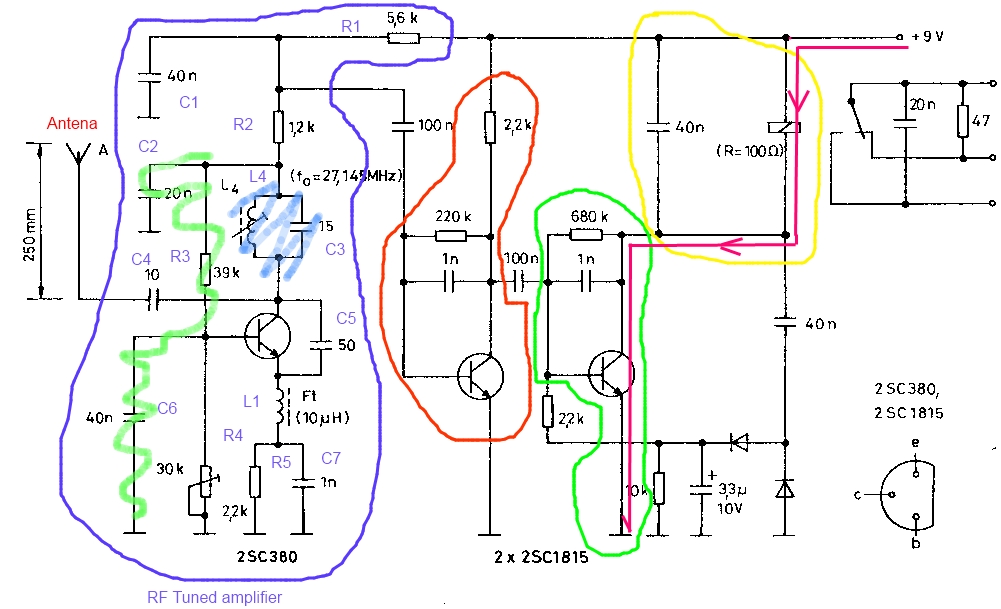
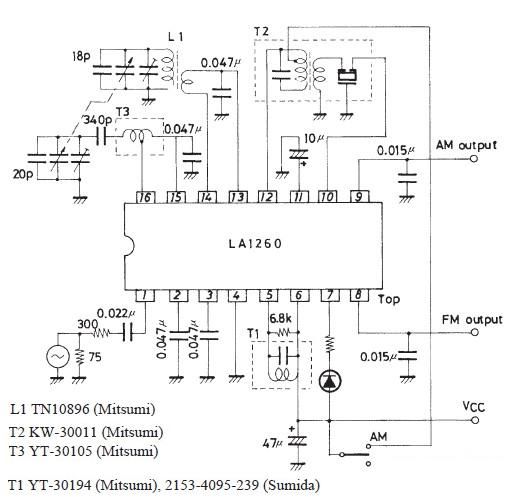
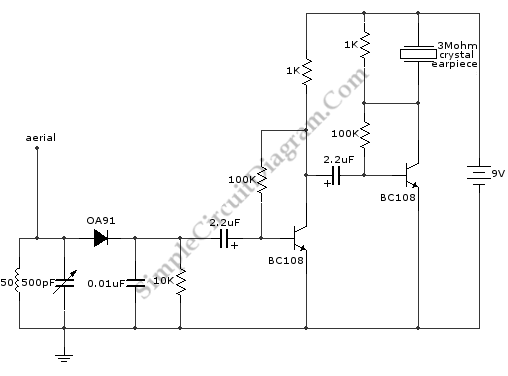
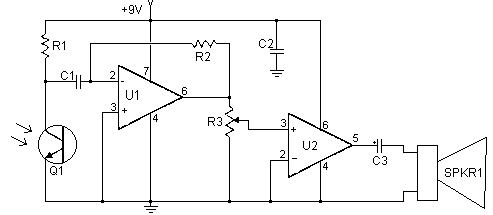
FM Data Receiver Module for Micro-controllers
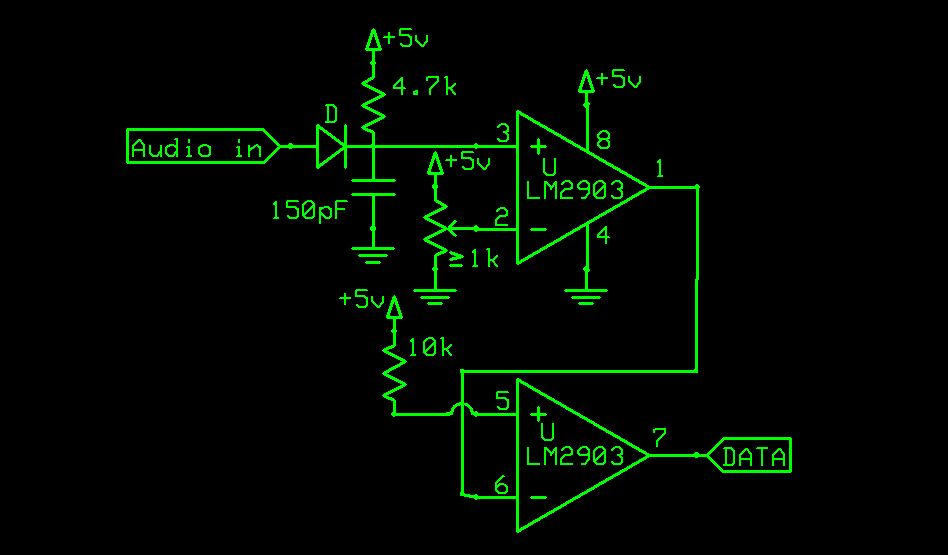
There is a vast array of TX and RX modules available for microcontrollers. The least expensive option identified was priced at $9.99, which is reasonable, although there are memories of encountering FM receiver modules in the past.
The TX (transmitter) and RX (receiver) modules play a crucial role in wireless communication systems, particularly in microcontroller applications. These modules enable the transmission and reception of data over radio frequencies, allowing for remote control and data acquisition in various projects.
Typically, TX and RX modules operate on different frequency bands, such as 433 MHz, 868 MHz, or 915 MHz, depending on regional regulations and application requirements. The choice of frequency affects the range, power consumption, and data rate of the communication link.
A common configuration involves pairing a TX module with an RX module, where the TX module encodes and transmits data packets, while the RX module decodes and processes these packets. The modules often utilize protocols such as ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying) or FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) for modulation, which helps to ensure reliable data transmission.
When designing a circuit that incorporates these modules, it is essential to consider the power supply requirements, antenna design, and the necessary interfacing with the microcontroller. Proper grounding and shielding techniques should also be implemented to minimize interference and enhance signal integrity.
In addition, it is important to account for the range and environmental factors that could impact the performance of the modules. Testing the communication link under various conditions can help to optimize the system for specific applications, whether it be for remote sensors, home automation, or robotics.
