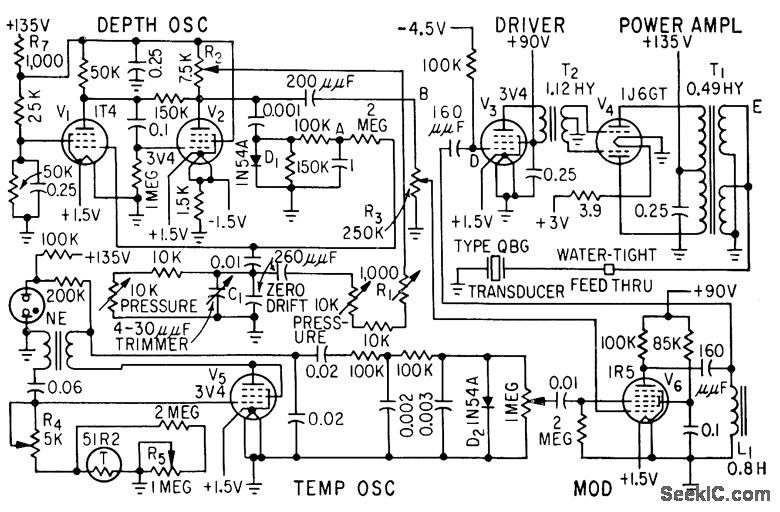
Float Switch Water Level Measurement
A float switch is a device commonly used to measure the depth or level of liquid in a container. When the liquid rises to the level of the float switch, the float rises, transitioning from a vertical to a horizontal position. This action closes an internal switch, which can be utilized to activate or deactivate a pump, alarm, or relay. An example is a submersible water pump equipped with an integrated float switch. To prevent damage from running dry, quality pumps are typically sold with a built-in float switch that automatically shuts off the pump when there is no water. Float switches can be simple devices, such as mercury tilt switches enclosed in watertight, floatable cases. However, due to the toxicity of mercury, a more common alternative is the reed switch, which is activated by a magnet mounted on the float. A typical automotive-grade float switch, which often includes a baffle to minimize rapid switching caused by surface turbulence, can handle a switching current of up to 1.5 Amps, sufficient for triggering a relay or alarm. Float switches generally have switching currents ranging from 0.5 to 2 Amps. They can be configured to detect either rising or falling water levels, making them useful for various applications, including renewable energy systems. For instance, in rainwater toilet flushing, a pump can be automatically activated when the cistern is not full, ensuring a ready supply of water. This technique can also be applied to fill a water tank in an attic for adequate gravity-fed water pressure. In garden irrigation, water can be pumped from a rainwater or greywater storage tank to a smaller tank as needed, preventing overfilling. However, float switches have moving parts and may fail before the pump they protect. An alternative is a liquid sensor, which uses two gold-plated probes that activate an internal reed switch when submerged, minimizing mechanical failure. This type can handle a switching current of 0.5 Amps. Often, the current required by the device to be switched on exceeds the float switch's rating, necessitating a relay to manage the load. A low-power source, such as a PV solar panel with battery backup, can power the sensing circuit, which then connects to a high-power source, like mains electricity, to drive the pump.
Float switches are versatile devices that play a crucial role in various liquid management systems. They are employed in applications ranging from household water systems to industrial processes, ensuring that liquid levels are monitored and controlled effectively. The design typically involves a float mechanism that moves with the liquid level, either rising or falling, to trigger the switch. The internal switch mechanism can vary; while traditional mercury switches are effective, they pose environmental hazards. Reed switches, activated by magnetic floats, are more commonly used due to their safety and reliability.
In practical applications, the float switch is integrated into a circuit that includes a relay. The relay serves as a bridge between the low-power float switch circuit and the higher power load, such as a water pump. When the float switch is activated, it energizes the relay coil, which then closes the relay contacts to allow current to flow to the pump. This configuration is particularly beneficial in renewable energy setups, where a solar panel can provide the necessary power for the float switch circuit, ensuring that the pump operates only when needed.
