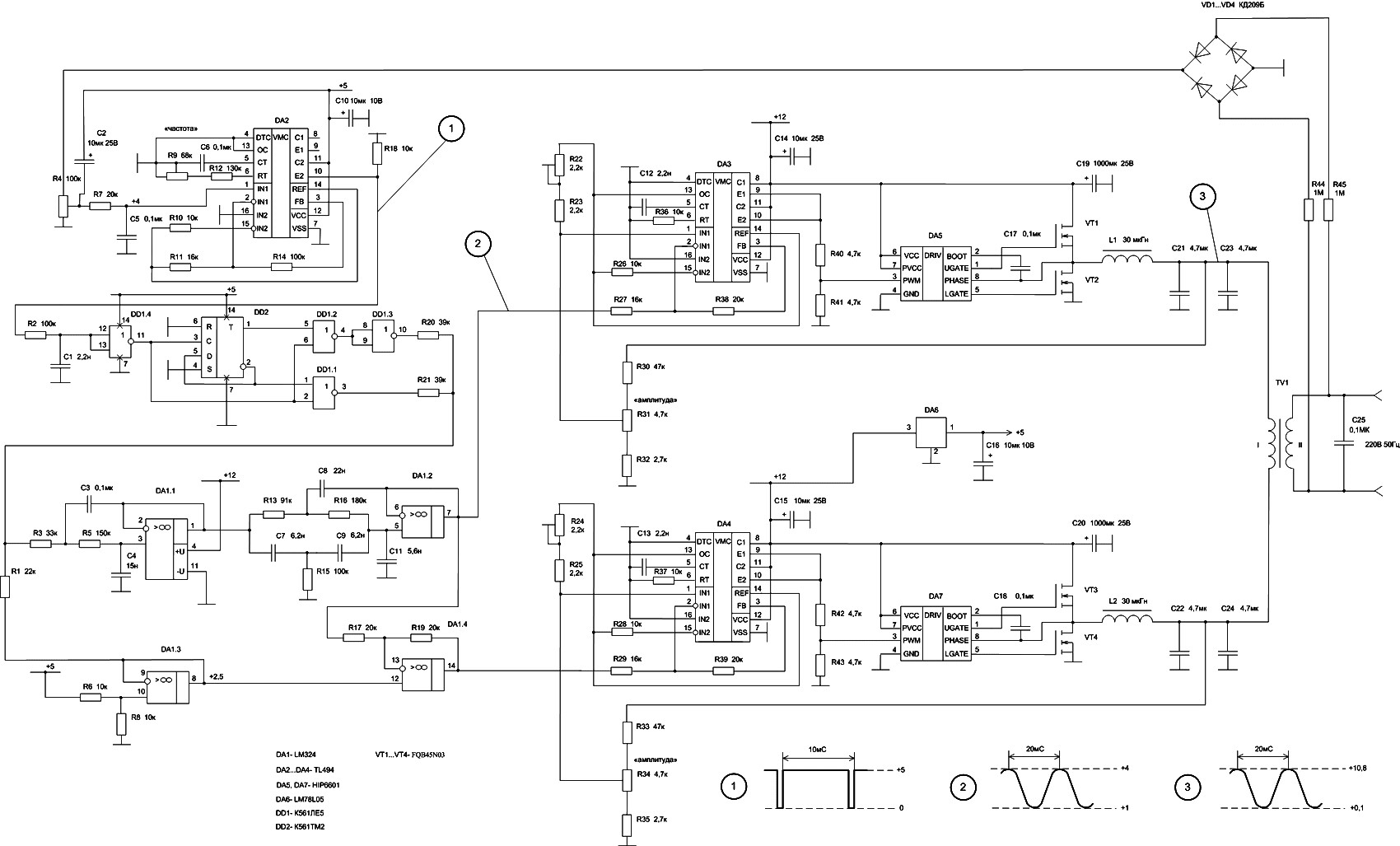
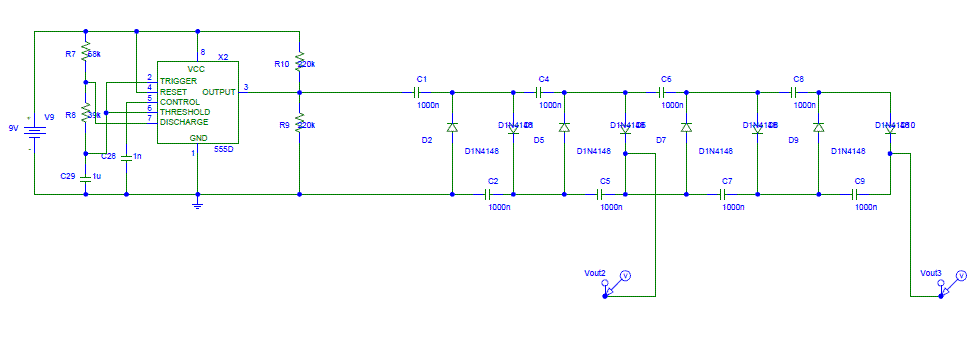
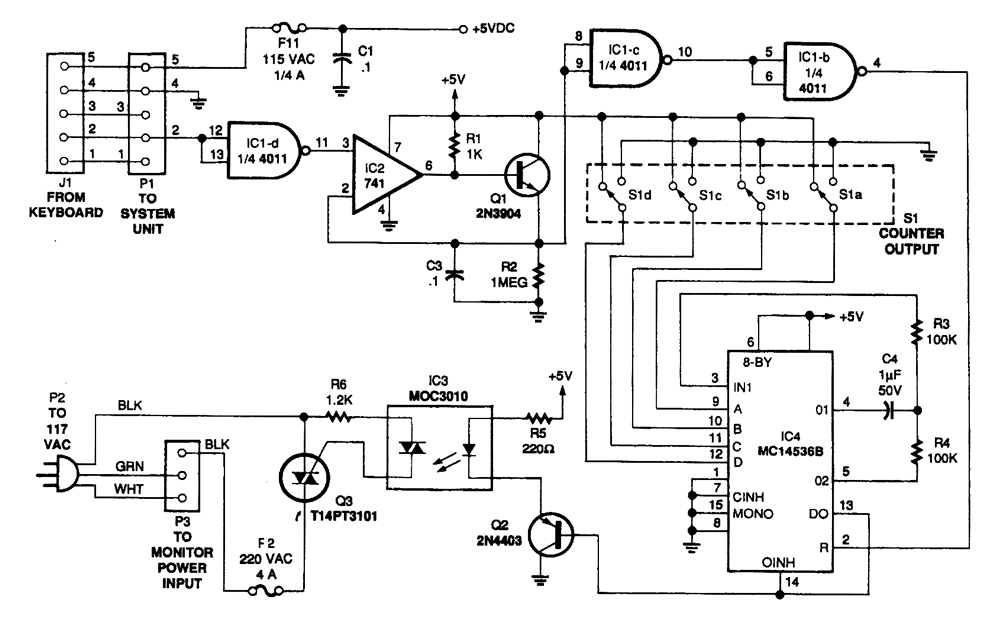
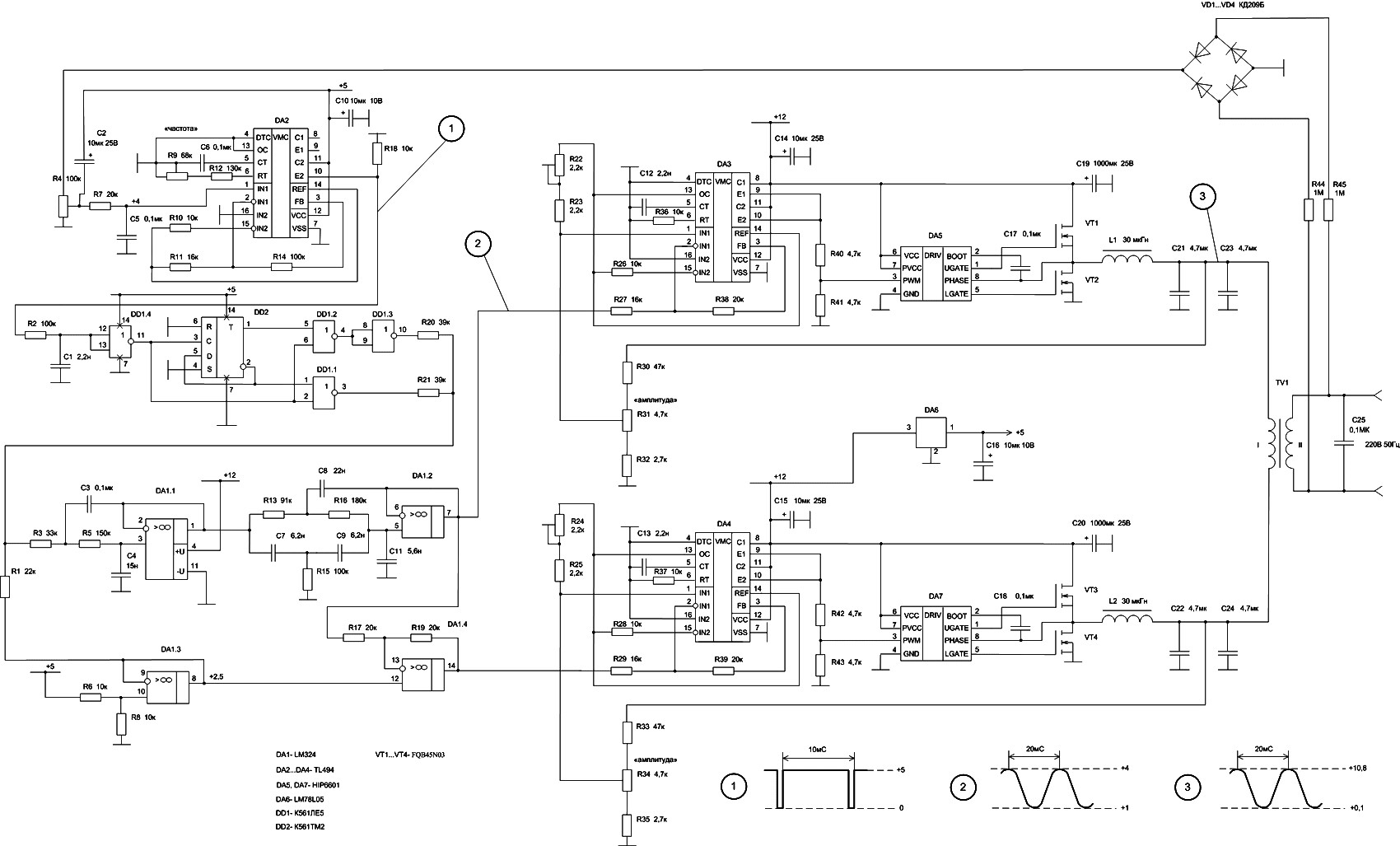
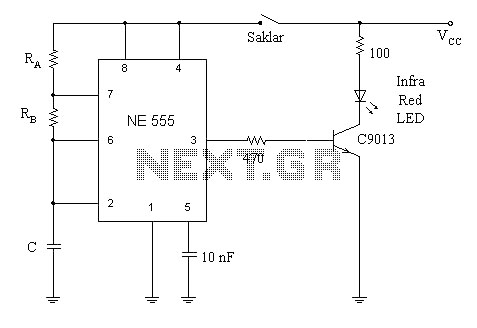
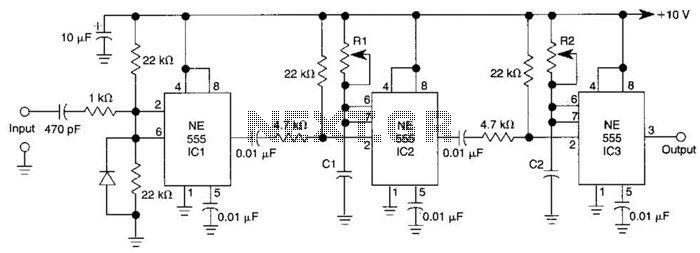
Long delay timer using put
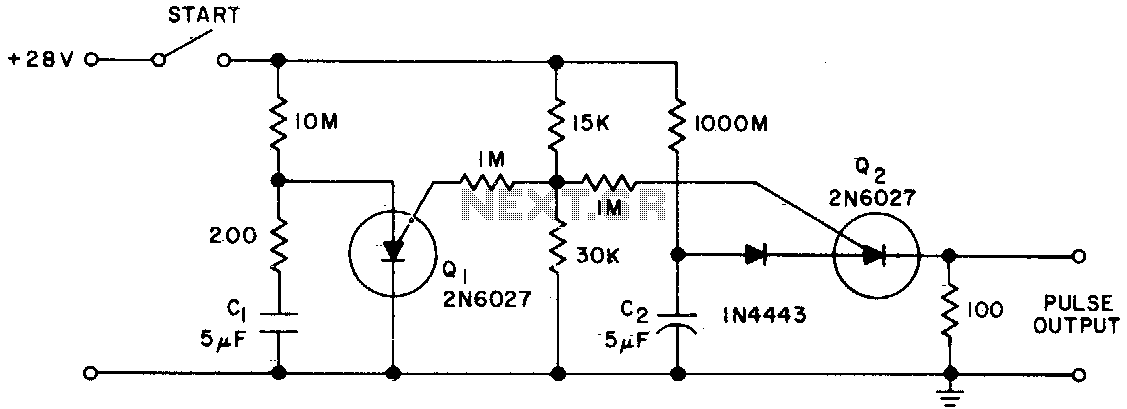
The Programmable Unijunction Transistor (PUT) serves as both a timing element and a sampling oscillator. A low leakage film capacitor is required for capacitor C2 because of the minimal current supplied to it.
The Programmable Unijunction Transistor (PUT) is a semiconductor device that is widely utilized in various timing and oscillator applications due to its unique characteristics. In circuits where the PUT is employed, it functions by generating a timing pulse or oscillation based on external components such as resistors and capacitors. The timing element aspect of the PUT allows for precise control over the duration and frequency of the output signal.
