long range ir transmitter
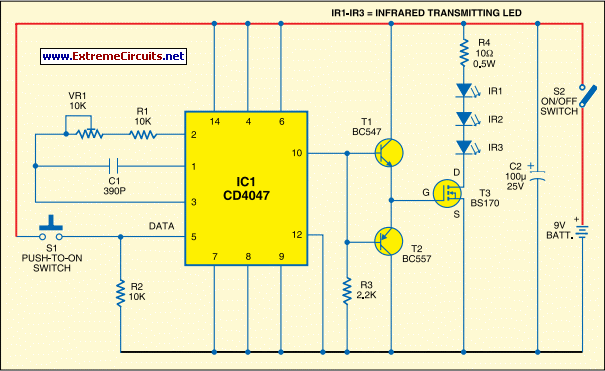
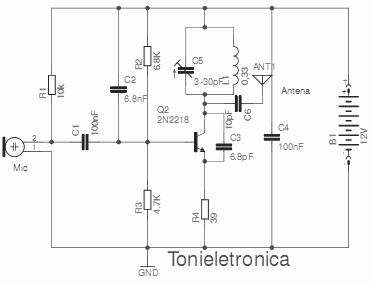
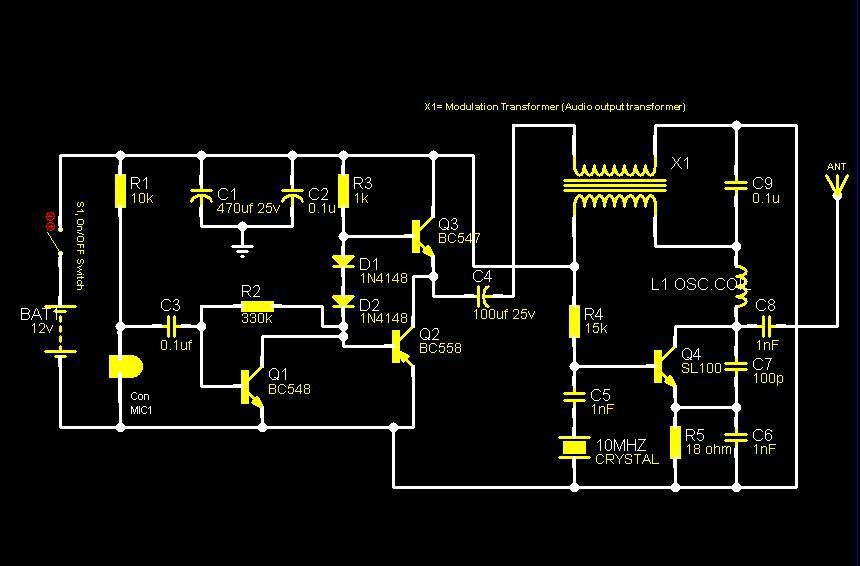
Most IR remotes function effectively within a range of 5 meters. Designing an IR transmitter for dependable operation over a longer distance, such as 10 meters, increases circuit complexity. To achieve this doubled range, the transmitted power must be increased fourfold. For a highly directional IR beam, a suitable choice is to utilize an IR laser pointer as the IR signal source.
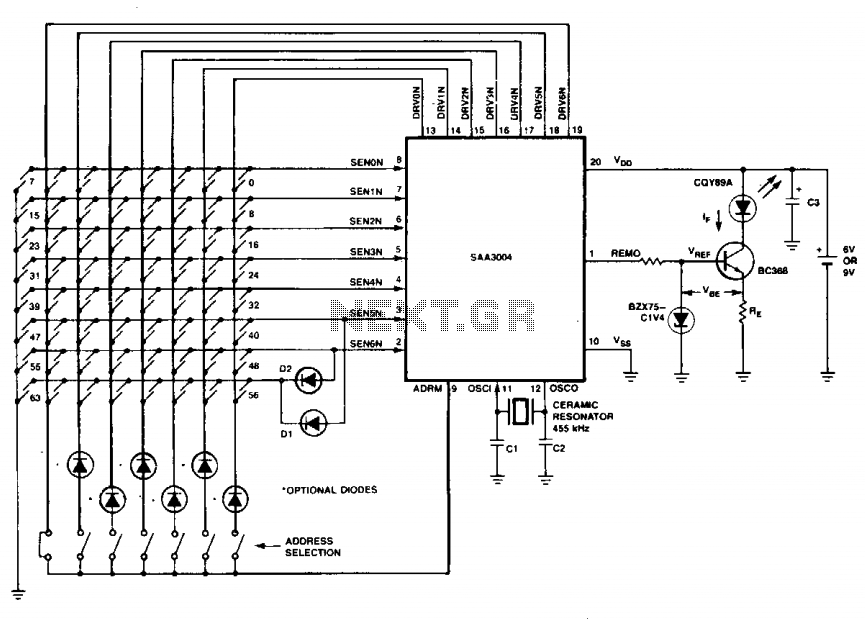
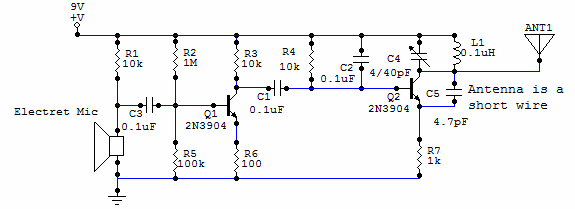
To design an IR transmitter capable of operating reliably at a distance of 10 meters, several key factors must be considered. The circuit typically consists of an IR LED or an IR laser diode, a modulator circuit to encode the signals, and a power supply. The choice between an IR LED and an IR laser diode impacts the beam's directionality and intensity. An IR laser diode can produce a narrow, focused beam, which is advantageous for long-range applications.
