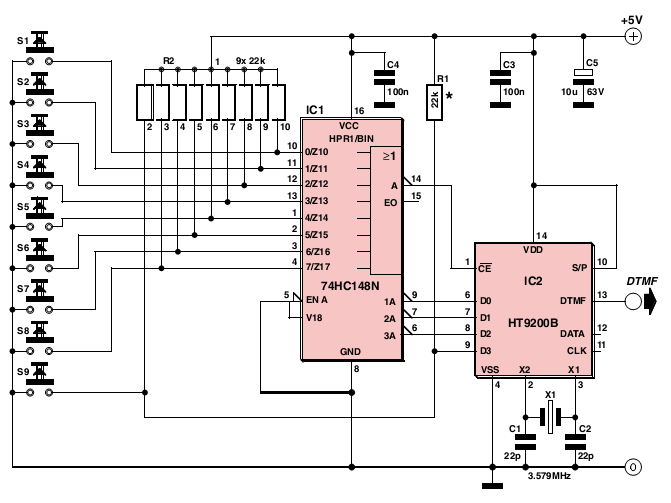
DTMF Multi-channel code decoding infrared remote control circuit
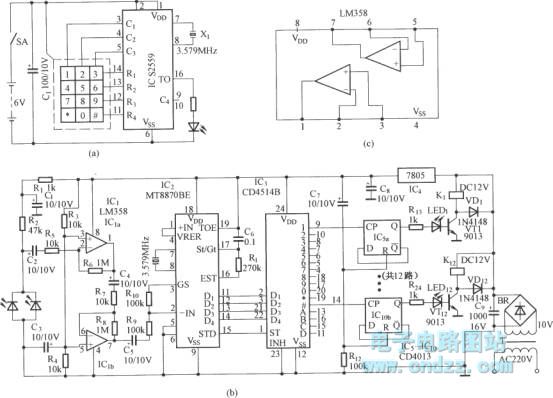
Figure (a) illustrates an infrared emission circuit composed of a 12-key keyboard and an S2559. Figure (b) displays a DTMF decoder circuit along with a channel control circuit utilizing the MT8870. Figure (c) presents a voltage amplifier circuit constructed with two operational amplifiers, specifically the LM358.
The infrared emission circuit in Figure (a) employs a 12-key keyboard to facilitate user input, where each key corresponds to a specific infrared signal generated by the S2559 infrared emitter. The S2559 is a compact, high-performance infrared emitter that operates efficiently within the designated wavelength range, ensuring reliable communication in various applications.
Figure (b) features the DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) decoder circuit, which is primarily based on the MT8870 integrated circuit. This circuit is designed to decode the dual-tone signals produced by the keypad input. The MT8870 processes the audio signals and converts them into digital signals, which can be used for further processing or control within the system. Additionally, the channel control circuit manages the routing of the decoded signals to the appropriate outputs, allowing for effective communication and control in telecommunication applications.
In Figure (c), the voltage amplifier circuit utilizes two LM358 operational amplifiers to amplify the input signal. The LM358 is a dual operational amplifier that provides high gain and bandwidth while maintaining low power consumption. This circuit configuration allows for a significant increase in signal strength, making it suitable for applications that require precise signal amplification. The use of two op-amps enables differential amplification, which can help reduce noise and improve overall signal integrity.
Overall, these three figures represent essential components of a comprehensive electronic system, integrating user input, signal decoding, and amplification to achieve effective communication and control.Figure (a) is the infrared emission circuit that composed of 12 the keyboard and S2559. Figure (b)shows DTMF decoder circuit and channel control circuit composedof the MT8870. Figure (c) is the voltage amplifier circuit composed of two-op ampLM358.. 🔗 External reference
The infrared emission circuit in Figure (a) employs a 12-key keyboard to facilitate user input, where each key corresponds to a specific infrared signal generated by the S2559 infrared emitter. The S2559 is a compact, high-performance infrared emitter that operates efficiently within the designated wavelength range, ensuring reliable communication in various applications.
Figure (b) features the DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) decoder circuit, which is primarily based on the MT8870 integrated circuit. This circuit is designed to decode the dual-tone signals produced by the keypad input. The MT8870 processes the audio signals and converts them into digital signals, which can be used for further processing or control within the system. Additionally, the channel control circuit manages the routing of the decoded signals to the appropriate outputs, allowing for effective communication and control in telecommunication applications.
In Figure (c), the voltage amplifier circuit utilizes two LM358 operational amplifiers to amplify the input signal. The LM358 is a dual operational amplifier that provides high gain and bandwidth while maintaining low power consumption. This circuit configuration allows for a significant increase in signal strength, making it suitable for applications that require precise signal amplification. The use of two op-amps enables differential amplification, which can help reduce noise and improve overall signal integrity.
Overall, these three figures represent essential components of a comprehensive electronic system, integrating user input, signal decoding, and amplification to achieve effective communication and control.Figure (a) is the infrared emission circuit that composed of 12 the keyboard and S2559. Figure (b)shows DTMF decoder circuit and channel control circuit composedof the MT8870. Figure (c) is the voltage amplifier circuit composed of two-op ampLM358.. 🔗 External reference