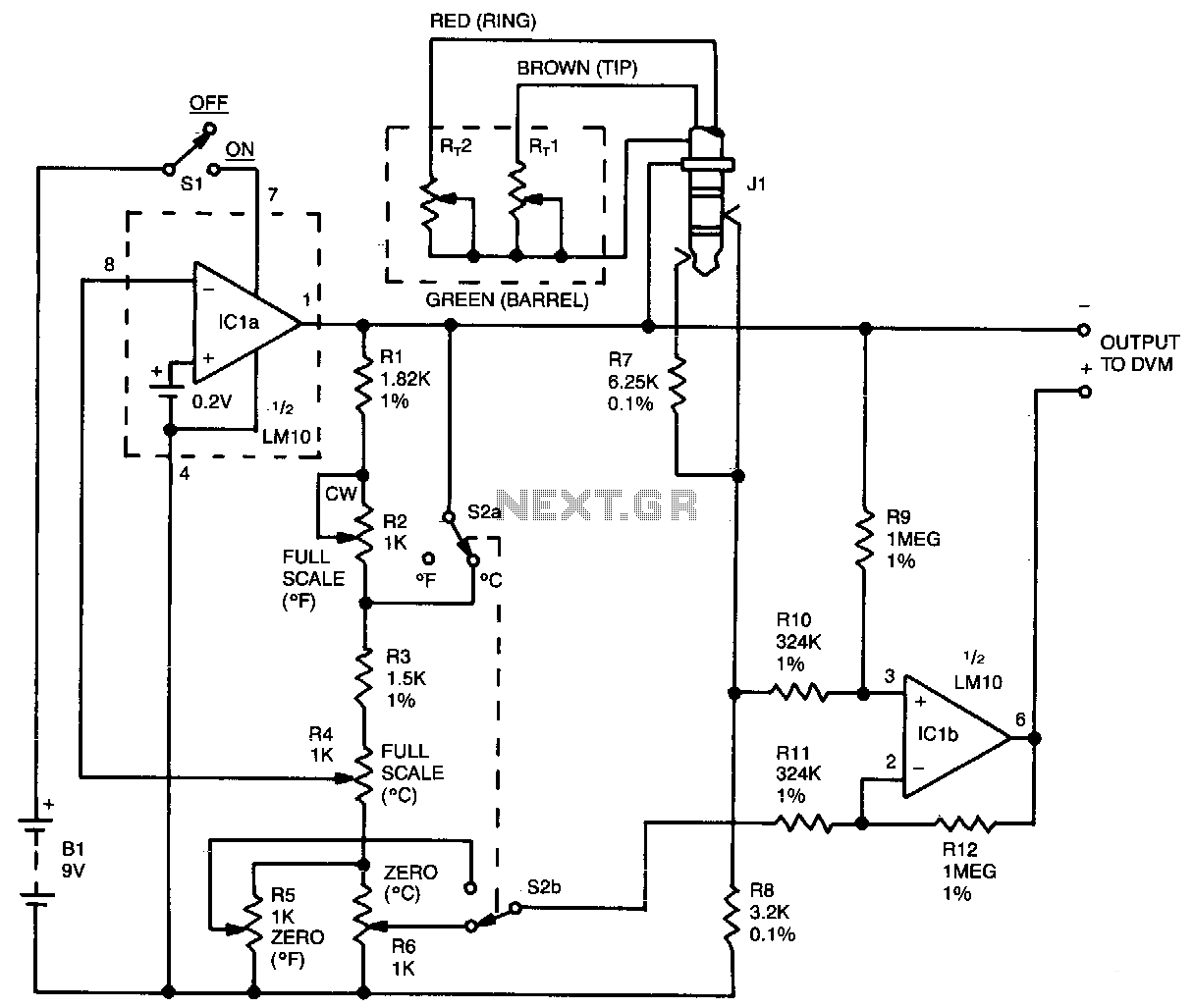
Electronic-thermometer
This circuit utilizes a +5 V reference output and an operational amplifier (op amp) to level shift and amplify the 2.1 mV/°C Tempco output into a voltage signal that varies with ambient temperature. Different scaling options can be achieved by selecting appropriate resistors from a provided table, which gives output slopes calibrated in degrees Celsius or degrees Fahrenheit. To calibrate the circuit, first measure the voltage at the Tempco pin, VTEMPCO, and the ambient room temperature, TA, in °C. The scale factor, S, for the circuit can be selected from the table in millivolts. Next, power down the circuit, short the output voltage (VouT) at pin 6 of the REF-02 to ground, and apply exactly 100.00 mV to the op amp output. Adjust resistor R82 so that V8 equals (X) times 100 mV. After this adjustment, remove the short and the 100 mV source, reapply power to the circuit, and adjust resistor Rp until the op-amp output voltage equals (7A) times S. The system is now precisely calibrated.
