and CMRR.This differential amplifier uses a CA3193 BiMOS op amp. This classical, differential input-tosignal- ended output converter when used with lowresistance signal source will maintain level of CMRR, if R1 = R3 + R4. 🔗 External reference