The reliability of float switches is paramount, especially in critical applications like water supply systems. To enhance longevity, some designs incorporate protective features such as baffles that reduce fluctuations caused by turbulence, which can lead to premature switching. Additionally, the use of liquid sensors with minimal moving parts presents an alternative that can mitigate the risk of mechanical failure.
Overall, the float switch is an essential component in liquid level monitoring systems, providing automated control and enhancing the efficiency of water management processes across various sectors.A Float Switch is a device which is typically used to measure the depth/level of liquid in a container. As the water rises and reaches the level of the float switch, it begins to float going from the vertical to the horizontal.
This closes an internal switch which can then be used to turn on/off a pump, alarm, relay. Pictured above is a submersi ble water pump with an integrated float switch (the red part). If a pump is run dry, it will quickly burn out - therefore, all good quality pumps are sold with a built-in float switch to automatically switch off pumping when there is no more water to pump. A float switch can be as simple as a mercury tilt switch fitted into watertight floatable case. Since mercury is very toxic, a far more common alternative is to use a reed switch which is triggered by a small float-mounted magnet.
Pictured above is a typical automotive-grade float switch (available from the REUK Shop ). This unit is supplied with a baffle which greatly reduces rapid multiswitching* caused by surface turbulence without the need for complicated electronics. This particular float switch can manage a switching current of up to 1. 5 Amps - plenty to trigger a relay or a light/alarm. Typically float switch switching currents range from 0. 5 to 2 Amps. Click here to search eBay for Float Switch - there is usually a good selection available mostly marketed for use with bilge pumps, but which can be used in many other applications.
Float switches can be set up to sense either rising or falling water levels - rising water to measure when a container is full or water has reached a certain maximum level, falling water to measure when a container is empty or has reached a certain minimum level. Therefore, float switches have many uses - particularly in renewable energy applications One example is rainwater toilet flushing.
If a pump is required to get collected rainwater up to the toilet cistern from the main rainwater store, the pump can be automatically switched on when cistern is not full. This ensures there is always water ready in the cistern to flush the toilet when required. This same technique can be used to safely fill a water tank in the loft so that there is decent (gravity-fed) water pressure for a shower, or the washing machine.
Another example is in garden irrigation. Water from a main rainwater/ greywater storage tank can be pumped up to a smaller tank located near to a greenhouse or vegetable beds as and when it is required without the risk of overfilling. Float switches contain moving parts and are therefore prone to breakage - quite often failing before the pump they are designed to protect.
One alternative is to use a liquid sensor such as the example pictured below. Two gold-plated metal probes can be seen fitted into the body of the liquid sensor. When both are submerged, the change in resistance activates an internal reed switch closing the contact and making the circuit. The only moving part in such a device is the reed switch reducing its chance of mechanical failure. This particulary (typical) example can handle a switching current of 0. 5 Amps. More information about liquid sensors, their use and their limitations, is available in our new article Understanding Liquid Sensors In most cases when using a float switch, the current required by the device to be switched on is in excess of the switching current rating of the switch.
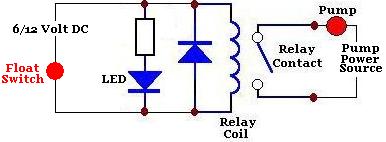
Therefore, a relay * is used such as the 6 Volt example pictured above (and sold in the REUK Shop ). Since a relay is being used, a low power source such as a PV solar panel with battery back up can be used for the water level sensing circuit. This can then be used to connect a high power source such as mains electricity or a battery bank to drive the pump.
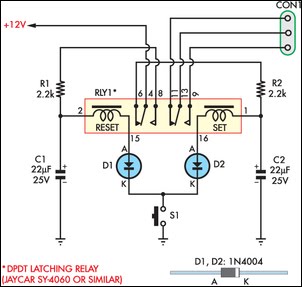
The circuit diagram schematic above shows such a relay-based solution to switching a pump off automatically when the tank to which it is pumping is full. A 6 or 12 Vo 🔗 External reference
Float switches are versatile devices that play a crucial role in various liquid management systems. They are employed in applications ranging from household water systems to industrial processes, ensuring that liquid levels are monitored and controlled effectively. The design typically involves a float mechanism that moves with the liquid level, either rising or falling, to trigger the switch. The internal switch mechanism can vary; while traditional mercury switches are effective, they pose environmental hazards. Reed switches, activated by magnetic floats, are more commonly used due to their safety and reliability.
