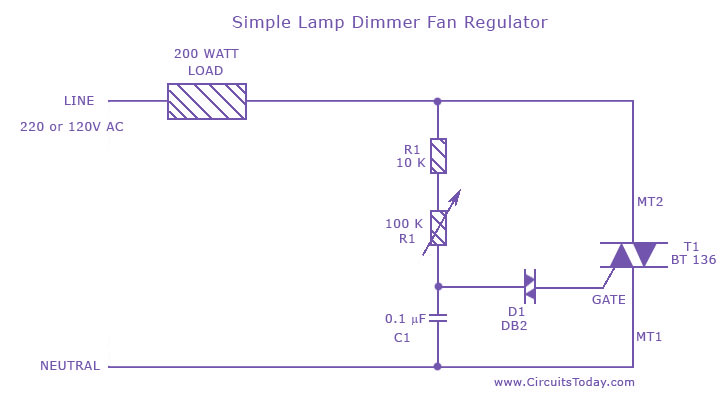
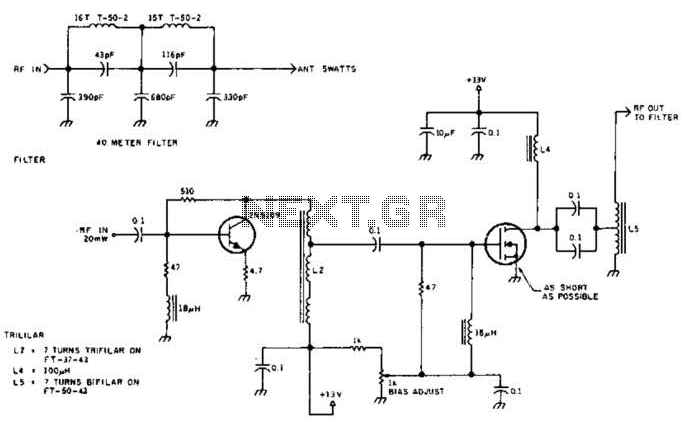
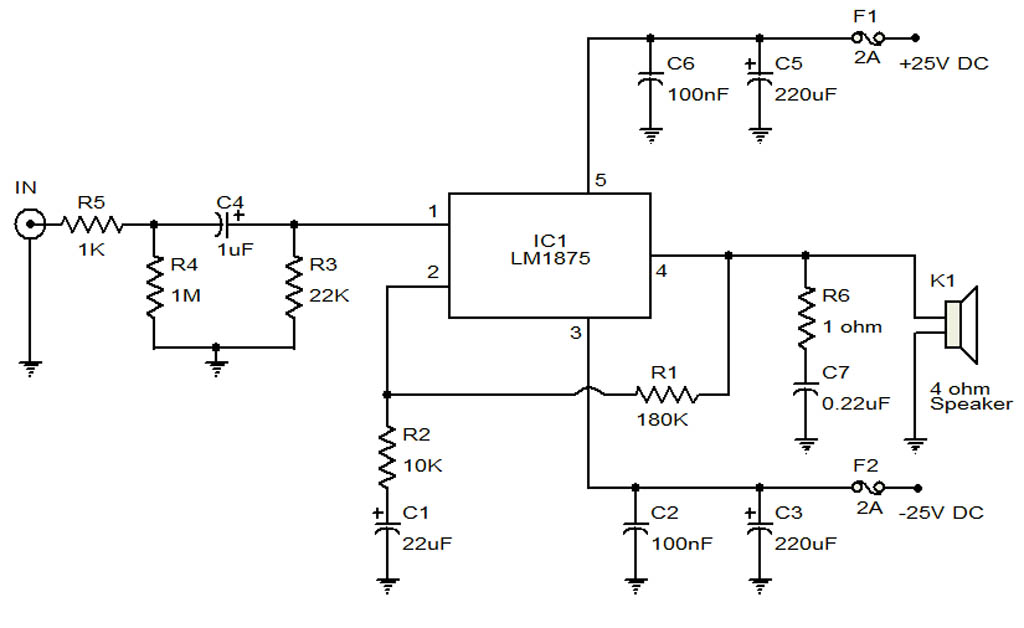
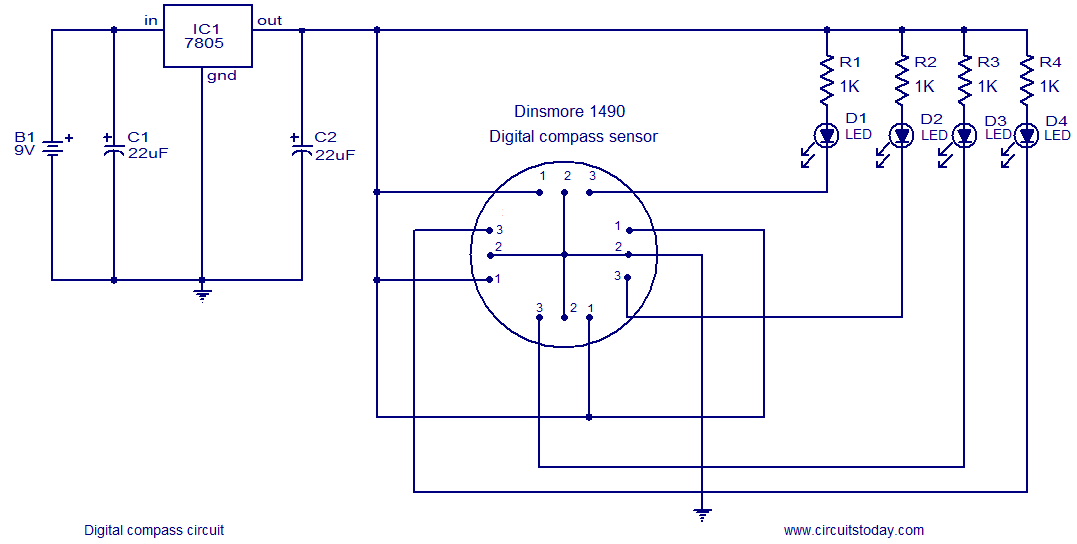
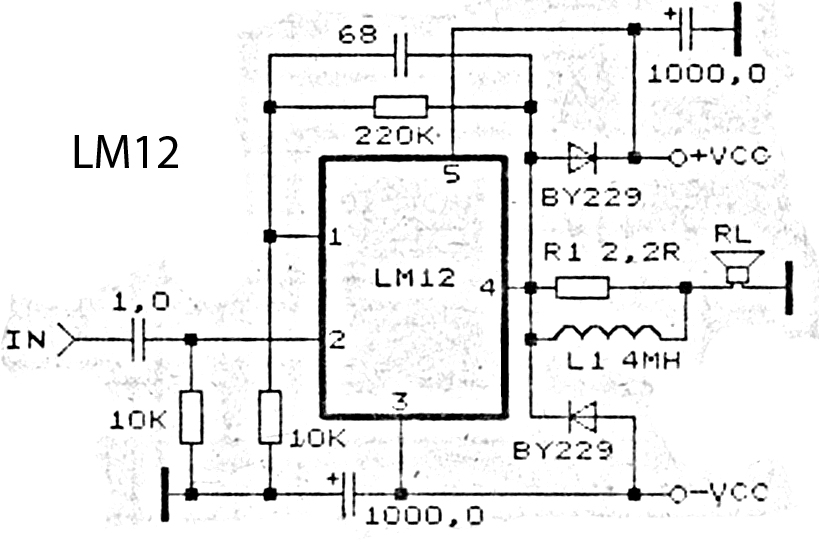
Diode digital thermometer circuit
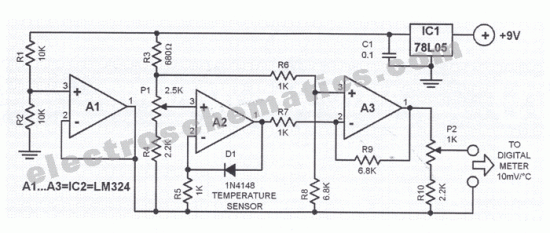
This digital thermometer circuit diagram utilizes a standard 1N4148 diode as the temperature sensor. The temperature coefficient of the diode is -2 mV/°C.
The digital thermometer circuit leverages the characteristics of the 1N4148 diode, which exhibits a predictable voltage drop that varies with temperature. As the temperature changes, the forward voltage drop across the diode decreases at a rate of approximately 2 mV for every degree Celsius increase in temperature. This property allows the diode to function effectively as a temperature sensor.
In the schematic, the 1N4148 diode is connected in a forward-biased configuration. The output voltage from the diode is fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which translates the analog voltage signal into a digital format suitable for further processing. The ADC is typically integrated into a microcontroller or a dedicated digital thermometer chip.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to stabilize the readings and filter out noise. A reference voltage source is often employed to calibrate the output of the ADC, ensuring accurate temperature readings. The microcontroller processes the digital signals received from the ADC and can display the temperature on an LCD or LED screen, or transmit the data wirelessly for remote monitoring.
