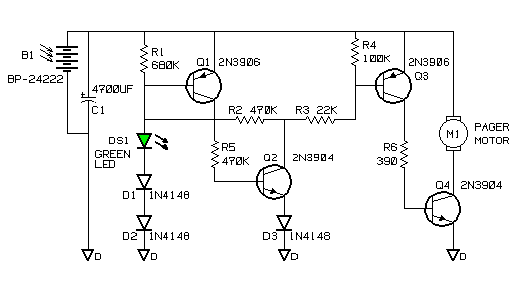
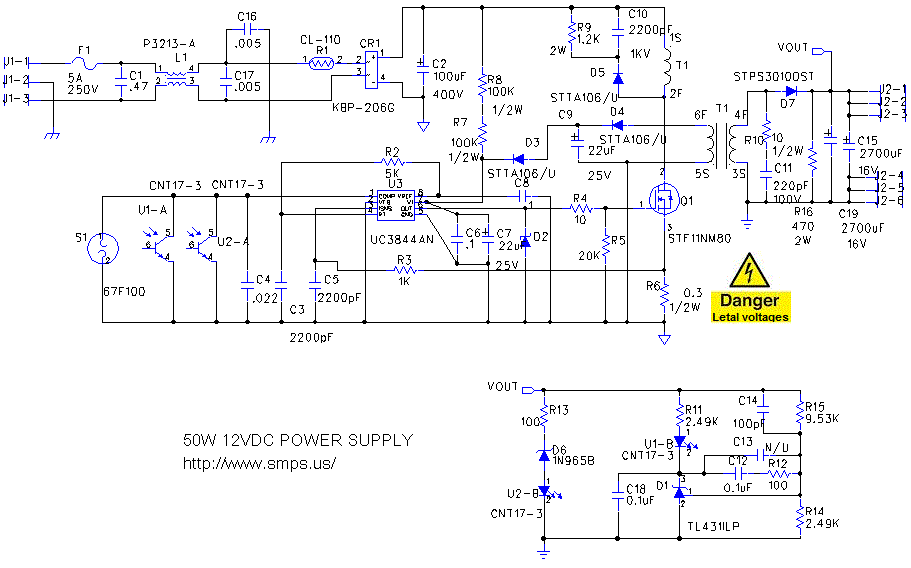
HIGH POWER SIREN
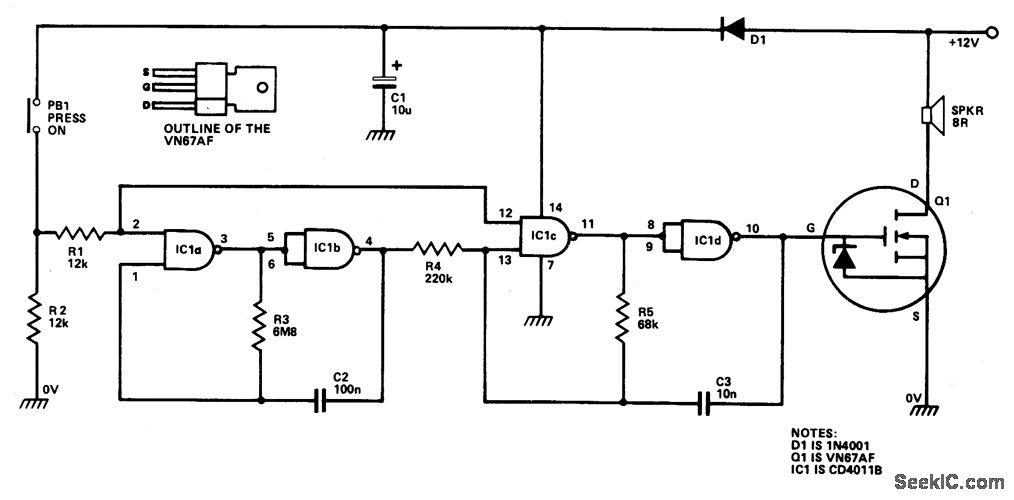
IC1a and IC1b are configured as a slow astable multivibrator, while IC1c and IC1d are set up as a fast astable multivibrator. Both configurations are of the "gated" type, allowing them to be activated or deactivated through push button PB1. The output from the slow astable modulates the frequency of the fast astable, and the output from the fast astable is transmitted to an external speaker through the Q1 VMOS power FET amplifier stage.
The circuit utilizes integrated circuits (ICs) configured in astable multivibrator arrangements to generate square wave signals at different frequencies. The slow astable multivibrator, comprising IC1a and IC1b, produces a lower frequency output. This output serves as a modulation signal for the fast astable multivibrator, which is implemented with IC1c and IC1d. The fast astable configuration generates a higher frequency signal that can be influenced by the modulation from the slow astable.
The gating mechanism, controlled by push button PB1, allows for the entire circuit to be turned on or off as needed. This feature is particularly useful in applications where power conservation is critical or where the circuit needs to be temporarily disabled without disconnecting power.
The output from the fast astable is fed to an external speaker through a VMOS (Vertical Metal Oxide Semiconductor) power FET amplifier stage, designated as Q1. This stage is responsible for amplifying the fast astable's output signal to a level suitable for driving the speaker. The use of a VMOS power FET is advantageous due to its high efficiency and ability to handle significant power levels, ensuring that the audio output is clear and loud enough for the intended application.
Overall, the described circuit provides a flexible and efficient means of generating audio signals with variable frequency modulation, suitable for various electronic applications, including sound synthesis or alert signaling systems.IC1a and IC1b are wired as a slow astable multivibrator and IC1c-IC1d are wired as a fast astable. Both are "gated" types, which can be turned on and off via PB1. The output of the slow astable modulates the frequency of the fast astable, and the output of the fast astable is fed to the external speaker via the Q1 VMOS power FET amplifier stage. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes integrated circuits (ICs) configured in astable multivibrator arrangements to generate square wave signals at different frequencies. The slow astable multivibrator, comprising IC1a and IC1b, produces a lower frequency output. This output serves as a modulation signal for the fast astable multivibrator, which is implemented with IC1c and IC1d. The fast astable configuration generates a higher frequency signal that can be influenced by the modulation from the slow astable.
The gating mechanism, controlled by push button PB1, allows for the entire circuit to be turned on or off as needed. This feature is particularly useful in applications where power conservation is critical or where the circuit needs to be temporarily disabled without disconnecting power.
The output from the fast astable is fed to an external speaker through a VMOS (Vertical Metal Oxide Semiconductor) power FET amplifier stage, designated as Q1. This stage is responsible for amplifying the fast astable's output signal to a level suitable for driving the speaker. The use of a VMOS power FET is advantageous due to its high efficiency and ability to handle significant power levels, ensuring that the audio output is clear and loud enough for the intended application.
Overall, the described circuit provides a flexible and efficient means of generating audio signals with variable frequency modulation, suitable for various electronic applications, including sound synthesis or alert signaling systems.IC1a and IC1b are wired as a slow astable multivibrator and IC1c-IC1d are wired as a fast astable. Both are "gated" types, which can be turned on and off via PB1. The output of the slow astable modulates the frequency of the fast astable, and the output of the fast astable is fed to the external speaker via the Q1 VMOS power FET amplifier stage. 🔗 External reference