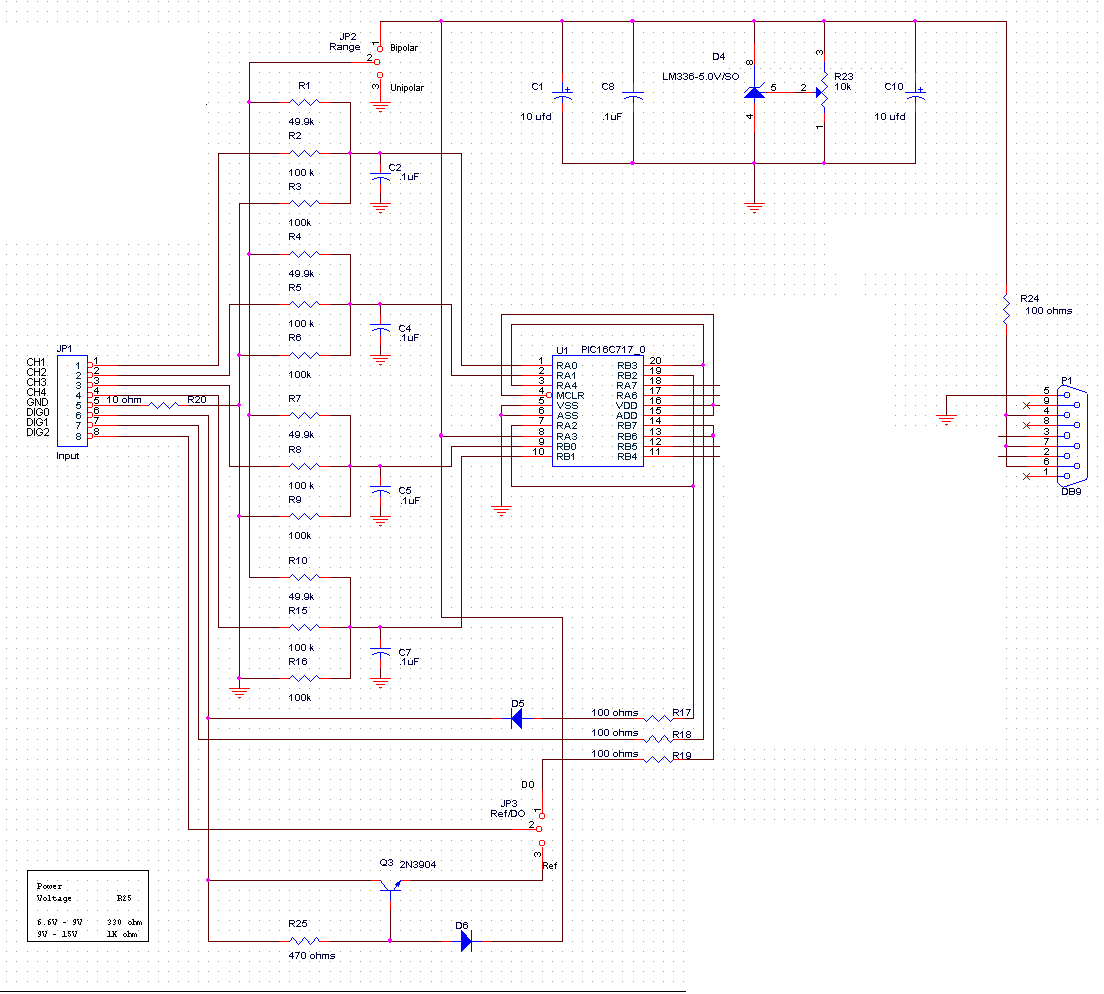
DTMF Decoder Using MT8870
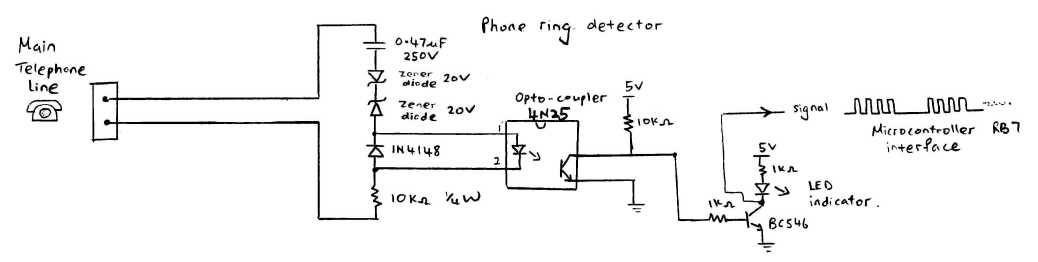
This circuit detects the dial tone from a telephone line and decodes the keypad pressed on the remote telephone. The dial tone heard when picking up the phone is referred to as Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF). This name originates from the fact that the tone consists of two distinct frequency tones. The DTMF tone serves as a form of one-way communication between the dialer and the telephone exchange. Complete communication involves both a tone generator and a tone decoder. The primary component used in this circuit is the MT8870DE IC, which decodes the input dial tone into five digital outputs. These digital bits can interface with a computer or microcontroller for various applications, such as remote control, phone line transfer operations, and LED activation. Historically, telephone systems relied on human operators in exchange rooms to connect calls. As technology advanced, the pulse/dial tone method was developed for telephony communication, utilizing electronics and computers to facilitate line connections. On the caller's side, a dial tone generator produces a unique tone when a key is pressed on the matrix keypad. For instance, pressing the key '1' generates a tone composed of 697 Hz and 1209 Hz sine waves, while pressing '9' produces a tone made up of 852 Hz and 1477 Hz. The frequencies used in the dial tone system fall within the audible range, suitable for transmission over telephone cables. On the telephone exchange side, a decoder circuit translates the tones into digital codes. For example, a tone of 941 Hz and 1336 Hz is decoded to the binary output '1010'. This digital output can be read by a computer, which acts as an operator to connect the caller's telephone line to the intended destination. The telephone exchange center generates a high voltage signal to ring the receiving telephone, notifying the user of an incoming call. This project focuses on a simple DTMF decoder circuit that can interface with a computer, enabling caller-computer interaction. Numerous communication applications can be developed, such as a computerized call receiving/diverting phone network system or remote control of electrical appliances using a telephone network. DTMF is a popular project, particularly in the field of digital signal processing (DSP). DSP software algorithms can be implemented to generate and decode DTMF tones. This hardware approach will be explored in this context.
The DTMF decoder circuit primarily utilizes the MT8870DE integrated circuit, which is designed specifically for decoding DTMF signals. The circuit requires a power supply, typically in the range of 5V to 12V, depending on the specifications of the MT8870DE and the connected components. The input from the telephone line is connected to the MT8870DE's input pins, which are responsible for detecting the DTMF tones. The output pins of the IC provide a binary representation of the pressed key, which can be interfaced with microcontrollers or computers for further processing.
