
Low-frequency-oscillator
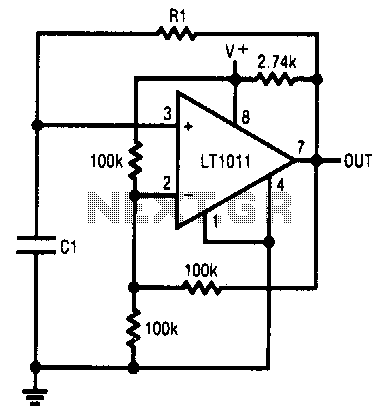
This simple RC oscillator utilizes a medium-speed comparator with hysteresis and feedback through R1 and C1 as timing elements. The frequency of oscillation is theoretically independent of the power supply voltage. Additionally, the comparator swings to the supply rails when the pull-up resistor is significantly smaller than the resistor R_h, and the propagation delay is negligible compared to the RC time constant.
The described RC oscillator circuit operates based on the principles of feedback and timing elements, specifically utilizing a medium-speed comparator to achieve oscillation. The key components involved in this circuit include resistors R1 and R_h, as well as capacitor C1. The configuration allows the circuit to generate a square wave output, where the frequency of oscillation remains relatively stable despite variations in the power supply voltage, which is a desirable characteristic for many applications.
In this circuit, the comparator plays a crucial role by providing hysteresis, which helps to stabilize the oscillation by preventing rapid toggling due to noise or small voltage variations. The feedback is established through R1 and C1, where R1 influences the charging and discharging time of C1, thereby determining the oscillation frequency. The relationship between the resistor and capacitor values can be expressed using the formula for the frequency of oscillation, which is typically given by:
\[ f = \frac{1}{T} = \frac{1}{2 \cdot R \cdot C} \]
In this case, T represents the period of the oscillation, while R and C are the effective resistance and capacitance in the timing circuit.
When the comparator output swings to the supply rails, it indicates that the output voltage has reached either the maximum or minimum limit of the power supply. The condition that the pull-up resistor is much smaller than R_h ensures that the feedback from R1 does not dominate the circuit behavior, allowing for stable oscillation. Furthermore, the assumption of negligible propagation delay ensures that the timing of the comparator's switching action aligns closely with the RC time constant, thereby maintaining a consistent frequency output.
This RC oscillator circuit can be applied in various electronic applications, including clock generation, waveform synthesis, and signal modulation, due to its simplicity and effectiveness in providing a reliable oscillation frequency.This simple rc oscillator uses a medium-speed comparator with hysteresis and feedback through Rl and Cl as timing elements. The frequency of oscillation is, at least theoretically, independent from the power supply voltage. If the comparator swings to the supply rails, if the pull-up resistor is much smaller than the resistor Rh, and if the propagation delay is negligible compared to the rc time constant. 🔗 External reference
The described RC oscillator circuit operates based on the principles of feedback and timing elements, specifically utilizing a medium-speed comparator to achieve oscillation. The key components involved in this circuit include resistors R1 and R_h, as well as capacitor C1. The configuration allows the circuit to generate a square wave output, where the frequency of oscillation remains relatively stable despite variations in the power supply voltage, which is a desirable characteristic for many applications.
In this circuit, the comparator plays a crucial role by providing hysteresis, which helps to stabilize the oscillation by preventing rapid toggling due to noise or small voltage variations. The feedback is established through R1 and C1, where R1 influences the charging and discharging time of C1, thereby determining the oscillation frequency. The relationship between the resistor and capacitor values can be expressed using the formula for the frequency of oscillation, which is typically given by:
\[ f = \frac{1}{T} = \frac{1}{2 \cdot R \cdot C} \]
In this case, T represents the period of the oscillation, while R and C are the effective resistance and capacitance in the timing circuit.
When the comparator output swings to the supply rails, it indicates that the output voltage has reached either the maximum or minimum limit of the power supply. The condition that the pull-up resistor is much smaller than R_h ensures that the feedback from R1 does not dominate the circuit behavior, allowing for stable oscillation. Furthermore, the assumption of negligible propagation delay ensures that the timing of the comparator's switching action aligns closely with the RC time constant, thereby maintaining a consistent frequency output.
This RC oscillator circuit can be applied in various electronic applications, including clock generation, waveform synthesis, and signal modulation, due to its simplicity and effectiveness in providing a reliable oscillation frequency.This simple rc oscillator uses a medium-speed comparator with hysteresis and feedback through Rl and Cl as timing elements. The frequency of oscillation is, at least theoretically, independent from the power supply voltage. If the comparator swings to the supply rails, if the pull-up resistor is much smaller than the resistor Rh, and if the propagation delay is negligible compared to the rc time constant. 🔗 External reference