
Efficient-supply-splitter
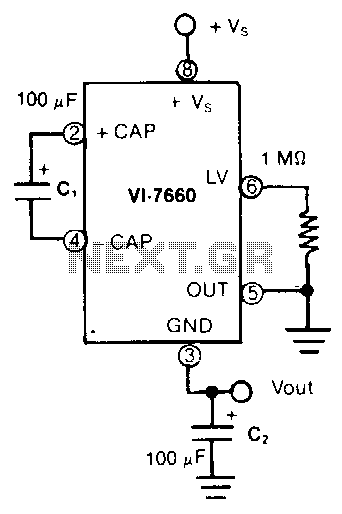
In this application, the VL-7660 is configured as a voltage splitter. The normal output pin is connected to ground, while the normal ground pin serves as the output. The switches facilitating charge pumping are bidirectional, allowing for reverse charge transfer. A 1 MΩ resistor is utilized to prevent start-up issues by ensuring the internal regulator remains active. This circuit can be employed to drive low-voltage, ±7.5 V DC circuits from ±15 V DC supplies or to power low-voltage logic from 9 to 12 V batteries.
The VL-7660 is a versatile charge pump voltage converter that can generate negative voltages or split positive voltages effectively. In the described configuration, the device operates by utilizing its internal switching mechanism to alternate between charging and discharging capacitors, which results in voltage inversion or splitting. The connection of the output pin to ground allows the circuit to create a virtual ground at the output, effectively producing a split supply.
The inclusion of a 1 MΩ resistor is critical for stabilizing the circuit during the initial power-up phase. This resistor ensures that the internal regulator of the VL-7660 is activated promptly, thereby allowing the charge pump to function correctly from the moment power is applied.
This voltage splitter configuration is particularly useful in applications where low-voltage components require a dual supply derived from a higher voltage source. For instance, circuits that operate at ±7.5 V can be powered efficiently from a ±15 V DC supply, which is common in many analog and digital applications. Additionally, the circuit can accommodate low-voltage logic operations using battery supplies ranging from 9 to 12 V, making it suitable for portable electronic devices.
Overall, the VL-7660 in this voltage splitter setup provides an efficient solution for voltage conversion, offering flexibility and reliability in powering various electronic circuits.In this application, the Vl-7660 is connected as a voltage splitter. Note that the normal output pin is connected to ground and the normal ground pin is used as the output. The switches that allow the charge pumping are bidirectional; therefore, charge transfer can be performed in reverse.
The 1-MO resistor is used to avoid start-up problems by forcing the internal regulator on. An application for this circuit would be driving low-voltage, ± 7.5 Vdc, circuits from ± 15 Vdc supplies, or low-voltage logic from 9 to 12 V batteries. 🔗 External reference
The VL-7660 is a versatile charge pump voltage converter that can generate negative voltages or split positive voltages effectively. In the described configuration, the device operates by utilizing its internal switching mechanism to alternate between charging and discharging capacitors, which results in voltage inversion or splitting. The connection of the output pin to ground allows the circuit to create a virtual ground at the output, effectively producing a split supply.
The inclusion of a 1 MΩ resistor is critical for stabilizing the circuit during the initial power-up phase. This resistor ensures that the internal regulator of the VL-7660 is activated promptly, thereby allowing the charge pump to function correctly from the moment power is applied.
This voltage splitter configuration is particularly useful in applications where low-voltage components require a dual supply derived from a higher voltage source. For instance, circuits that operate at ±7.5 V can be powered efficiently from a ±15 V DC supply, which is common in many analog and digital applications. Additionally, the circuit can accommodate low-voltage logic operations using battery supplies ranging from 9 to 12 V, making it suitable for portable electronic devices.
Overall, the VL-7660 in this voltage splitter setup provides an efficient solution for voltage conversion, offering flexibility and reliability in powering various electronic circuits.In this application, the Vl-7660 is connected as a voltage splitter. Note that the normal output pin is connected to ground and the normal ground pin is used as the output. The switches that allow the charge pumping are bidirectional; therefore, charge transfer can be performed in reverse.
The 1-MO resistor is used to avoid start-up problems by forcing the internal regulator on. An application for this circuit would be driving low-voltage, ± 7.5 Vdc, circuits from ± 15 Vdc supplies, or low-voltage logic from 9 to 12 V batteries. 🔗 External reference