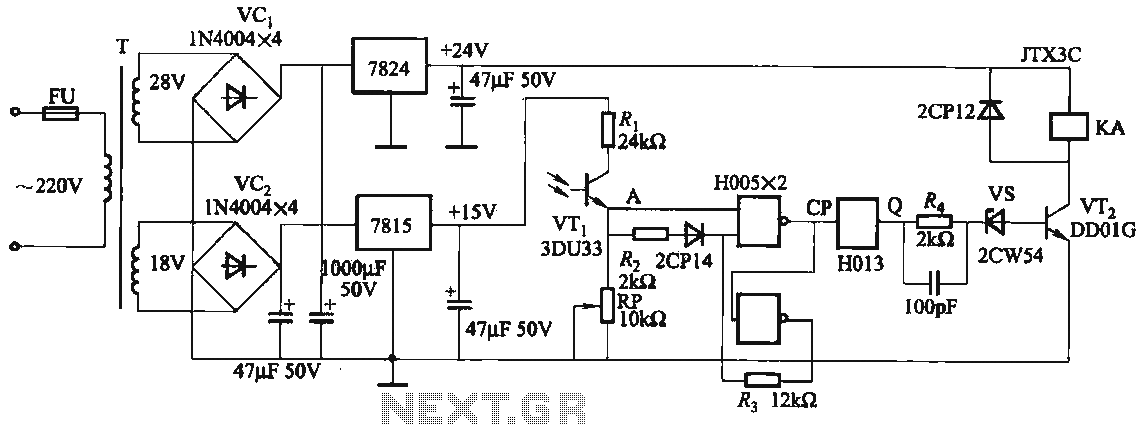
JB-22 transistor relay circuit
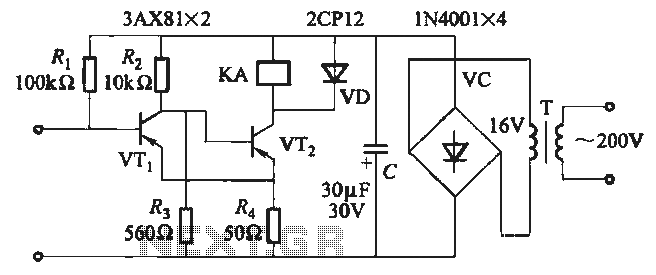
When the input is disconnected, the transistor VTi conducts, while VTz is in cutoff, causing relay KA to release. When the input is shorted, VTi is cut off, VTz conducts, and relay KA is activated.
In this circuit configuration, the operation of the transistors VTi and VTz plays a critical role in controlling the relay KA based on the input state. When the input signal is disconnected, VTi enters a conducting state, allowing current to flow through it. This condition keeps VTz in a cutoff state, which prevents any current from flowing to the relay KA, resulting in the relay being released. The release of the relay can be utilized to deactivate connected loads or activate a signaling mechanism indicating that the input is not present.
Conversely, when the input is shorted, the state of VTi changes to cutoff, which interrupts its conduction path. In this scenario, VTz transitions to a conducting state, allowing current to flow through it and energizing relay KA. The activation of the relay indicates that the input is present and can be used to engage connected loads or trigger other components in the circuit.
This configuration can be beneficial in various applications, such as safety systems, where the presence or absence of an input signal needs to control the operation of other devices. The transistors act as switches that respond to input conditions, effectively managing the state of the relay and the overall functionality of the circuit. Proper biasing and component selection are essential to ensure reliable operation and to handle the expected input signal levels.When the input is disconnected, the transistor VTi conduction, VTz cutoff relay KA released. When the input is shorted. VTi deadline, VTz conduction, KA pull.
In this circuit configuration, the operation of the transistors VTi and VTz plays a critical role in controlling the relay KA based on the input state. When the input signal is disconnected, VTi enters a conducting state, allowing current to flow through it. This condition keeps VTz in a cutoff state, which prevents any current from flowing to the relay KA, resulting in the relay being released. The release of the relay can be utilized to deactivate connected loads or activate a signaling mechanism indicating that the input is not present.
Conversely, when the input is shorted, the state of VTi changes to cutoff, which interrupts its conduction path. In this scenario, VTz transitions to a conducting state, allowing current to flow through it and energizing relay KA. The activation of the relay indicates that the input is present and can be used to engage connected loads or trigger other components in the circuit.
This configuration can be beneficial in various applications, such as safety systems, where the presence or absence of an input signal needs to control the operation of other devices. The transistors act as switches that respond to input conditions, effectively managing the state of the relay and the overall functionality of the circuit. Proper biasing and component selection are essential to ensure reliable operation and to handle the expected input signal levels.When the input is disconnected, the transistor VTi conduction, VTz cutoff relay KA released. When the input is shorted. VTi deadline, VTz conduction, KA pull.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713