In this specific application, capacitor C2 plays a critical role in the performance of the circuit. The requirement for a low leakage film capacitor is essential because any leakage current can significantly affect the timing accuracy and stability of the oscillator. A low leakage capacitor ensures that the charge stored within the capacitor is maintained effectively, allowing for more reliable operation of the timing circuit.
The selection of components in conjunction with the PUT is crucial for achieving the desired performance. Resistors connected to the PUT will determine the timing intervals, while the value and type of capacitor will influence the frequency of oscillation. Additionally, the circuit layout should be designed to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can introduce unwanted variations in timing and frequency response.
Overall, the integration of the PUT as a timing element and sampling oscillator, along with the careful selection of a low leakage film capacitor for C2, forms the foundation of a stable and precise electronic timing circuit.The PUT is used as both a timing element and sampling oscillator A low leakage film capacitor is required for C2 due to the low current supplied to it. 🔗 External reference
The Programmable Unijunction Transistor (PUT) is a semiconductor device that is widely utilized in various timing and oscillator applications due to its unique characteristics. In circuits where the PUT is employed, it functions by generating a timing pulse or oscillation based on external components such as resistors and capacitors. The timing element aspect of the PUT allows for precise control over the duration and frequency of the output signal.
In this specific application, capacitor C2 plays a critical role in the performance of the circuit. The requirement for a low leakage film capacitor is essential because any leakage current can significantly affect the timing accuracy and stability of the oscillator. A low leakage capacitor ensures that the charge stored within the capacitor is maintained effectively, allowing for more reliable operation of the timing circuit.
The selection of components in conjunction with the PUT is crucial for achieving the desired performance. Resistors connected to the PUT will determine the timing intervals, while the value and type of capacitor will influence the frequency of oscillation. Additionally, the circuit layout should be designed to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can introduce unwanted variations in timing and frequency response.
Overall, the integration of the PUT as a timing element and sampling oscillator, along with the careful selection of a low leakage film capacitor for C2, forms the foundation of a stable and precise electronic timing circuit.The PUT is used as both a timing element and sampling oscillator A low leakage film capacitor is required for C2 due to the low current supplied to it. 🔗 External reference