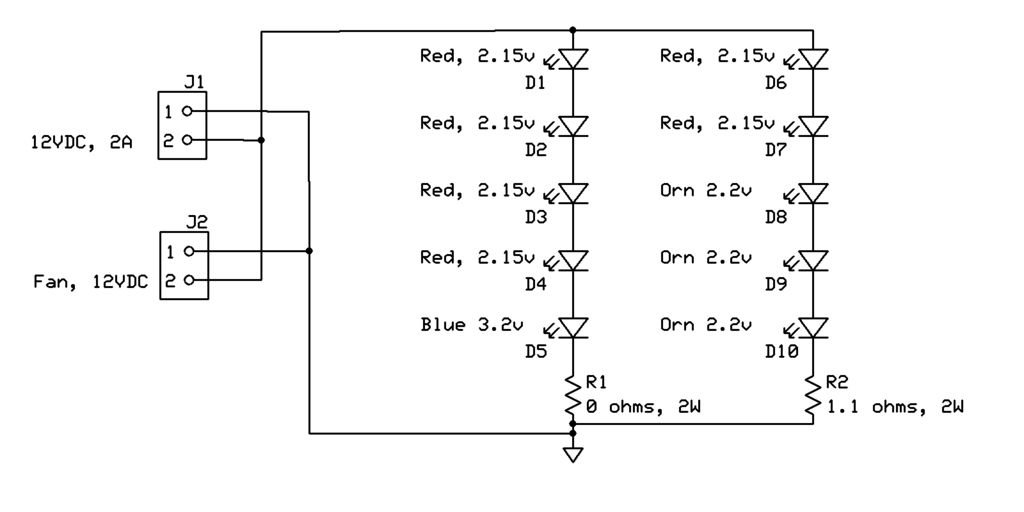
High-Brightness LED-Driver
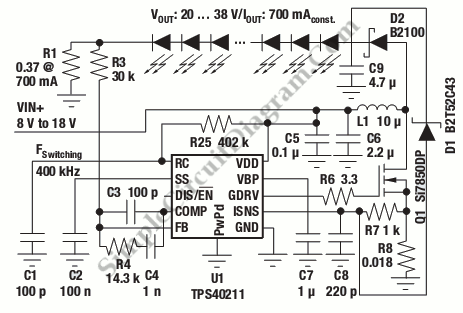
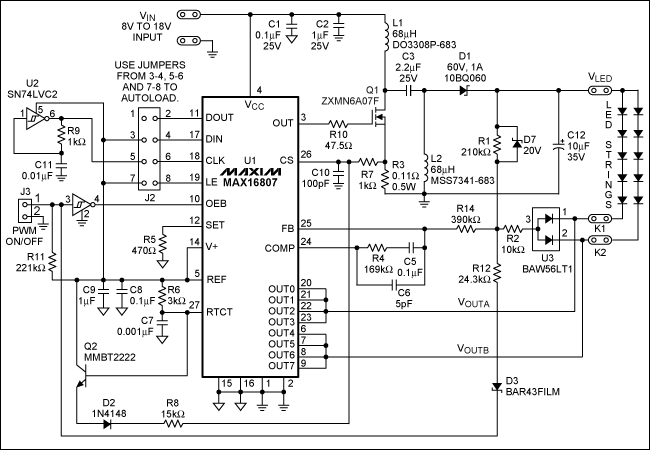
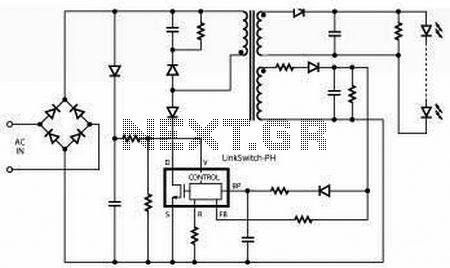
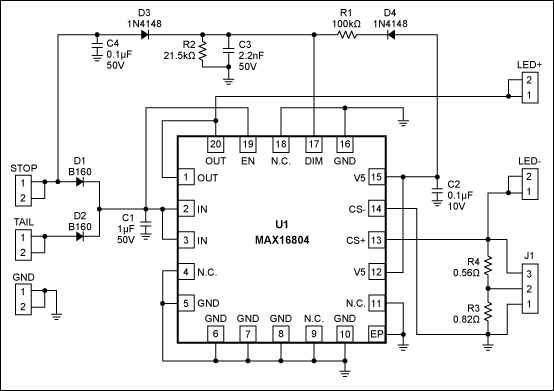
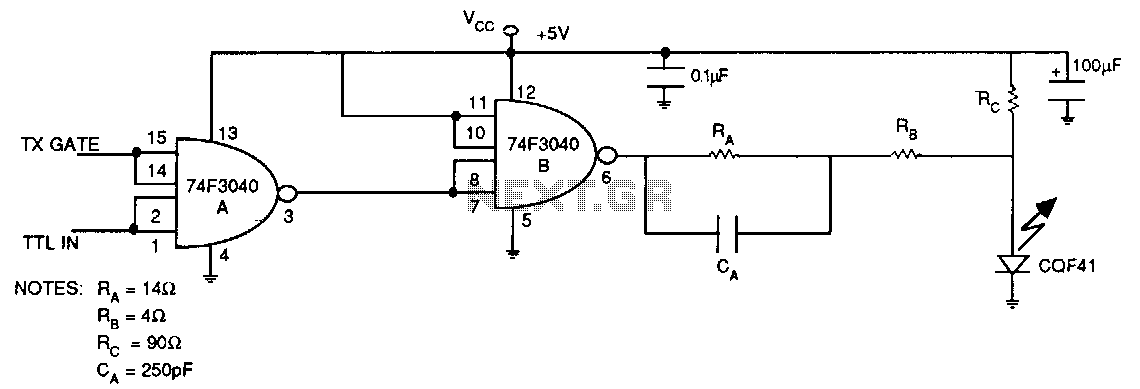
This is a high-brightness LED driver circuit. To provide a constant-voltage output, DC/DC regulators are typically used. However, a constant-current output is the preferred method for driving LEDs.
The high-brightness LED driver circuit is designed to efficiently manage the power supplied to LEDs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The circuit typically employs a constant-current source, which is crucial for LED operation, as variations in current can lead to significant changes in brightness and can even damage the LED.
The architecture of the circuit may include a DC/DC converter configured in either buck (step-down) or boost (step-up) mode, depending on the input and output voltage requirements. The circuit generally consists of a control loop that regulates the output current by adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal driving the switching element (usually a MOSFET). Feedback is obtained from a current-sensing resistor placed in series with the LED load, allowing for precise current regulation.
In addition, the circuit may incorporate protection features such as thermal shutdown, over-voltage protection, and short-circuit protection to enhance reliability. The use of high-frequency switching techniques allows for compact designs and minimizes heat generation, which is essential for high-brightness applications.
Moreover, the LED driver circuit can be designed to accommodate multiple LEDs in series or parallel configurations, depending on the desired output characteristics. The choice of components, such as inductors and capacitors, is critical and should be selected based on the operating frequency and load requirements to ensure stable operation.
