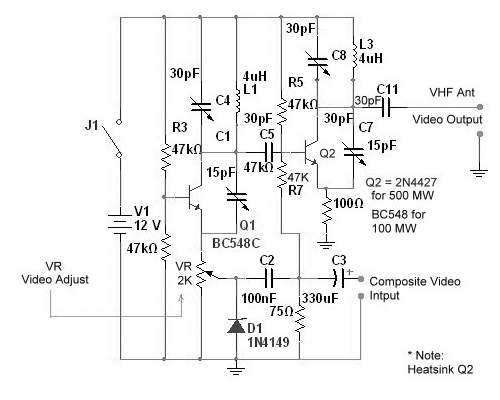
High Power IR Infrared Transmitter
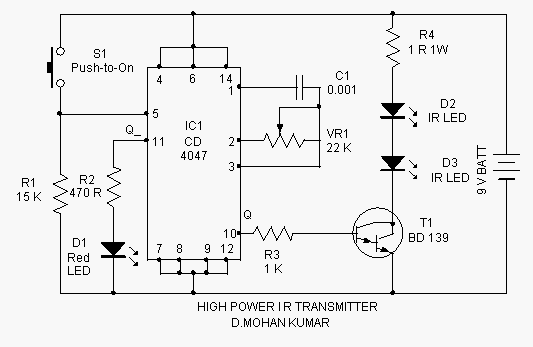
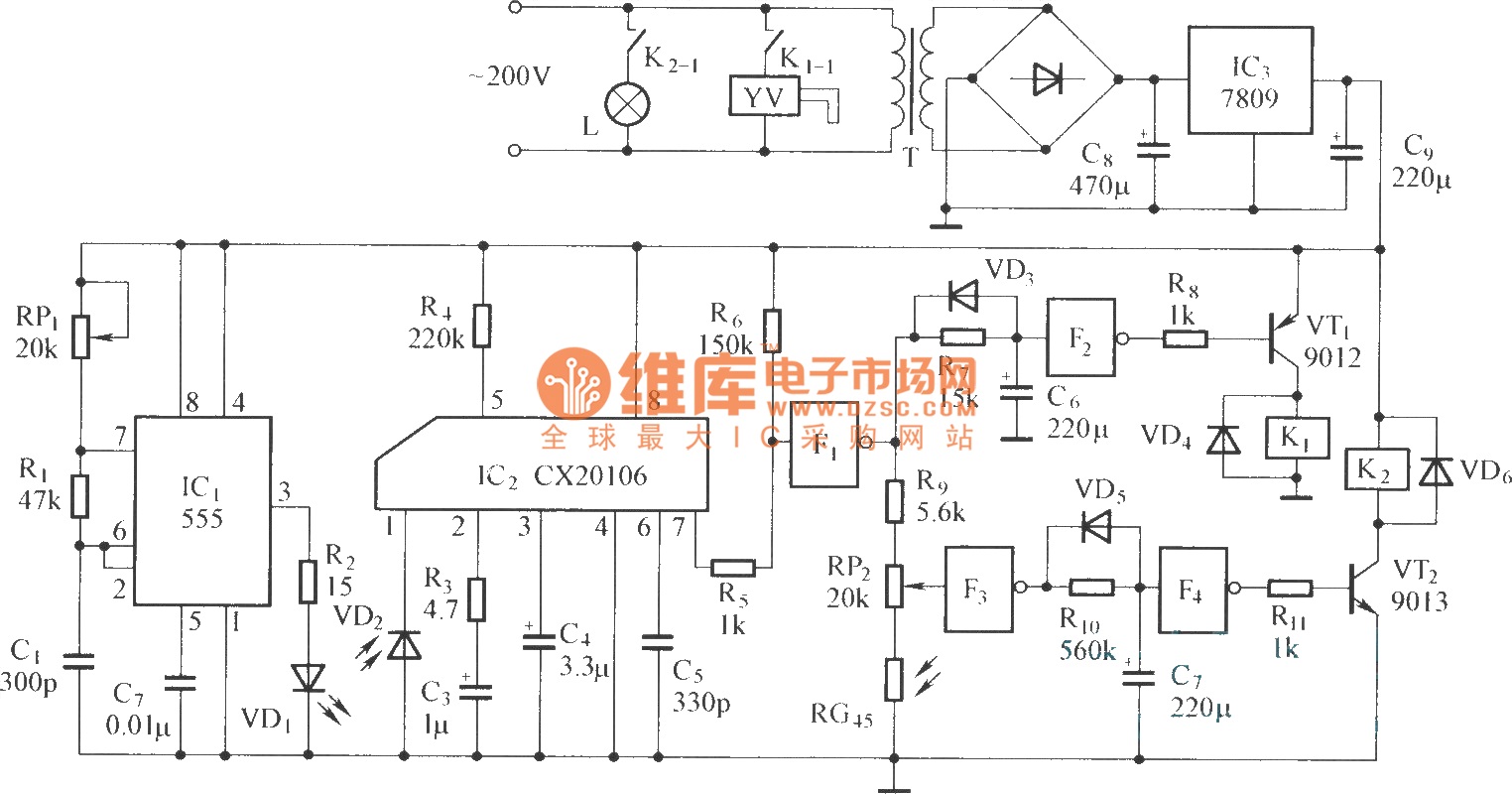
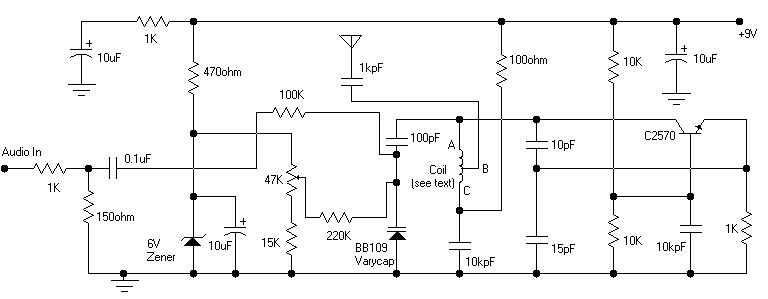
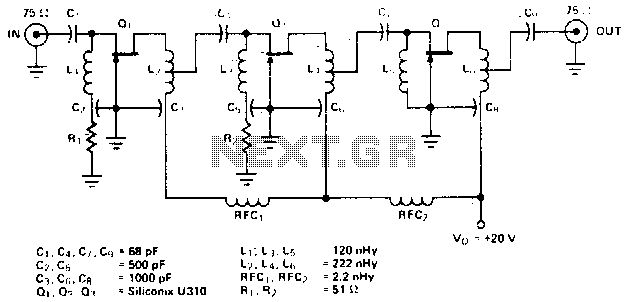
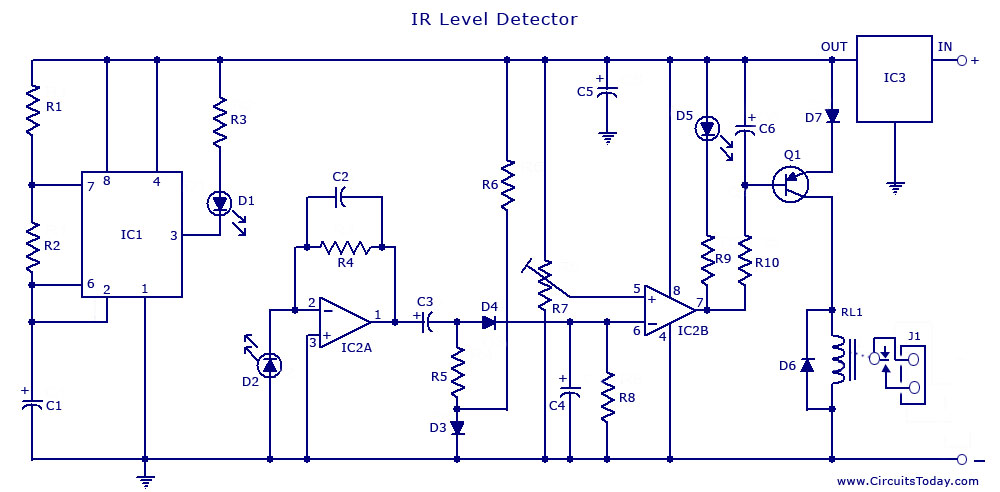
This infrared transmitter is capable of activating IR-based switching circuits from a distance of 10 meters or more. It features a high-power IR transmitter that drives two infrared LEDs.
The infrared transmitter circuit is designed for remote activation of devices using infrared light signals. It typically consists of a microcontroller or a signal generator that modulates the output signal to control the infrared LEDs. The modulation can be achieved through various techniques, such as pulse-width modulation (PWM), which allows for efficient power management and signal integrity over longer distances.
The circuit may include a power supply section that provides the necessary voltage and current to the IR LEDs. The choice of infrared LEDs is crucial, as their wavelength and output power determine the effective range and performance of the transmitter. Commonly used wavelengths for IR communication are around 850 nm to 940 nm, which are well-suited for most IR receivers.
To ensure reliable operation at distances exceeding 10 meters, the circuit should incorporate appropriate lensing or focusing elements that help direct the emitted infrared light toward the intended receiver. Additionally, the use of a suitable housing can protect the components from environmental factors while maintaining the integrity of the emitted signal.
The output stage of the transmitter circuit typically includes a driver circuit capable of supplying the required current to the infrared LEDs. This may involve the use of transistors or MOSFETs to switch the LEDs on and off rapidly, allowing for effective communication with the IR receiver.
