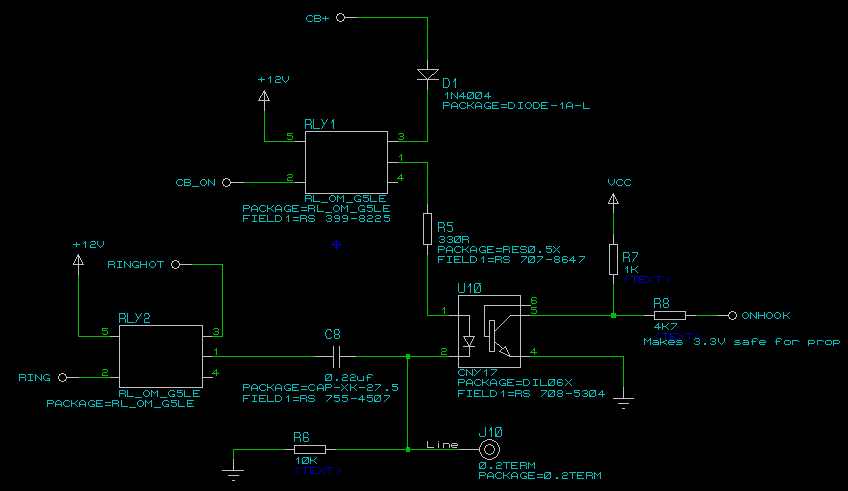
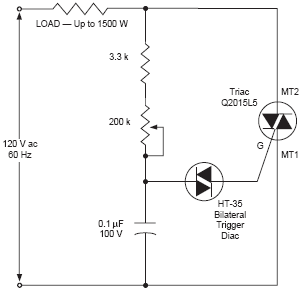
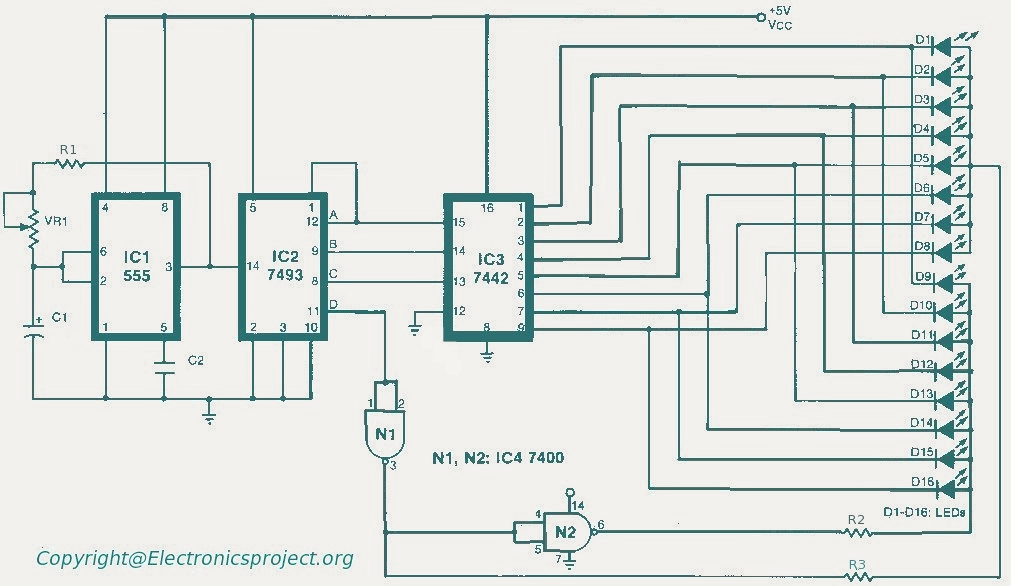
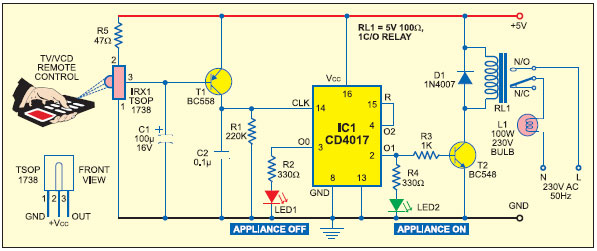
Implementing Adaptive Brightness Control to Seven Segment LED Displays

An automatic brightness adjustment is a closed-loop system that has the capability to assess ambient light and adjust the brightness of the display accordingly.
The automatic brightness adjustment circuit operates by utilizing a light sensor, typically a photoresistor (LDR) or photodiode, to detect the level of ambient light in the environment. The sensor generates a voltage signal proportional to the intensity of the light. This signal is fed into a microcontroller or an operational amplifier configured as a comparator.
The microcontroller processes the input from the light sensor and compares it to predefined threshold levels. Based on this comparison, the microcontroller generates a control signal that adjusts the brightness of the display. This is typically achieved through a pulse-width modulation (PWM) technique, which varies the duty cycle of the voltage supplied to the display backlight, allowing for smooth transitions in brightness levels.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors to form a voltage divider with the light sensor, capacitors for filtering noise, and possibly a transistor or MOSFET to handle the power requirements of the display backlight. The design ensures that the display remains easily readable in varying lighting conditions, enhancing user experience and reducing eye strain.
To further enhance the system, a feedback loop can be implemented where the actual brightness level of the display is monitored and compared to the desired level, allowing for real-time adjustments. This closed-loop feedback mechanism ensures optimal performance and responsiveness to changes in ambient lighting conditions.An automatic brightness adjustment is a closed loop system that has the capability to assess ambient light and adjust the brightness of the display accordingly. In .. 🔗 External reference
The automatic brightness adjustment circuit operates by utilizing a light sensor, typically a photoresistor (LDR) or photodiode, to detect the level of ambient light in the environment. The sensor generates a voltage signal proportional to the intensity of the light. This signal is fed into a microcontroller or an operational amplifier configured as a comparator.
The microcontroller processes the input from the light sensor and compares it to predefined threshold levels. Based on this comparison, the microcontroller generates a control signal that adjusts the brightness of the display. This is typically achieved through a pulse-width modulation (PWM) technique, which varies the duty cycle of the voltage supplied to the display backlight, allowing for smooth transitions in brightness levels.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors to form a voltage divider with the light sensor, capacitors for filtering noise, and possibly a transistor or MOSFET to handle the power requirements of the display backlight. The design ensures that the display remains easily readable in varying lighting conditions, enhancing user experience and reducing eye strain.
To further enhance the system, a feedback loop can be implemented where the actual brightness level of the display is monitored and compared to the desired level, allowing for real-time adjustments. This closed-loop feedback mechanism ensures optimal performance and responsiveness to changes in ambient lighting conditions.An automatic brightness adjustment is a closed loop system that has the capability to assess ambient light and adjust the brightness of the display accordingly. In .. 🔗 External reference