
Hi-ficompressor-with-pre-emphasis
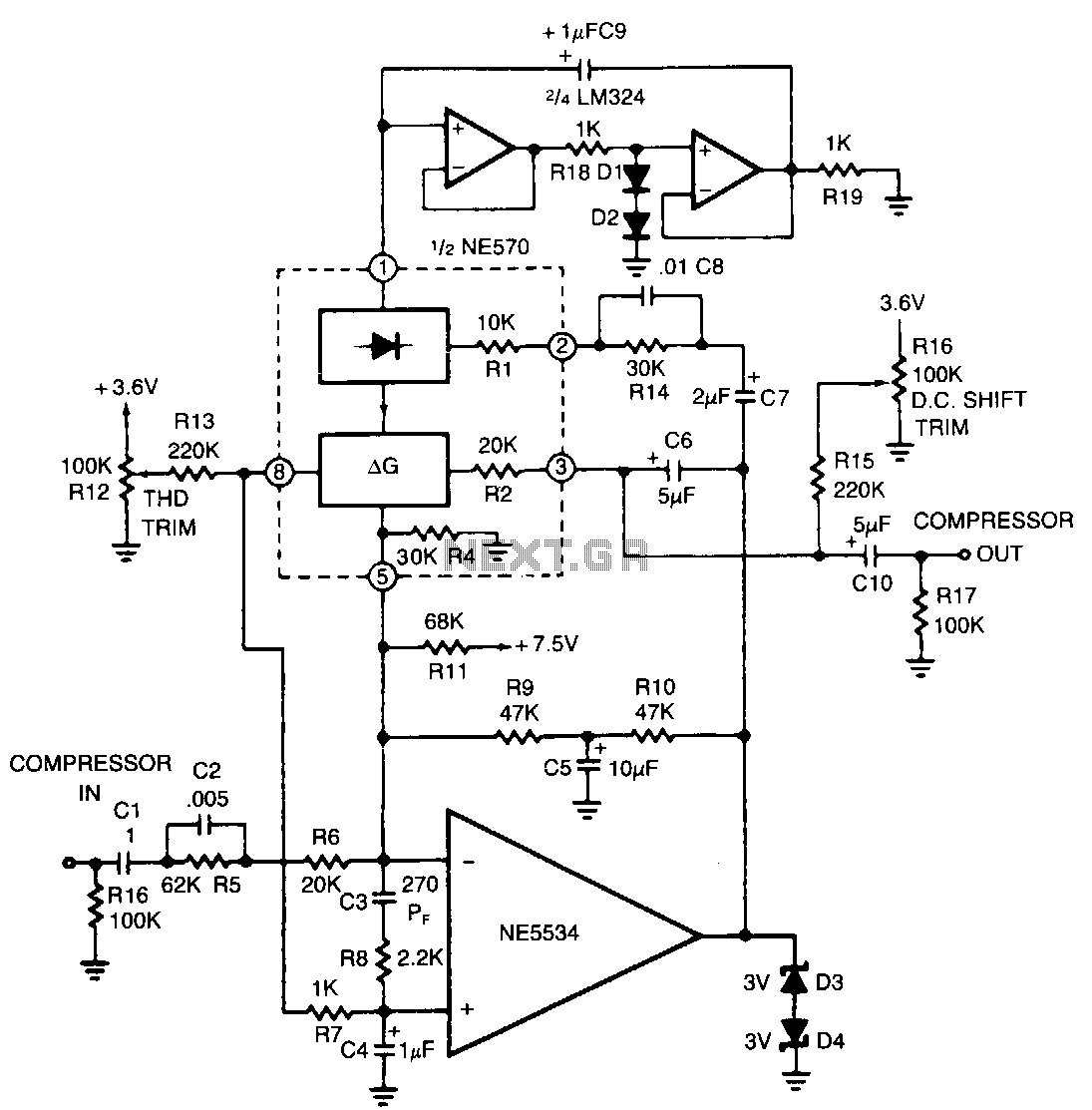
The compressor includes a high-frequency pre-emphasis circuit (C2, R5, CS, R14) that addresses this issue. A corresponding de-emphasis circuit on the expander is necessary. More sophisticated designs may allow for variable pre-emphasis.
The compressor's high-frequency pre-emphasis circuit is crucial for enhancing signal integrity by boosting certain frequency ranges, which compensates for potential losses or distortions in the audio signal during compression. The components involved, specifically capacitor C2 and resistors R5 and R14, work together to shape the frequency response of the circuit.
In practical terms, C2 is typically positioned to block DC while allowing AC signals to pass, effectively coupling the audio signal into the pre-emphasis stage. Resistor R5, in conjunction with C2, forms a high-pass filter that emphasizes higher frequencies, ensuring that these frequencies are preserved during the compression process. The additional resistor, R14, plays a role in setting the time constant of the circuit, which influences how quickly the pre-emphasis effect can respond to changes in the input signal.
For the expander, a matching de-emphasis circuit is essential to restore the original frequency balance of the audio signal after it has been processed by the compressor. This circuit typically mirrors the characteristics of the pre-emphasis circuit to ensure that the frequency response is flattened, preventing any unwanted coloration of the sound.
In more advanced designs, the ability to adjust the pre-emphasis dynamically can be beneficial. This could involve using variable resistors or digital control mechanisms to alter the emphasis based on the input signal's characteristics. Such flexibility allows for more tailored audio processing, accommodating different types of audio material and achieving optimal sound quality across various applications.
Overall, the integration of a high-frequency pre-emphasis circuit within a compressor, along with a corresponding de-emphasis circuit in the expander, forms a critical part of audio signal processing, enabling clearer and more defined sound reproduction.The compressor contains a high-frequency, pre-emphasis circuit (C2, R5, and CS, Rl4), which helps solve this problem. Matching de-emphasis on the expander is required. More complex designs could make the pre-emphasis variable.
The compressor's high-frequency pre-emphasis circuit is crucial for enhancing signal integrity by boosting certain frequency ranges, which compensates for potential losses or distortions in the audio signal during compression. The components involved, specifically capacitor C2 and resistors R5 and R14, work together to shape the frequency response of the circuit.
In practical terms, C2 is typically positioned to block DC while allowing AC signals to pass, effectively coupling the audio signal into the pre-emphasis stage. Resistor R5, in conjunction with C2, forms a high-pass filter that emphasizes higher frequencies, ensuring that these frequencies are preserved during the compression process. The additional resistor, R14, plays a role in setting the time constant of the circuit, which influences how quickly the pre-emphasis effect can respond to changes in the input signal.
For the expander, a matching de-emphasis circuit is essential to restore the original frequency balance of the audio signal after it has been processed by the compressor. This circuit typically mirrors the characteristics of the pre-emphasis circuit to ensure that the frequency response is flattened, preventing any unwanted coloration of the sound.
In more advanced designs, the ability to adjust the pre-emphasis dynamically can be beneficial. This could involve using variable resistors or digital control mechanisms to alter the emphasis based on the input signal's characteristics. Such flexibility allows for more tailored audio processing, accommodating different types of audio material and achieving optimal sound quality across various applications.
Overall, the integration of a high-frequency pre-emphasis circuit within a compressor, along with a corresponding de-emphasis circuit in the expander, forms a critical part of audio signal processing, enabling clearer and more defined sound reproduction.The compressor contains a high-frequency, pre-emphasis circuit (C2, R5, and CS, Rl4), which helps solve this problem. Matching de-emphasis on the expander is required. More complex designs could make the pre-emphasis variable.