The power supply must provide sufficient voltage and current to the IR emitter. For an IR LED, a typical forward voltage of around 1.2 volts is common, while laser diodes may require higher voltages. A transistor can be used to switch the IR emitter on and off, allowing for modulation of the signal. The modulation frequency should be chosen based on the application, usually in the range of 36 kHz to 40 kHz, which helps to minimize interference from ambient light sources.
To ensure that the transmitted power is increased four times to achieve the desired range, the circuit may incorporate a power amplifier. This component boosts the signal before it reaches the IR emitter, ensuring that the output power is sufficient for long-distance transmission. The amplifier's design must account for the load presented by the IR emitter and the power supply limitations.
In addition to the transmitter design, consideration must also be given to the receiver circuit, which typically includes a photodiode or phototransistor that detects the IR signal. The receiver should be sensitive enough to detect the signal at the increased range while also being capable of filtering out noise and interference.
Overall, the design of an IR transmitter for extended ranges involves careful selection of components, modulation techniques, and power management to ensure reliable operation at distances beyond the typical 5 meters. The use of an IR laser pointer can enhance the system's performance by providing a focused beam, which is particularly useful in applications requiring precise control over the direction of the IR signal.Most of the IR remotes work reliably within a range of 5 metres. The circuit complexity increases if you design the IR transmitter for reliable operation over a longer range, say, 10 metres. To double the range from 5 metres to 10 metres, you need to increase the transmitted power four times.
If you wish to real i se a highly directional IR beam (very narrow beam), you can suitably use an IR laser pointer as the IR signal source.. 🔗 External reference
To design an IR transmitter capable of operating reliably at a distance of 10 meters, several key factors must be considered. The circuit typically consists of an IR LED or an IR laser diode, a modulator circuit to encode the signals, and a power supply. The choice between an IR LED and an IR laser diode impacts the beam's directionality and intensity. An IR laser diode can produce a narrow, focused beam, which is advantageous for long-range applications.
The power supply must provide sufficient voltage and current to the IR emitter. For an IR LED, a typical forward voltage of around 1.2 volts is common, while laser diodes may require higher voltages. A transistor can be used to switch the IR emitter on and off, allowing for modulation of the signal. The modulation frequency should be chosen based on the application, usually in the range of 36 kHz to 40 kHz, which helps to minimize interference from ambient light sources.
To ensure that the transmitted power is increased four times to achieve the desired range, the circuit may incorporate a power amplifier. This component boosts the signal before it reaches the IR emitter, ensuring that the output power is sufficient for long-distance transmission. The amplifier's design must account for the load presented by the IR emitter and the power supply limitations.
In addition to the transmitter design, consideration must also be given to the receiver circuit, which typically includes a photodiode or phototransistor that detects the IR signal. The receiver should be sensitive enough to detect the signal at the increased range while also being capable of filtering out noise and interference.
Overall, the design of an IR transmitter for extended ranges involves careful selection of components, modulation techniques, and power management to ensure reliable operation at distances beyond the typical 5 meters. The use of an IR laser pointer can enhance the system's performance by providing a focused beam, which is particularly useful in applications requiring precise control over the direction of the IR signal.Most of the IR remotes work reliably within a range of 5 metres. The circuit complexity increases if you design the IR transmitter for reliable operation over a longer range, say, 10 metres. To double the range from 5 metres to 10 metres, you need to increase the transmitted power four times.
If you wish to real i se a highly directional IR beam (very narrow beam), you can suitably use an IR laser pointer as the IR signal source.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713