To implement this circuit, a matrix keypad can be used alongside the MT8870DE to facilitate user input. Each key on the keypad corresponds to a unique DTMF tone combination. The decoder's output can be connected to a microcontroller, which can interpret the digital signals and execute commands based on the received input. For instance, if the '5' key is pressed, the microcontroller can be programmed to turn on a specific device or trigger an action.
In addition to basic decoding functionalities, the circuit can be expanded with additional features such as LED indicators to visually confirm the key presses or to display system status. Furthermore, the integration of a relay module can allow for the control of high-voltage appliances directly through the DTMF commands received via the telephone line.
Overall, the DTMF decoder circuit not only demonstrates the principles of tone detection and decoding but also showcases the potential for various practical applications in telecommunications and automation.This circuit detects the dial tone from a telephone line and decodes the keypad pressed on the remote telephone. The dial tone we heard when we pick up the phone set is call Dual Tone Multi-Frequency, DTMF in short.
The name was given because the tone that we heard over the phone is actually make up of two distinct frequency tone, hence the name d ual tone. The DTMF tone is a form of one way communication between the dialer and the telephone exchange. A complete communication consist of the tone generator and the tone decoder. In this article, we are use the IC MT8870DE, the main component to decode the input dial tone to 5 digital output. These digital bits can be interface to a computer or microcontroller for further application eg. remote control, phone line transfer operation, LEDs, etc. In the early days, our phone system used to be operated by human operator in a telephone exchange room.
The caller will pick up the phone, giving instruction to the operator to connect their line to the destination over the other end of the telephone. As more and more people find phone technology a useful communication tools, line connection use human operator has become a tedious task.
As technology matures, pulse/dial tone method was inverted for telephony communication. It uses electronics and computer to assist in the phone line connection. Basically on the caller side, it is a dial tone generator. When a key is being pressed on the matrix keypad, it generate a unique tone consisting of two audible tone frequency. For example, if the key `1` is being press on the phone, the tone you hear is actually consist of a 697hz & 1209hz sine signal.
