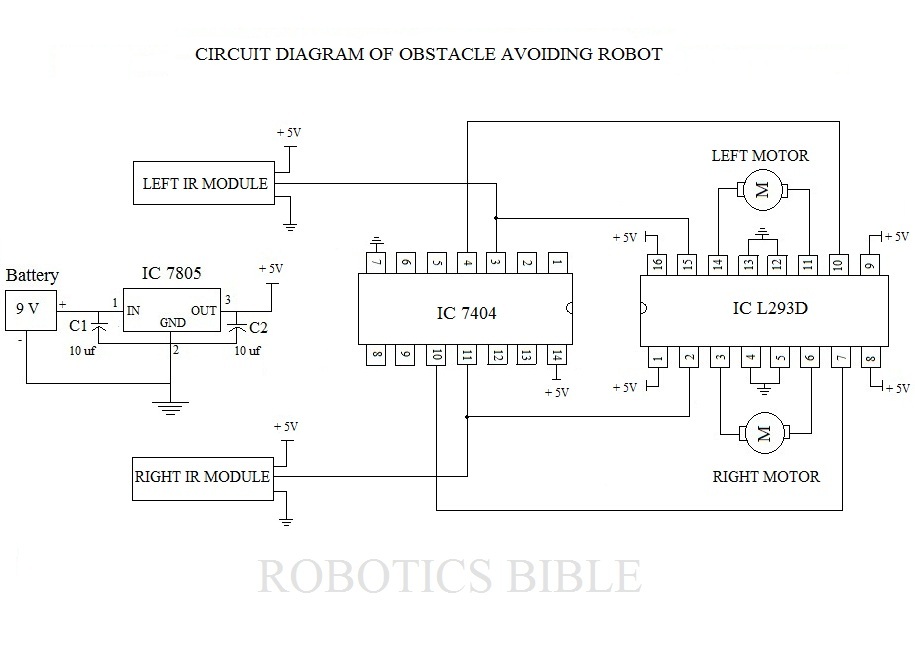
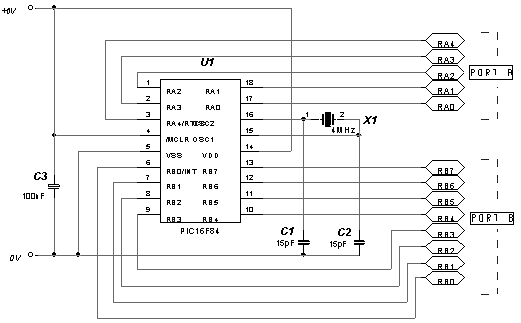
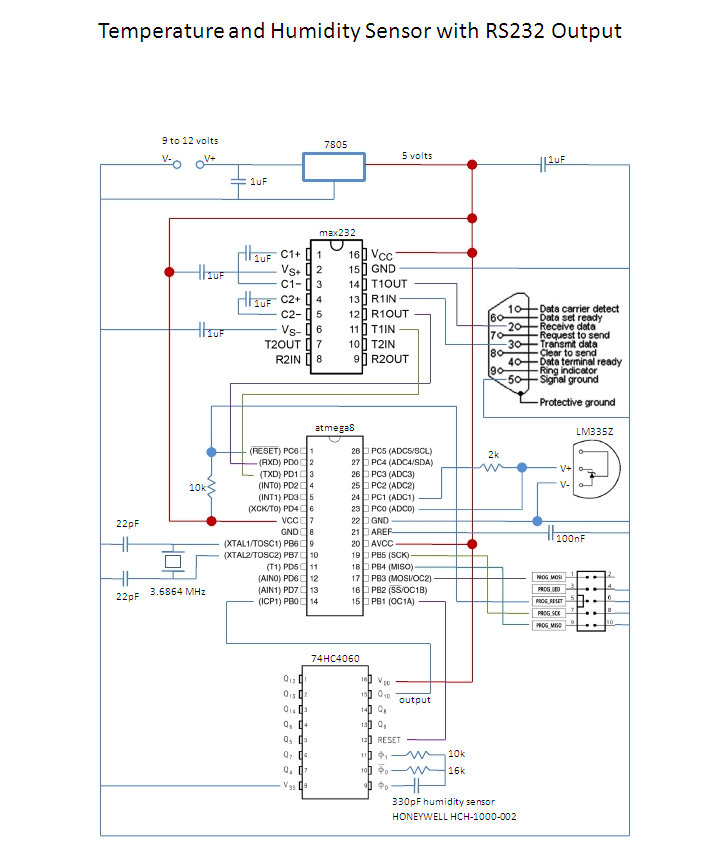
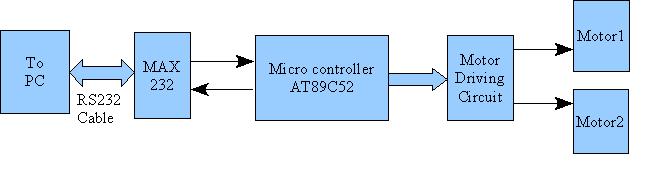
Edge Avoider Robot without microcontroller
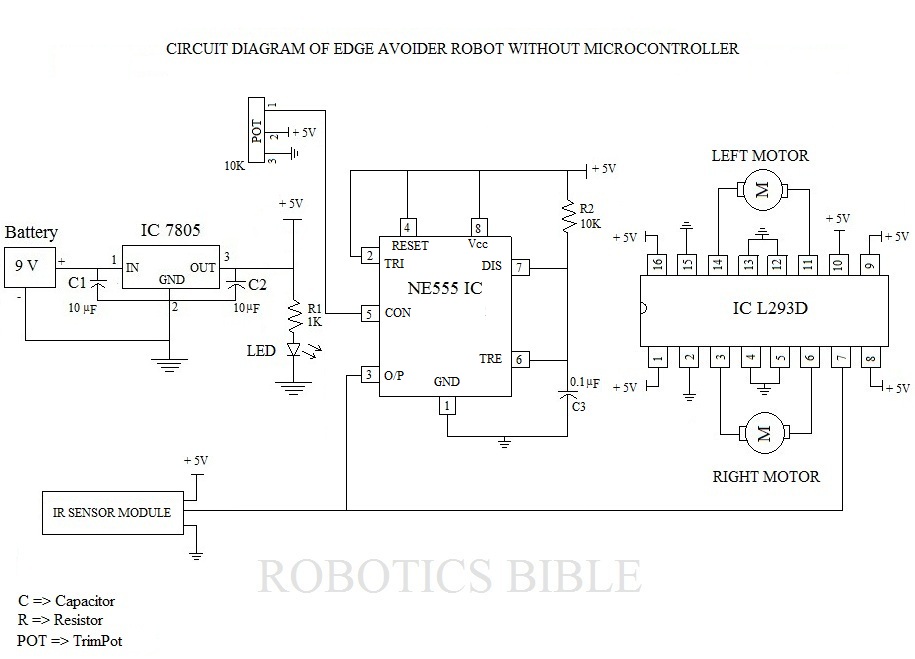
The Edge Avoider Robot (EAR) is a mobile device that detects and avoids areas where there is no surface beneath it.
The Edge Avoider Robot (EAR) operates using a combination of sensors and microcontroller technology to navigate its environment effectively. The primary function of the EAR is to prevent it from falling off edges, such as tables or staircases, by utilizing proximity sensors that detect the presence of a surface. These sensors are typically mounted on the front and sides of the robot, allowing it to sense the distance to nearby edges.
In terms of circuit design, the EAR can be constructed using a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or Raspberry Pi, which processes the sensor inputs and controls the motors that drive the robot. The sensors used may include infrared (IR) or ultrasonic distance sensors, which emit signals and measure the time it takes for the signals to reflect back. This information is crucial for determining the proximity of the edge.
The power supply for the EAR can be achieved through rechargeable batteries, ensuring that the device remains mobile. The motors are usually controlled via a motor driver circuit, which can handle the current requirements of the motors while allowing the microcontroller to send control signals.
The software aspect involves programming the microcontroller to interpret sensor data and make real-time decisions on motor control. The robot can be programmed with various algorithms to enhance its edge-avoiding capabilities, such as simple reactive behaviors or more complex navigation strategies.
Overall, the Edge Avoider Robot is a practical application of basic robotics principles, integrating hardware and software to achieve a specific task of edge detection and avoidance. This project not only serves as an educational tool for understanding robotics but also demonstrates the importance of sensor integration and control systems in mobile devices.Edge Avoider Robot (EAR) is a mobile device, which senses and avoids the absence of surface below it.. 🔗 External reference