Overall, this digital thermometer circuit is a cost-effective and straightforward solution for temperature measurement, leveraging the well-documented properties of the 1N4148 diode.This digital thermometer circuit diagram uses a common 1N4148 diode as the temperature sensor. The temperature coefficient of the diode, -2 mV / 0C is expl. 🔗 External reference
The digital thermometer circuit leverages the characteristics of the 1N4148 diode, which exhibits a predictable voltage drop that varies with temperature. As the temperature changes, the forward voltage drop across the diode decreases at a rate of approximately 2 mV for every degree Celsius increase in temperature. This property allows the diode to function effectively as a temperature sensor.
In the schematic, the 1N4148 diode is connected in a forward-biased configuration. The output voltage from the diode is fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which translates the analog voltage signal into a digital format suitable for further processing. The ADC is typically integrated into a microcontroller or a dedicated digital thermometer chip.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to stabilize the readings and filter out noise. A reference voltage source is often employed to calibrate the output of the ADC, ensuring accurate temperature readings. The microcontroller processes the digital signals received from the ADC and can display the temperature on an LCD or LED screen, or transmit the data wirelessly for remote monitoring.
Overall, this digital thermometer circuit is a cost-effective and straightforward solution for temperature measurement, leveraging the well-documented properties of the 1N4148 diode.This digital thermometer circuit diagram uses a common 1N4148 diode as the temperature sensor. The temperature coefficient of the diode, -2 mV / 0C is expl. 🔗 External reference