Overall, the implementation of a high-brightness LED driver circuit requires careful consideration of electrical parameters, component selection, and thermal management to achieve efficient and reliable LED illumination.This is a high-brightness LED-driver circuit. To provide a constant-voltage output we usually use DC/DC regulators. But constant-current output is the one that.. 🔗 External reference
The high-brightness LED driver circuit is designed to efficiently manage the power supplied to LEDs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The circuit typically employs a constant-current source, which is crucial for LED operation, as variations in current can lead to significant changes in brightness and can even damage the LED.
The architecture of the circuit may include a DC/DC converter configured in either buck (step-down) or boost (step-up) mode, depending on the input and output voltage requirements. The circuit generally consists of a control loop that regulates the output current by adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal driving the switching element (usually a MOSFET). Feedback is obtained from a current-sensing resistor placed in series with the LED load, allowing for precise current regulation.
In addition, the circuit may incorporate protection features such as thermal shutdown, over-voltage protection, and short-circuit protection to enhance reliability. The use of high-frequency switching techniques allows for compact designs and minimizes heat generation, which is essential for high-brightness applications.
Moreover, the LED driver circuit can be designed to accommodate multiple LEDs in series or parallel configurations, depending on the desired output characteristics. The choice of components, such as inductors and capacitors, is critical and should be selected based on the operating frequency and load requirements to ensure stable operation.
Overall, the implementation of a high-brightness LED driver circuit requires careful consideration of electrical parameters, component selection, and thermal management to achieve efficient and reliable LED illumination.This is a high-brightness LED-driver circuit. To provide a constant-voltage output we usually use DC/DC regulators. But constant-current output is the one that.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713