The Edge Avoider Robot (EAR) operates using a combination of sensors and microcontroller technology to navigate its environment effectively. The primary function of the EAR is to prevent it from falling off edges, such as tables or staircases, by utilizing proximity sensors that detect the presence of a surface. These sensors are typically mounted on the front and sides of the robot, allowing it to sense the distance to nearby edges.
In terms of circuit design, the EAR can be constructed using a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or Raspberry Pi, which processes the sensor inputs and controls the motors that drive the robot. The sensors used may include infrared (IR) or ultrasonic distance sensors, which emit signals and measure the time it takes for the signals to reflect back. This information is crucial for determining the proximity of the edge.
The power supply for the EAR can be achieved through rechargeable batteries, ensuring that the device remains mobile. The motors are usually controlled via a motor driver circuit, which can handle the current requirements of the motors while allowing the microcontroller to send control signals.
The software aspect involves programming the microcontroller to interpret sensor data and make real-time decisions on motor control. The robot can be programmed with various algorithms to enhance its edge-avoiding capabilities, such as simple reactive behaviors or more complex navigation strategies.
Overall, the Edge Avoider Robot is a practical application of basic robotics principles, integrating hardware and software to achieve a specific task of edge detection and avoidance. This project not only serves as an educational tool for understanding robotics but also demonstrates the importance of sensor integration and control systems in mobile devices.Edge Avoider Robot (EAR) is a mobile device, which senses and avoids the absence of surface below it.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713