how to make simple earthquake sensor
The article presents a circuit concept that features an innovative method for detecting minimal shocks caused by potential earthquake tremors. This circuit is highly sensitive, capable of detecting tremors of magnitude 4 on the Richter scale, while remaining unaffected by loud noises or irrelevant sounds. Various seismic sensor circuits are available online; however, most utilize piezo transducers as the sensing element, which raises questions about the effectiveness of piezo sensors for detecting earthquake tremors. A piezo sensor would only be effective if configured as a load cell, requiring integration with a load to create oscillation during tremors. An alternative approach, such as using an LED/LDR arrangement, was considered for detecting these ripples. However, the focus is on sensing swaying actions rather than vibrations, leading to a different method. Previous discussions have included water level sensor circuits that exploit the conductive properties of water. In this design, the positive supply from the circuit is submerged in water, while the hot end of the input is positioned just a millimeter above the water's surface. When the positive supply makes contact with the hot end through the water, the circuit is triggered and latches immediately.
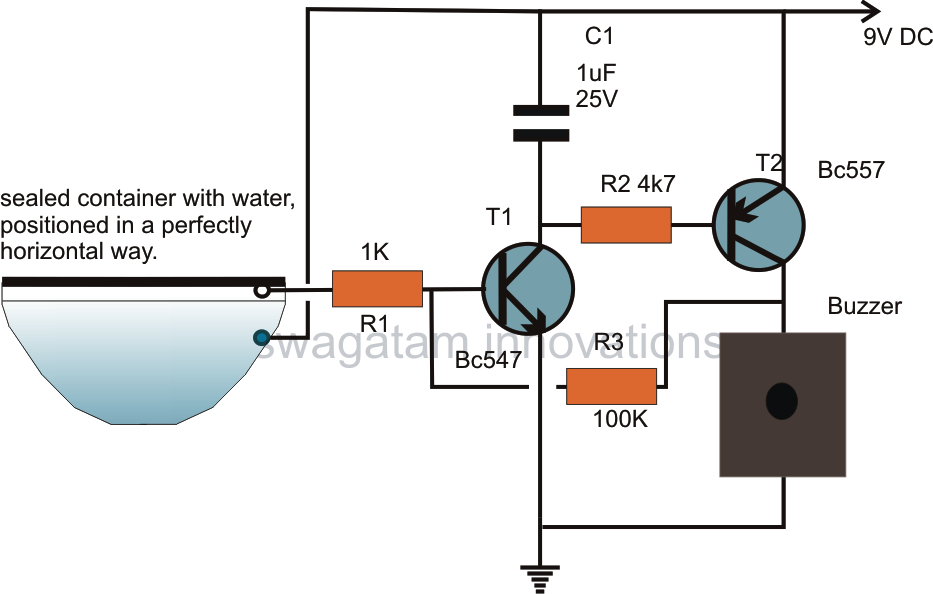
The circuit design utilizes a water-based sensing mechanism to detect swaying motions indicative of seismic activity. The key components include a conductive positive supply immersed in water and a hot end positioned above the water surface. This configuration allows for the detection of changes in water conductivity caused by tremors. When an earthquake occurs, the resulting swaying motion causes the water to create a conductive path between the submerged positive supply and the hot end of the circuit. This triggers the circuit, which can be designed to activate an alarm or indicator to warn of potential seismic activity.
The sensitivity of the circuit can be adjusted by modifying the distance between the hot end and the water surface, as well as by selecting appropriate electronic components such as resistors and capacitors that define the circuit's response time. Additionally, the use of a microcontroller can enhance the functionality of the circuit by allowing for data logging and analysis of seismic events over time. This design is particularly advantageous as it minimizes false triggers from environmental noise, focusing solely on the specific swaying motion associated with earthquake tremors. Overall, this innovative approach provides a reliable and effective means of detecting seismic activity, contributing to safety and preparedness in earthquake-prone regions.The article shows a circuit idea which incorporates an innovative way of detecting the minutest of shocks caused by a possible earthquake tremor. The circuit is so sensitive that it is able to detect tremor of 4 on the Richter scale, yet remains unaffected to loud sounds or irrelevant bangs or noises.
I have seen a number of different circuits of seismic sensors on the net, however most of these have utilized a piezo transducer as the sensor element, God knows how a piezo would detect earthquake tremors. Of course a piezo would detect tremors only if it were used in the form of a load-cell, by integrating some kind of load, assembled for implementing an oscillating action during tremors.
I could have used an LED/LDR arrangement for detecting these ripples, however since we are not interested in sensing vibrations rather only swaying actions, I made a little out of the way approach. Through a few of my previous posts I have already discussed water level sensor circuits where the water`s conducting property is well exploited for the purpose.
The positive supply from the circuit is dipped inside the water while the hot end of the input is placed in such a way that it stands just a mm above the water. The positive of the supply immersed in the water instantly makes contact with the HOT end of the circuit via the water, the circuit gets triggered and immediately latches.
🔗 External reference
The circuit design utilizes a water-based sensing mechanism to detect swaying motions indicative of seismic activity. The key components include a conductive positive supply immersed in water and a hot end positioned above the water surface. This configuration allows for the detection of changes in water conductivity caused by tremors. When an earthquake occurs, the resulting swaying motion causes the water to create a conductive path between the submerged positive supply and the hot end of the circuit. This triggers the circuit, which can be designed to activate an alarm or indicator to warn of potential seismic activity.
The sensitivity of the circuit can be adjusted by modifying the distance between the hot end and the water surface, as well as by selecting appropriate electronic components such as resistors and capacitors that define the circuit's response time. Additionally, the use of a microcontroller can enhance the functionality of the circuit by allowing for data logging and analysis of seismic events over time. This design is particularly advantageous as it minimizes false triggers from environmental noise, focusing solely on the specific swaying motion associated with earthquake tremors. Overall, this innovative approach provides a reliable and effective means of detecting seismic activity, contributing to safety and preparedness in earthquake-prone regions.The article shows a circuit idea which incorporates an innovative way of detecting the minutest of shocks caused by a possible earthquake tremor. The circuit is so sensitive that it is able to detect tremor of 4 on the Richter scale, yet remains unaffected to loud sounds or irrelevant bangs or noises.
I have seen a number of different circuits of seismic sensors on the net, however most of these have utilized a piezo transducer as the sensor element, God knows how a piezo would detect earthquake tremors. Of course a piezo would detect tremors only if it were used in the form of a load-cell, by integrating some kind of load, assembled for implementing an oscillating action during tremors.
I could have used an LED/LDR arrangement for detecting these ripples, however since we are not interested in sensing vibrations rather only swaying actions, I made a little out of the way approach. Through a few of my previous posts I have already discussed water level sensor circuits where the water`s conducting property is well exploited for the purpose.
The positive supply from the circuit is dipped inside the water while the hot end of the input is placed in such a way that it stands just a mm above the water. The positive of the supply immersed in the water instantly makes contact with the HOT end of the circuit via the water, the circuit gets triggered and immediately latches.
🔗 External reference