
Digital-data-line-receiver
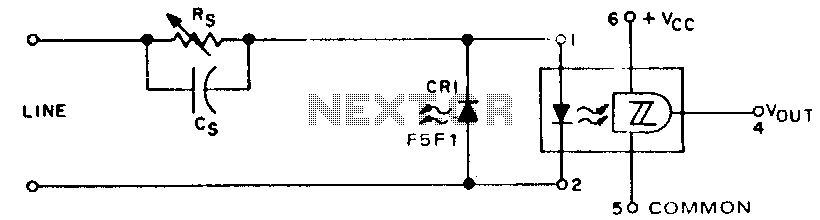
When digital data is transmitted over long distances (greater than 1 meter), the integrity of the transfer can be compromised by parasitic effects such as ground level shifts and ground loops, in addition to extraneous noise that may be picked up during transmission. An optocoupler, like the HilL, provides galvanic isolation to minimize ground loop currents and their associated common-mode voltages, while also offering predictable switching levels to improve noise immunity, thereby significantly reducing erratic behavior. Additionally, resistor Rs is configured to establish the desired switching threshold, Cs serves as an optional speed-up capacitor, and CR1 functions as an LED acting as a simple diode to ensure proper line balance and provide a discharge path for Cs when the speed-up capacitor is utilized.
The circuit configuration described utilizes an optocoupler to achieve reliable digital data transmission over extended distances. The optocoupler effectively isolates the transmitting and receiving sections of the circuit, mitigating the risks associated with ground loops and common-mode voltage fluctuations. This isolation is critical in environments where multiple devices share a common ground, as it prevents unwanted current paths that can lead to data corruption.
In the circuit, the resistor Rs is a key component that sets the threshold at which the optocoupler will switch states. By selecting an appropriate value for Rs, the designer can tailor the circuit's response to specific signal levels, ensuring that the optocoupler activates only when the incoming signal reaches a predetermined voltage. This customization enhances the reliability of the data transmission by reducing the likelihood of false triggering due to noise.
The speed-up capacitor Cs is an optional addition that can enhance the performance of the circuit, particularly in applications requiring rapid switching. By providing a temporary charge storage, Cs allows the optocoupler to respond more quickly to changes in the input signal, thereby improving the overall speed of the data transfer. When utilized, the LED CR1 acts as a simple diode, ensuring that the circuit maintains balance and providing a discharge path for Cs. This functionality is crucial for preventing voltage spikes that could disrupt the operation of the optocoupler.
Overall, this configuration is particularly effective in applications involving long-distance digital communication, where maintaining data integrity is paramount. The combination of galvanic isolation, adjustable switching thresholds, and optional speed enhancement creates a robust solution for overcoming the challenges presented by parasitic effects and noise in the transmission medium.When digital data is transmitted over long lines (longer than 1 meter), proper transfer is often disturbed by the parasitic effects of ground level shifts and ground loops, as well as by extraneous noise picked up along the way. An optocoupler, such as the HilL, combining galvanic isolation to minimize ground loop currents and their concomitant common-mode voltages, with predictable switching levels to enhance noise immunity, can significantly reduce erratic behavior.
Resistor Rs is programmed for the desired switching threshold, Cs is an optional speed-up capacitor, and CR1 is an LED used as a simple diode to provide perfect line balance and a discharge path for Cs if the speed-up capacitor is used. 🔗 External reference
The circuit configuration described utilizes an optocoupler to achieve reliable digital data transmission over extended distances. The optocoupler effectively isolates the transmitting and receiving sections of the circuit, mitigating the risks associated with ground loops and common-mode voltage fluctuations. This isolation is critical in environments where multiple devices share a common ground, as it prevents unwanted current paths that can lead to data corruption.
In the circuit, the resistor Rs is a key component that sets the threshold at which the optocoupler will switch states. By selecting an appropriate value for Rs, the designer can tailor the circuit's response to specific signal levels, ensuring that the optocoupler activates only when the incoming signal reaches a predetermined voltage. This customization enhances the reliability of the data transmission by reducing the likelihood of false triggering due to noise.
The speed-up capacitor Cs is an optional addition that can enhance the performance of the circuit, particularly in applications requiring rapid switching. By providing a temporary charge storage, Cs allows the optocoupler to respond more quickly to changes in the input signal, thereby improving the overall speed of the data transfer. When utilized, the LED CR1 acts as a simple diode, ensuring that the circuit maintains balance and providing a discharge path for Cs. This functionality is crucial for preventing voltage spikes that could disrupt the operation of the optocoupler.
Overall, this configuration is particularly effective in applications involving long-distance digital communication, where maintaining data integrity is paramount. The combination of galvanic isolation, adjustable switching thresholds, and optional speed enhancement creates a robust solution for overcoming the challenges presented by parasitic effects and noise in the transmission medium.When digital data is transmitted over long lines (longer than 1 meter), proper transfer is often disturbed by the parasitic effects of ground level shifts and ground loops, as well as by extraneous noise picked up along the way. An optocoupler, such as the HilL, combining galvanic isolation to minimize ground loop currents and their concomitant common-mode voltages, with predictable switching levels to enhance noise immunity, can significantly reduce erratic behavior.
Resistor Rs is programmed for the desired switching threshold, Cs is an optional speed-up capacitor, and CR1 is an LED used as a simple diode to provide perfect line balance and a discharge path for Cs if the speed-up capacitor is used. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713