Pressing key `9` will generate the tone form by 852hz & 1477hz. The frequency use in the dial tone system is of audible range suitable for transmission over the telephone cable. On the telephone exchange side, it has a decoder circuit to decode the tone to digital code. For example, the tone of 941hz + 1336hz will be decoded as binary `1010` as the output. This digital output will be read in by a computer, which will then act as a operator to connect the caller`s telephone line to the designated phone line.
The telephone exchange center will generate a high voltage signal to the receiving telephone, so as to ring the telephone bell, to notified the receiving user that there is an incoming call. This project article focus on a simple DTMF (dual tone multi-frequency) decoder circuit. This circuit can be interface to a computer, allowing caller to computer interaction. Many communication application can be build for example, a computerize call receiving/diverting phone network system.
Remote control to Home/Office electrical appliances using a telephone network. DTMF is a popular project especially in DSP (digital signal processing) subject. DSP software algorithm can be implement to generate as well as to decode DTMF tone. It is very interesting, and I will try to cover that aspect in near future. For now we do the hardware way. 🔗 External reference
The DTMF decoder circuit primarily utilizes the MT8870DE integrated circuit, which is designed specifically for decoding DTMF signals. The circuit requires a power supply, typically in the range of 5V to 12V, depending on the specifications of the MT8870DE and the connected components. The input from the telephone line is connected to the MT8870DE's input pins, which are responsible for detecting the DTMF tones. The output pins of the IC provide a binary representation of the pressed key, which can be interfaced with microcontrollers or computers for further processing.
To implement this circuit, a matrix keypad can be used alongside the MT8870DE to facilitate user input. Each key on the keypad corresponds to a unique DTMF tone combination. The decoder's output can be connected to a microcontroller, which can interpret the digital signals and execute commands based on the received input. For instance, if the '5' key is pressed, the microcontroller can be programmed to turn on a specific device or trigger an action.
In addition to basic decoding functionalities, the circuit can be expanded with additional features such as LED indicators to visually confirm the key presses or to display system status. Furthermore, the integration of a relay module can allow for the control of high-voltage appliances directly through the DTMF commands received via the telephone line.
Overall, the DTMF decoder circuit not only demonstrates the principles of tone detection and decoding but also showcases the potential for various practical applications in telecommunications and automation.This circuit detects the dial tone from a telephone line and decodes the keypad pressed on the remote telephone. The dial tone we heard when we pick up the phone set is call Dual Tone Multi-Frequency, DTMF in short.
The name was given because the tone that we heard over the phone is actually make up of two distinct frequency tone, hence the name d ual tone. The DTMF tone is a form of one way communication between the dialer and the telephone exchange. A complete communication consist of the tone generator and the tone decoder. In this article, we are use the IC MT8870DE, the main component to decode the input dial tone to 5 digital output. These digital bits can be interface to a computer or microcontroller for further application eg. remote control, phone line transfer operation, LEDs, etc. In the early days, our phone system used to be operated by human operator in a telephone exchange room.
The caller will pick up the phone, giving instruction to the operator to connect their line to the destination over the other end of the telephone. As more and more people find phone technology a useful communication tools, line connection use human operator has become a tedious task.
As technology matures, pulse/dial tone method was inverted for telephony communication. It uses electronics and computer to assist in the phone line connection. Basically on the caller side, it is a dial tone generator. When a key is being pressed on the matrix keypad, it generate a unique tone consisting of two audible tone frequency. For example, if the key `1` is being press on the phone, the tone you hear is actually consist of a 697hz & 1209hz sine signal.
Pressing key `9` will generate the tone form by 852hz & 1477hz. The frequency use in the dial tone system is of audible range suitable for transmission over the telephone cable. On the telephone exchange side, it has a decoder circuit to decode the tone to digital code. For example, the tone of 941hz + 1336hz will be decoded as binary `1010` as the output. This digital output will be read in by a computer, which will then act as a operator to connect the caller`s telephone line to the designated phone line.
The telephone exchange center will generate a high voltage signal to the receiving telephone, so as to ring the telephone bell, to notified the receiving user that there is an incoming call. This project article focus on a simple DTMF (dual tone multi-frequency) decoder circuit. This circuit can be interface to a computer, allowing caller to computer interaction. Many communication application can be build for example, a computerize call receiving/diverting phone network system.
Remote control to Home/Office electrical appliances using a telephone network. DTMF is a popular project especially in DSP (digital signal processing) subject. DSP software algorithm can be implement to generate as well as to decode DTMF tone. It is very interesting, and I will try to cover that aspect in near future. For now we do the hardware way. 🔗 External reference