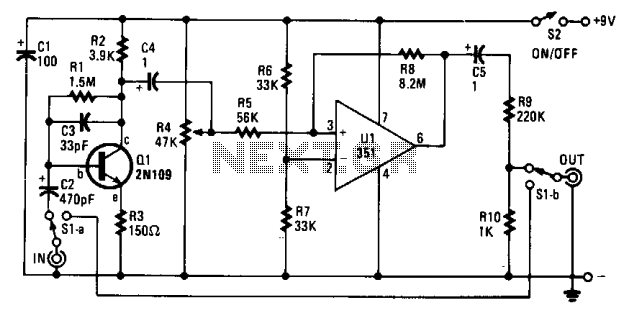
FUZZ_CIRCUIT
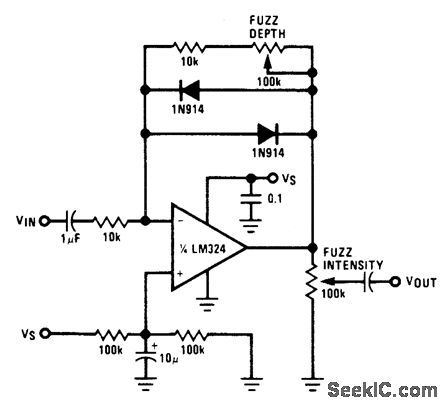
Two diodes in the feedback path of an LM324 operational amplifier create a musical instrument effect known as fuzz by limiting the output voltage swing to ±0.7 V. The resultant square wave primarily contains odd harmonics, resembling the sounds of a clarinet. A fuzz depth potentiometer controls the level at which clipping begins, while a fuzz intensity potentiometer regulates the output level.
The circuit utilizes an LM324 operational amplifier, which is a quad op-amp offering multiple amplification stages. The two diodes are placed in the feedback loop to introduce non-linear characteristics to the output signal. When the input voltage exceeds the forward voltage drop of the diodes (approximately 0.7 V), they conduct and clamp the output, resulting in a clipped waveform. This clipping process generates a square wave signal rich in odd harmonics, which is a desirable trait for achieving the characteristic sound of fuzz in musical applications.
The fuzz depth potentiometer allows the user to adjust the threshold at which the diodes begin to limit the output signal, effectively controlling the saturation level of the audio. By adjusting this potentiometer, the user can achieve a range of fuzz effects, from subtle distortion to aggressive clipping. The fuzz intensity potentiometer adjusts the overall output level of the circuit, enabling the user to match the fuzz effect to the desired volume in the audio chain.
In practical applications, this circuit can be integrated into electric guitars or synthesizers to produce unique tonal qualities. The use of the LM324 op-amp ensures a robust performance with low noise, while the simple diode clipping design keeps the circuit compact and cost-effective. The combination of these elements results in a versatile fuzz effect that can enhance the musical expression of the instrument.Two diodes in feedback path or LM324 opamp create musical-instrument effect known as fuzz by limiting output voltage swing to ±0. 7 V. Resultant square wave contains chiefly odd harmonics, resembling sounds of clarinet. Fuzz depth pot controls level at which clipping begins, and fuzz intensity pot controls output level.
- Audio Handbook, National Semiconductor. Santa Clara. CA. 1977. p 5-11. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes an LM324 operational amplifier, which is a quad op-amp offering multiple amplification stages. The two diodes are placed in the feedback loop to introduce non-linear characteristics to the output signal. When the input voltage exceeds the forward voltage drop of the diodes (approximately 0.7 V), they conduct and clamp the output, resulting in a clipped waveform. This clipping process generates a square wave signal rich in odd harmonics, which is a desirable trait for achieving the characteristic sound of fuzz in musical applications.
The fuzz depth potentiometer allows the user to adjust the threshold at which the diodes begin to limit the output signal, effectively controlling the saturation level of the audio. By adjusting this potentiometer, the user can achieve a range of fuzz effects, from subtle distortion to aggressive clipping. The fuzz intensity potentiometer adjusts the overall output level of the circuit, enabling the user to match the fuzz effect to the desired volume in the audio chain.
In practical applications, this circuit can be integrated into electric guitars or synthesizers to produce unique tonal qualities. The use of the LM324 op-amp ensures a robust performance with low noise, while the simple diode clipping design keeps the circuit compact and cost-effective. The combination of these elements results in a versatile fuzz effect that can enhance the musical expression of the instrument.Two diodes in feedback path or LM324 opamp create musical-instrument effect known as fuzz by limiting output voltage swing to ±0. 7 V. Resultant square wave contains chiefly odd harmonics, resembling sounds of clarinet. Fuzz depth pot controls level at which clipping begins, and fuzz intensity pot controls output level.
- Audio Handbook, National Semiconductor. Santa Clara. CA. 1977. p 5-11. 🔗 External reference