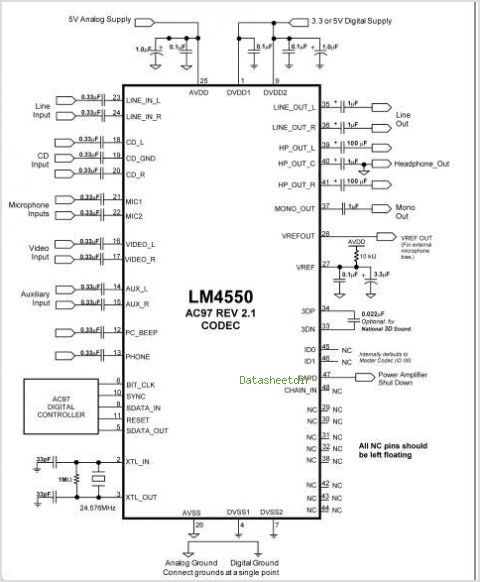
Jfet sample and hold
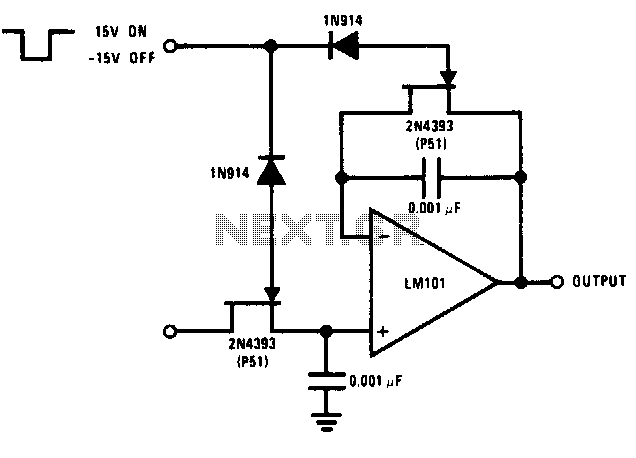
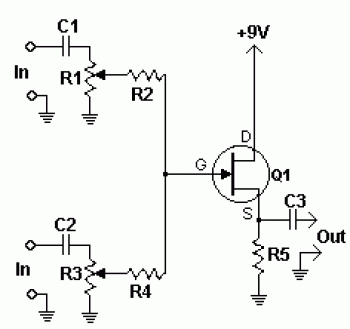
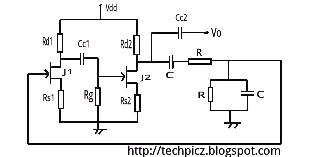
The logic voltage is applied simultaneously to the sample and hold JFETs. By matching input impedance and feedback resistance and capacitance, errors due to the drain-source on-resistance (rdson) of the JFETs are minimized.
The circuit employs a sample and hold configuration utilizing Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFETs) to capture and maintain a voltage level for a specific duration. The simultaneous application of logic voltage to the JFETs ensures that the switching action occurs consistently, allowing for accurate sampling of the input signal.
To optimize performance, careful attention is given to matching the input impedance of the circuit with the feedback resistance and capacitance. This matching process is crucial as it helps to mitigate the errors introduced by the drain-source on-resistance (rdson) inherent in the JFETs. The rdson contributes to voltage drops that can lead to inaccuracies in the sampled signal, and by minimizing this effect, the integrity of the sampled data is preserved.
The schematic typically includes a pair of JFETs configured as a sample and hold circuit, where one JFET is responsible for sampling the input voltage while the other holds the sampled voltage steady. Additional components, such as operational amplifiers, may be integrated to buffer the output and provide necessary gain, further enhancing the circuit's performance. Capacitors are strategically placed to store the sampled voltage, while resistors are used to fine-tune the input impedance and feedback loop, ensuring optimal functionality and minimal signal distortion.
In summary, the design of the JFET-based sample and hold circuit emphasizes precision and accuracy through careful component selection and configuration, addressing potential errors to achieve reliable performance in various electronic applications.The logic voltage is applied simultaneously to the sample and hold JFETs By matching input impedance and feedback resistance and capacitance, errors due to rdston) of the JFETs are minimized. 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs a sample and hold configuration utilizing Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFETs) to capture and maintain a voltage level for a specific duration. The simultaneous application of logic voltage to the JFETs ensures that the switching action occurs consistently, allowing for accurate sampling of the input signal.
To optimize performance, careful attention is given to matching the input impedance of the circuit with the feedback resistance and capacitance. This matching process is crucial as it helps to mitigate the errors introduced by the drain-source on-resistance (rdson) inherent in the JFETs. The rdson contributes to voltage drops that can lead to inaccuracies in the sampled signal, and by minimizing this effect, the integrity of the sampled data is preserved.
The schematic typically includes a pair of JFETs configured as a sample and hold circuit, where one JFET is responsible for sampling the input voltage while the other holds the sampled voltage steady. Additional components, such as operational amplifiers, may be integrated to buffer the output and provide necessary gain, further enhancing the circuit's performance. Capacitors are strategically placed to store the sampled voltage, while resistors are used to fine-tune the input impedance and feedback loop, ensuring optimal functionality and minimal signal distortion.
In summary, the design of the JFET-based sample and hold circuit emphasizes precision and accuracy through careful component selection and configuration, addressing potential errors to achieve reliable performance in various electronic applications.The logic voltage is applied simultaneously to the sample and hold JFETs By matching input impedance and feedback resistance and capacitance, errors due to rdston) of the JFETs are minimized. 🔗 External reference