Overall, the selection of TX and RX modules should align with the project's specific needs, including budget constraints, operational range, and data throughput requirements.There are an incredibly large number of TX and RX Modules for micro-controllers. The cheapest I found was $9.99, not bad but I remember seeing FM rece.. 🔗 External reference
The TX (transmitter) and RX (receiver) modules play a crucial role in wireless communication systems, particularly in microcontroller applications. These modules enable the transmission and reception of data over radio frequencies, allowing for remote control and data acquisition in various projects.
Typically, TX and RX modules operate on different frequency bands, such as 433 MHz, 868 MHz, or 915 MHz, depending on regional regulations and application requirements. The choice of frequency affects the range, power consumption, and data rate of the communication link.
A common configuration involves pairing a TX module with an RX module, where the TX module encodes and transmits data packets, while the RX module decodes and processes these packets. The modules often utilize protocols such as ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying) or FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) for modulation, which helps to ensure reliable data transmission.
When designing a circuit that incorporates these modules, it is essential to consider the power supply requirements, antenna design, and the necessary interfacing with the microcontroller. Proper grounding and shielding techniques should also be implemented to minimize interference and enhance signal integrity.
In addition, it is important to account for the range and environmental factors that could impact the performance of the modules. Testing the communication link under various conditions can help to optimize the system for specific applications, whether it be for remote sensors, home automation, or robotics.
Overall, the selection of TX and RX modules should align with the project's specific needs, including budget constraints, operational range, and data throughput requirements.There are an incredibly large number of TX and RX Modules for micro-controllers. The cheapest I found was $9.99, not bad but I remember seeing FM rece.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713