Overall, this infrared transmitter is an essential component in various applications, including remote control systems, wireless data transmission, and automation solutions, where non-line-of-sight operation is required.This Infrared transmitter can activate IR based switching circuits from a distance of 10 meters or more. It is a high power IR transmitter driving two IR L.. 🔗 External reference
The infrared transmitter circuit is designed for remote activation of devices using infrared light signals. It typically consists of a microcontroller or a signal generator that modulates the output signal to control the infrared LEDs. The modulation can be achieved through various techniques, such as pulse-width modulation (PWM), which allows for efficient power management and signal integrity over longer distances.
The circuit may include a power supply section that provides the necessary voltage and current to the IR LEDs. The choice of infrared LEDs is crucial, as their wavelength and output power determine the effective range and performance of the transmitter. Commonly used wavelengths for IR communication are around 850 nm to 940 nm, which are well-suited for most IR receivers.
To ensure reliable operation at distances exceeding 10 meters, the circuit should incorporate appropriate lensing or focusing elements that help direct the emitted infrared light toward the intended receiver. Additionally, the use of a suitable housing can protect the components from environmental factors while maintaining the integrity of the emitted signal.
The output stage of the transmitter circuit typically includes a driver circuit capable of supplying the required current to the infrared LEDs. This may involve the use of transistors or MOSFETs to switch the LEDs on and off rapidly, allowing for effective communication with the IR receiver.
Overall, this infrared transmitter is an essential component in various applications, including remote control systems, wireless data transmission, and automation solutions, where non-line-of-sight operation is required.This Infrared transmitter can activate IR based switching circuits from a distance of 10 meters or more. It is a high power IR transmitter driving two IR L.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713