In practical applications, the float switch is integrated into a circuit that includes a relay. The relay serves as a bridge between the low-power float switch circuit and the higher power load, such as a water pump. When the float switch is activated, it energizes the relay coil, which then closes the relay contacts to allow current to flow to the pump. This configuration is particularly beneficial in renewable energy setups, where a solar panel can provide the necessary power for the float switch circuit, ensuring that the pump operates only when needed.
The reliability of float switches is paramount, especially in critical applications like water supply systems. To enhance longevity, some designs incorporate protective features such as baffles that reduce fluctuations caused by turbulence, which can lead to premature switching. Additionally, the use of liquid sensors with minimal moving parts presents an alternative that can mitigate the risk of mechanical failure.
Overall, the float switch is an essential component in liquid level monitoring systems, providing automated control and enhancing the efficiency of water management processes across various sectors.A Float Switch is a device which is typically used to measure the depth/level of liquid in a container. As the water rises and reaches the level of the float switch, it begins to float going from the vertical to the horizontal.
This closes an internal switch which can then be used to turn on/off a pump, alarm, relay. Pictured above is a submersi ble water pump with an integrated float switch (the red part). If a pump is run dry, it will quickly burn out - therefore, all good quality pumps are sold with a built-in float switch to automatically switch off pumping when there is no more water to pump. A float switch can be as simple as a mercury tilt switch fitted into watertight floatable case. Since mercury is very toxic, a far more common alternative is to use a reed switch which is triggered by a small float-mounted magnet.
Pictured above is a typical automotive-grade float switch (available from the REUK Shop ). This unit is supplied with a baffle which greatly reduces rapid multiswitching* caused by surface turbulence without the need for complicated electronics. This particular float switch can manage a switching current of up to 1. 5 Amps - plenty to trigger a relay or a light/alarm. Typically float switch switching currents range from 0. 5 to 2 Amps. Click here to search eBay for Float Switch - there is usually a good selection available mostly marketed for use with bilge pumps, but which can be used in many other applications.
Float switches can be set up to sense either rising or falling water levels - rising water to measure when a container is full or water has reached a certain maximum level, falling water to measure when a container is empty or has reached a certain minimum level. Therefore, float switches have many uses - particularly in renewable energy applications One example is rainwater toilet flushing.
If a pump is required to get collected rainwater up to the toilet cistern from the main rainwater store, the pump can be automatically switched on when cistern is not full. This ensures there is always water ready in the cistern to flush the toilet when required. This same technique can be used to safely fill a water tank in the loft so that there is decent (gravity-fed) water pressure for a shower, or the washing machine.
Another example is in garden irrigation. Water from a main rainwater/ greywater storage tank can be pumped up to a smaller tank located near to a greenhouse or vegetable beds as and when it is required without the risk of overfilling. Float switches contain moving parts and are therefore prone to breakage - quite often failing before the pump they are designed to protect.
One alternative is to use a liquid sensor such as the example pictured below. Two gold-plated metal probes can be seen fitted into the body of the liquid sensor. When both are submerged, the change in resistance activates an internal reed switch closing the contact and making the circuit. The only moving part in such a device is the reed switch reducing its chance of mechanical failure. This particulary (typical) example can handle a switching current of 0. 5 Amps. More information about liquid sensors, their use and their limitations, is available in our new article Understanding Liquid Sensors In most cases when using a float switch, the current required by the device to be switched on is in excess of the switching current rating of the switch.
Therefore, a relay * is used such as the 6 Volt example pictured above (and sold in the REUK Shop ). Since a relay is being used, a low power source such as a PV solar panel with battery back up can be used for the water level sensing circuit. This can then be used to connect a high power source such as mains electricity or a battery bank to drive the pump.
The circuit diagram schematic above shows such a relay-based solution to switching a pump off automatically when the tank to which it is pumping is full. A 6 or 12 Vo 🔗 External reference