This circuit design is centered around the use of an operational amplifier in conjunction with a temperature coefficient (Tempco) sensor, which outputs a voltage signal that is linearly proportional to temperature changes. The op amp serves two critical functions: it amplifies the small voltage output from the Tempco sensor and shifts the level to match the desired output range.
The circuit includes a +5 V reference output, which provides a stable supply voltage necessary for the op amp's operation. The choice of resistors in the feedback and input network allows for flexible scaling of the output voltage, enabling the selection of either Celsius or Fahrenheit as the output unit. The provided table serves as a reference for determining the appropriate resistor values based on the desired output characteristics.
Calibration is a crucial step in ensuring the accuracy of the temperature measurements. The process begins by measuring the voltage at the Tempco pin while simultaneously recording the ambient temperature. This establishes a baseline for the calibration. The adjustment of R82 while applying a known voltage (100.00 mV) allows for the fine-tuning of the op amp's gain, ensuring that the output is correctly scaled to the input temperature signal.
After the initial gain adjustment, the circuit is powered back up, and further calibration is achieved by adjusting Rp. This final adjustment is necessary to align the op amp output with the desired temperature scale, completing the calibration process.
Overall, this circuit provides an effective means of converting temperature variations into a corresponding voltage signal, suitable for various applications in temperature monitoring and control systems.This circuit uses the +5 V reference output and the op amp to level shift and amplify the 2.1 mV/°C Tempco output into a voltage signal dependent on the ambient temperature. Different scaling can be obtained by selecting appropriate resistors from the table giving output slopes calibrated in degrees Celsius or degrees Fahrenheit.
To calibrate, first measure the voltage on the Tempco pin, VTEMPCO. and the ambient room temperature, TA in °C. Where S = Scale factor for your circuit selected from the table in mV. Then turn the circuit power off, short VouT at pin 6 of the REF-02 to ground, and while applying exactly 100.00 mV to the op amp output, adjust R82 to that V8 = (X) (100 mV). Now remove the short and the 100-mV source, reapply circuit power and adjust Rp so that the op-amp output voltage equals (7A) (S).
The system is now exactly calibrated. 🔗 External reference
This circuit design is centered around the use of an operational amplifier in conjunction with a temperature coefficient (Tempco) sensor, which outputs a voltage signal that is linearly proportional to temperature changes. The op amp serves two critical functions: it amplifies the small voltage output from the Tempco sensor and shifts the level to match the desired output range.
The circuit includes a +5 V reference output, which provides a stable supply voltage necessary for the op amp's operation. The choice of resistors in the feedback and input network allows for flexible scaling of the output voltage, enabling the selection of either Celsius or Fahrenheit as the output unit. The provided table serves as a reference for determining the appropriate resistor values based on the desired output characteristics.
Calibration is a crucial step in ensuring the accuracy of the temperature measurements. The process begins by measuring the voltage at the Tempco pin while simultaneously recording the ambient temperature. This establishes a baseline for the calibration. The adjustment of R82 while applying a known voltage (100.00 mV) allows for the fine-tuning of the op amp's gain, ensuring that the output is correctly scaled to the input temperature signal.
After the initial gain adjustment, the circuit is powered back up, and further calibration is achieved by adjusting Rp. This final adjustment is necessary to align the op amp output with the desired temperature scale, completing the calibration process.
Overall, this circuit provides an effective means of converting temperature variations into a corresponding voltage signal, suitable for various applications in temperature monitoring and control systems.This circuit uses the +5 V reference output and the op amp to level shift and amplify the 2.1 mV/°C Tempco output into a voltage signal dependent on the ambient temperature. Different scaling can be obtained by selecting appropriate resistors from the table giving output slopes calibrated in degrees Celsius or degrees Fahrenheit.
To calibrate, first measure the voltage on the Tempco pin, VTEMPCO. and the ambient room temperature, TA in °C. Where S = Scale factor for your circuit selected from the table in mV. Then turn the circuit power off, short VouT at pin 6 of the REF-02 to ground, and while applying exactly 100.00 mV to the op amp output, adjust R82 to that V8 = (X) (100 mV). Now remove the short and the 100-mV source, reapply circuit power and adjust Rp so that the op-amp output voltage equals (7A) (S).
The system is now exactly calibrated. 🔗 External reference