electromagnetic flow meter
Electromagnetic flow meter: How to measure fluid flow using a magnetic field.
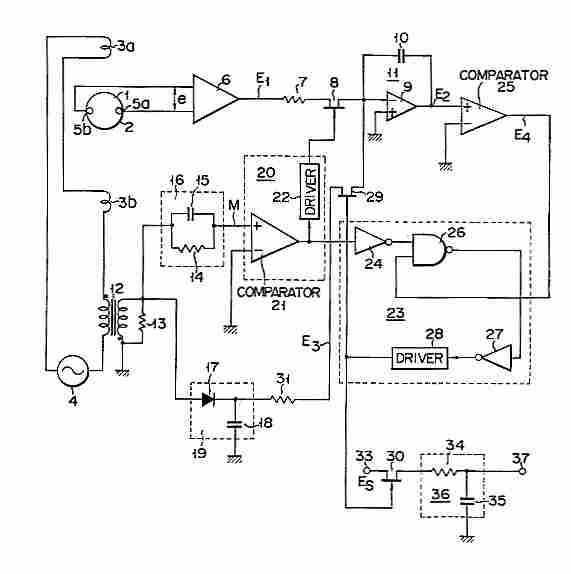
An electromagnetic flow meter is a device used to measure the flow rate of conductive fluids by utilizing Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. This principle states that when a conductor moves through a magnetic field, a voltage is induced across the conductor. In the context of flow measurement, the conductive fluid acts as the conductor, and the flow meter generates a magnetic field to facilitate the measurement.
The primary components of an electromagnetic flow meter include an electromagnetic coil, electrodes, and a flow tube. The flow tube is typically lined with a non-conductive material to prevent interference from the tube material. The electromagnetic coil generates a magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of fluid flow. As the conductive fluid flows through the magnetic field, a voltage is induced across the electrodes, which are positioned on opposite sides of the flow tube.
The induced voltage is directly proportional to the flow velocity of the fluid, and this relationship can be expressed mathematically. The flow meter's electronic circuitry processes the induced voltage signal, converting it into a flow rate measurement. The flow rate can be displayed in various units, such as liters per second or gallons per minute, depending on the application requirements.
Electromagnetic flow meters are particularly advantageous for measuring the flow of fluids with varying viscosities and temperatures, as they do not have moving parts that can wear out or become obstructed. Additionally, they are suitable for applications involving slurries or fluids with suspended solids, making them widely used in industries such as water treatment, food processing, and chemical manufacturing.
In summary, the electromagnetic flow meter operates based on the principles of electromagnetic induction to provide accurate and reliable flow measurements for conductive fluids across various industrial applications.Electromagnetic flow meter : How to measure fluid flow using a magnatic field.. 🔗 External reference
An electromagnetic flow meter is a device used to measure the flow rate of conductive fluids by utilizing Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. This principle states that when a conductor moves through a magnetic field, a voltage is induced across the conductor. In the context of flow measurement, the conductive fluid acts as the conductor, and the flow meter generates a magnetic field to facilitate the measurement.
The primary components of an electromagnetic flow meter include an electromagnetic coil, electrodes, and a flow tube. The flow tube is typically lined with a non-conductive material to prevent interference from the tube material. The electromagnetic coil generates a magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of fluid flow. As the conductive fluid flows through the magnetic field, a voltage is induced across the electrodes, which are positioned on opposite sides of the flow tube.
The induced voltage is directly proportional to the flow velocity of the fluid, and this relationship can be expressed mathematically. The flow meter's electronic circuitry processes the induced voltage signal, converting it into a flow rate measurement. The flow rate can be displayed in various units, such as liters per second or gallons per minute, depending on the application requirements.
Electromagnetic flow meters are particularly advantageous for measuring the flow of fluids with varying viscosities and temperatures, as they do not have moving parts that can wear out or become obstructed. Additionally, they are suitable for applications involving slurries or fluids with suspended solids, making them widely used in industries such as water treatment, food processing, and chemical manufacturing.
In summary, the electromagnetic flow meter operates based on the principles of electromagnetic induction to provide accurate and reliable flow measurements for conductive fluids across various industrial applications.Electromagnetic flow meter : How to measure fluid flow using a magnatic field.. 🔗 External reference