Flashing light indicates the light switch circuit
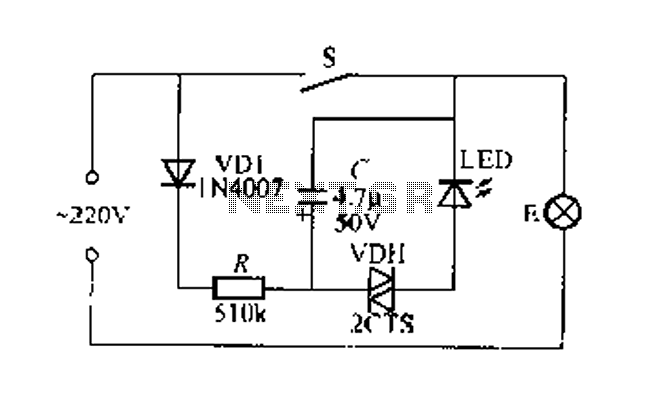
Figure 2 illustrates a circuit for a flashing light switch indicator. When switch S is closed, the normal light E illuminates, while the flashing light indicates a power loss when the system is not operational. When switch S is opened, 220V AC is supplied to lamp E through a rectifier diode VD1. Resistor R limits the charging current to capacitor C. The circuit employs a bidirectional trigger diode VDH, which operates on the principles of charge and discharge, forming a relaxation oscillator. This design causes the luminous tube I (LED) to flash at night, making it easy to locate the switch. If switch S is activated and the LED does not illuminate, it indicates that the filament of bulb E has blown, signaling a power outage. VDH operates within a voltage range of 20-40V and can utilize bidirectional trigger diodes such as 2CTSIA or DB3. The LED used is a high-brightness red light-emitting diode.
The circuit operates on the principle of providing a visual indication of the operational status of a lighting system. The primary component, the switch S, controls the flow of current through the circuit. When S is closed, the circuit is energized, allowing lamp E to light up, indicating normal operation. The inclusion of the rectifier diode VD1 ensures that the AC voltage is converted to a suitable form for charging capacitor C, which stores energy for the oscillation process.
Resistor R plays a crucial role in limiting the current that charges capacitor C, preventing damage to the components and ensuring stable operation. The relaxation oscillator is formed by the interaction between capacitor C and the bidirectional trigger diode VDH. As the capacitor charges and discharges, it creates a pulsing effect that causes the LED (light-emitting diode) to flash. The flashing light serves as an effective indicator, especially in low-light conditions, allowing users to easily identify the switch's location.
In the event of a power outage, if switch S is activated and the LED does not light up, this indicates that the main bulb E has failed, thereby alerting the user to check the bulb. The VDH diode is selected for its ability to trigger at a specific voltage range, making it suitable for this application. The use of a high-brightness red LED ensures maximum visibility, enhancing the overall functionality of the circuit. This design is particularly useful in residential and commercial settings, where reliable indicators of power status are essential for safety and convenience.Figure 2 foot emitting a flashing light switch circuit indication. when s is closed, normal light E lights flashing hair light indicates power loss of power does not work shoes . Open after s. 220V AC by lamp E and a rectifier diode VD1, R buck limit the flow of the charging capacitor c. Negative zoot Sui and capacitance C of the present circuit utilizes two-way trigger diode VDH of charge and discharge principle can constitute a relaxation oscillator, so luminous tube I, ED will flashing light at night is very eye-catching, makes it easy to find switch position. If s beat Ji, LED small light, not the light bulb filament E blown, it is a power outage. VDH may be a turning point in the voltage range of 20-40V bidirectional trigger diodes as 2CTSIA, DB3 type.
I.ED most tincture high-brightness red light emitting diodes.
The circuit operates on the principle of providing a visual indication of the operational status of a lighting system. The primary component, the switch S, controls the flow of current through the circuit. When S is closed, the circuit is energized, allowing lamp E to light up, indicating normal operation. The inclusion of the rectifier diode VD1 ensures that the AC voltage is converted to a suitable form for charging capacitor C, which stores energy for the oscillation process.
Resistor R plays a crucial role in limiting the current that charges capacitor C, preventing damage to the components and ensuring stable operation. The relaxation oscillator is formed by the interaction between capacitor C and the bidirectional trigger diode VDH. As the capacitor charges and discharges, it creates a pulsing effect that causes the LED (light-emitting diode) to flash. The flashing light serves as an effective indicator, especially in low-light conditions, allowing users to easily identify the switch's location.
In the event of a power outage, if switch S is activated and the LED does not light up, this indicates that the main bulb E has failed, thereby alerting the user to check the bulb. The VDH diode is selected for its ability to trigger at a specific voltage range, making it suitable for this application. The use of a high-brightness red LED ensures maximum visibility, enhancing the overall functionality of the circuit. This design is particularly useful in residential and commercial settings, where reliable indicators of power status are essential for safety and convenience.Figure 2 foot emitting a flashing light switch circuit indication. when s is closed, normal light E lights flashing hair light indicates power loss of power does not work shoes . Open after s. 220V AC by lamp E and a rectifier diode VD1, R buck limit the flow of the charging capacitor c. Negative zoot Sui and capacitance C of the present circuit utilizes two-way trigger diode VDH of charge and discharge principle can constitute a relaxation oscillator, so luminous tube I, ED will flashing light at night is very eye-catching, makes it easy to find switch position. If s beat Ji, LED small light, not the light bulb filament E blown, it is a power outage. VDH may be a turning point in the voltage range of 20-40V bidirectional trigger diodes as 2CTSIA, DB3 type.
I.ED most tincture high-brightness red light emitting diodes.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713